S-Tritylcysteine
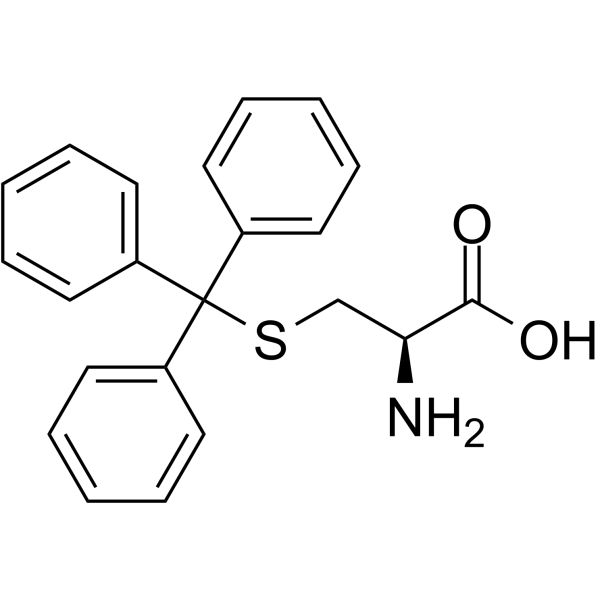
S-Tritylcysteine structure
|
Common Name | S-Tritylcysteine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2799-07-7 | Molecular Weight | 363.47 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 524.7±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C22H21NO2S | Melting Point | 182-183 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 271.2±30.1 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Cdk1 phosphorylates the Rac activator Tiam1 to activate centrosomal Pak and promote mitotic spindle formation.
Nat. Commun. 6 , 7437, (2015) Centrosome separation is critical for bipolar spindle formation and the accurate segregation of chromosomes during mammalian cell mitosis. Kinesin-5 (Eg5) is a microtubule motor essential for centrosome separation, and Tiam1 and its substrate Rac antagonize E... |
|
|
Structure-activity relationship of S-trityl-L-cysteine analogues as inhibitors of the human mitotic kinesin Eg5.
J. Med. Chem. 51 , 1115-25, (2008) The human kinesin Eg5 is a potential drug target for cancer chemotherapy. Eg5 specific inhibitors cause cells to block in mitosis with a characteristic monoastral spindle phenotype. Prolonged metaphase block eventually leads to apoptotic cell death. S-trityl-... |
|
|
Dynamics of Human Telomerase Holoenzyme Assembly and Subunit Exchange across the Cell Cycle.
J. Biol. Chem. 290 , 21320-35, (2015) Human telomerase acts on telomeres during the genome synthesis phase of the cell cycle, accompanied by its concentration in Cajal bodies and transient colocalization with telomeres. Whether the regulation of human telomerase holoenzyme assembly contributes to... |
|
|
Nuclear translocation of Cyclin B1 marks the restriction point for terminal cell cycle exit in G2 phase.
Cell Cycle 13(17) , 2733-43, (2014) Upon DNA damage, cell cycle progression is temporally blocked to avoid propagation of mutations. While transformed cells largely maintain the competence to recover from a cell cycle arrest, untransformed cells past the G1/S transition lose mitotic inducers, a... |
|
|
EGF-induced centrosome separation promotes mitotic progression and cell survival.
Dev. Cell 25(3) , 229-40, (2013) Timely and accurate assembly of the mitotic spindle is critical for the faithful segregation of chromosomes, and centrosome separation is a key step in this process. The timing of centrosome separation varies dramatically between cell types; however, the mech... |
|
|
Binding partner switching on microtubules and aurora-B in the mitosis to cytokinesis transition.
Mol. Cell. Proteomics 9(2) , 336-50, (2010) The cytoskeleton globally reorganizes between mitosis (M phase) and cytokinesis (C phase), which presumably requires extensive regulatory changes. To reveal these changes, we undertook a comparative proteomics analysis of cells tightly drug-synchronized in ea... |
|
|
Xenopus oocyte meiosis lacks spindle assembly checkpoint control.
J. Cell Biol. 201(2) , 191-200, (2013) The spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC) functions as a surveillance mechanism to detect chromosome misalignment and to delay anaphase until the errors are corrected. The SAC is thought to control mitosis and meiosis, including meiosis in mammalian eggs. However... |
|
|
Cysteine-S-trityl a key derivative to prepare N-methyl cysteines.
J. Comb. Chem. 10(1) , 69-78, (2008) S-Trt Cys are used as precursors for the synthesis of protected NMe-Cys. N-Methylation of Alloc-Cys(Trt)-OH and Boc-Cys(Trt)-OH gives the corresponding N-methylated derivatives in good yields and purities, which can be further derivatized in solution to obtai... |
|
|
Doing the methylene shuffle--further insights into the inhibition of mitotic kinesin Eg5 with S-trityl L-cysteine.
Eur. J. Med. Chem. 54 , 483-98, (2012) S-Trityl L-cysteine (STLC) is an inhibitor of the mitotic kinesin Eg5 with potential as an antimitotic chemotherapeutic agent. We previously reported the crystal structure of the ligand-protein complex, and now for the first time, have quantified the interact... |
|
|
The conserved L5 loop establishes the pre-powerstroke conformation of the Kinesin-5 motor, eg5.
Biophys. J. 98(11) , 2619-27, (2010) Kinesin superfamily motor proteins contain a structurally conserved loop near the ATP binding site, termed L5. The function of L5 is unknown, although several drug inhibitors of the mitotic kinesin Eg5 bind to L5. We used electron paramagnetic resonance spect... |