| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
L-Glutamine
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
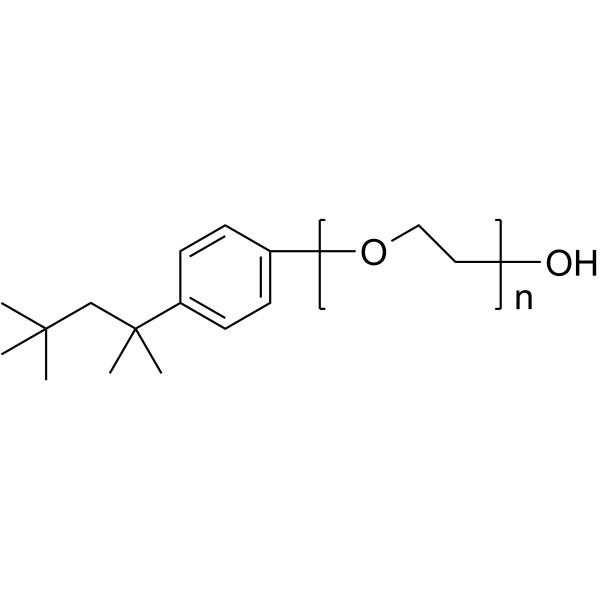 |
Triton X-100
CAS:9002-93-1 |
|
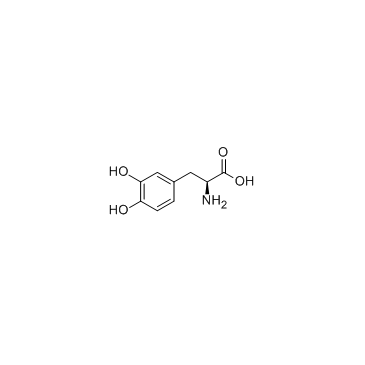 |
Levodopa
CAS:59-92-7 |
|
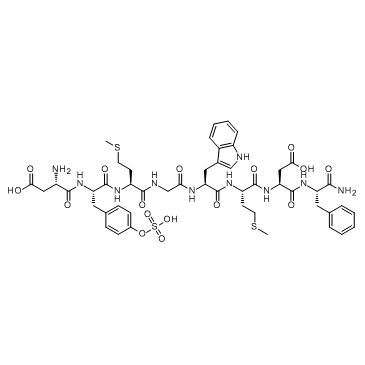 |
Cholecystokinin Octapeptide (sulfated) ammonium salt
CAS:25126-32-3 |
|
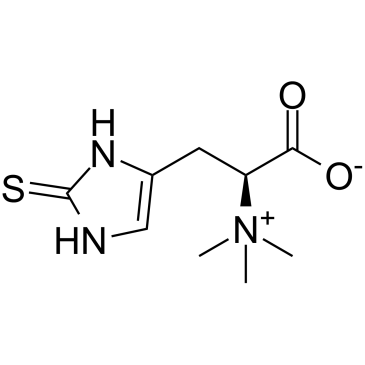 |
L-(+)-Ergothioneine
CAS:497-30-3 |