Levodopa
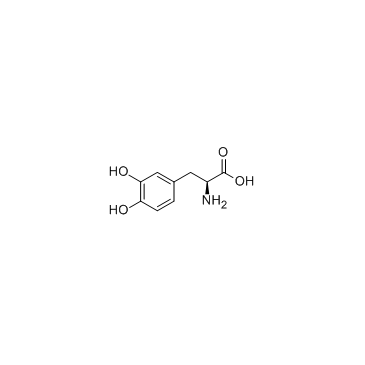
Levodopa structure
|
Common Name | Levodopa | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 59-92-7 | Molecular Weight | 197.188 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 448.4±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H11NO4 | Melting Point | 276-278 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 225.0±28.7 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of LevodopaL-DOPA is a natural form of DOPA used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. L-DOPA is the precursor of dopamine and product of tyrosine hydroxylase.Target: Dopamine ReceptorL-DOPA (L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine) is a chemical that is made and used as part of the normal biology of humans, some animals and plants. Some animals and humans make it via biosynthesis from the amino acid L-tyrosine. L-DOPA is the precursor to the neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and epinephrine collectively known as catecholamines. L-DOPA can be manufactured and in its pure form is sold as apsychoactive drug with the INN levodopa; trade names include Sinemet, Parcopa, Atamet, Stalevo, Madopar, Prolopa, etc. As a drug it is used in the clinical treatment of Parkinson's disease and dopamine-responsive dystonia.L-DOPA crosses the protective blood-brain barrier, whereas dopamine itself cannot. Thus, L-DOPA is used to increase dopamine concentrations in the treatment of Parkinson's disease and dopamine-responsive dystonia. This treatment was made practical and proven clinically by George Cotzias and his coworkers, for which they won the 1969 Lasker Prize. In addition, L-DOPA, co-administered with a peripheral DDCI, has been investigated as a potential treatment for restless leg syndrome. However, studieshave demonstrated "no clear picture of reduced symptoms". |
| Name | L-dopa |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | L-DOPA is a natural form of DOPA used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. L-DOPA is the precursor of dopamine and product of tyrosine hydroxylase.Target: Dopamine ReceptorL-DOPA (L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine) is a chemical that is made and used as part of the normal biology of humans, some animals and plants. Some animals and humans make it via biosynthesis from the amino acid L-tyrosine. L-DOPA is the precursor to the neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and epinephrine collectively known as catecholamines. L-DOPA can be manufactured and in its pure form is sold as apsychoactive drug with the INN levodopa; trade names include Sinemet, Parcopa, Atamet, Stalevo, Madopar, Prolopa, etc. As a drug it is used in the clinical treatment of Parkinson's disease and dopamine-responsive dystonia.L-DOPA crosses the protective blood-brain barrier, whereas dopamine itself cannot. Thus, L-DOPA is used to increase dopamine concentrations in the treatment of Parkinson's disease and dopamine-responsive dystonia. This treatment was made practical and proven clinically by George Cotzias and his coworkers, for which they won the 1969 Lasker Prize. In addition, L-DOPA, co-administered with a peripheral DDCI, has been investigated as a potential treatment for restless leg syndrome. However, studieshave demonstrated "no clear picture of reduced symptoms". |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 448.4±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 276-278 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C9H11NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 197.188 |
| Flash Point | 225.0±28.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 197.068802 |
| PSA | 103.78000 |
| LogP | -0.22 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.655 |
| InChIKey | WTDRDQBEARUVNC-LURJTMIESA-N |
| SMILES | NC(Cc1ccc(O)c(O)c1)C(=O)O |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P301 + P312 + P330-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Phrases | R22:Harmful if swallowed. R36/37/38:Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin . R20/21/22:Harmful by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed . |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | AY5600000 |
| HS Code | 2932999099 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2922509090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2922509090. other amino-alcohol-phenols, amino-acid-phenols and other amino-compounds with oxygen function. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Insights from reconstitution reactions of COPII vesicle formation using pure components and low mechanical perturbation.
Biol. Chem. 395(7-8) , 801-12, (2014) As shape transformations of membranes are vital for intracellular trafficking, it is crucial to understand both the mechanics and the biochemistry of these processes. The interplay of these two factor... |
|
|
Activation of PPAR gamma receptors reduces levodopa-induced dyskinesias in 6-OHDA-lesioned rats.
Neurobiol. Dis. 74 , 295-304, (2015) Long-term administration of l-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (levodopa), the mainstay treatment for Parkinson's disease (PD), is accompanied by fluctuations in its duration of action and motor complicatio... |
|
|
Brexpiprazole I: in vitro and in vivo characterization of a novel serotonin-dopamine activity modulator.
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 350(3) , 589-604, (2014) Brexpiprazole (OPC-34712, 7-{4-[4-(1-benzothiophen-4-yl)piperazin-1-yl]butoxy}quinolin-2(1H)-one) is a novel drug candidate in clinical development for psychiatric disorders with high affinity for ser... |
| (-)-dopa |
| L-3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine |
| l-dop |
| Dopar |
| Alanine, 3- (3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-, L- |
| 3,4-Dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine |
| Doprin |
| L-4,5-Dihydroxyphenylalanine |
| Parda |
| Doparl |
| Tyrosine, 3-hydroxy- |
| Beldopa |
| EINECS 200-445-2 |
| 3-Hydroxytyrosine |
| Levopa |
| Bendopa |
| (−)-dopa |
| L-DOPA |
| MFCD00002598 |
| L-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-Alanine |
| Levodopa |
| Ledopa |
 CAS#:60-18-4
CAS#:60-18-4 CAS#:330455-62-4
CAS#:330455-62-4 CAS#:330455-56-6
CAS#:330455-56-6 CAS#:63-84-3
CAS#:63-84-3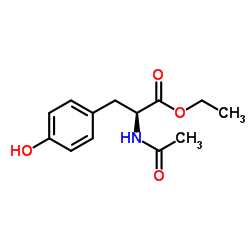 CAS#:840-97-1
CAS#:840-97-1 CAS#:60470-82-8
CAS#:60470-82-8 CAS#:68706-13-8
CAS#:68706-13-8 CAS#:63-91-2
CAS#:63-91-2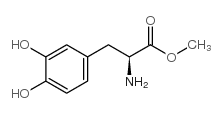 CAS#:7101-51-1
CAS#:7101-51-1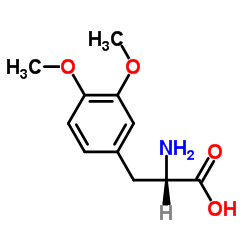 CAS#:32161-30-1
CAS#:32161-30-1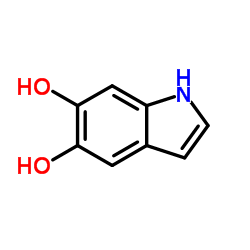 CAS#:3131-52-0
CAS#:3131-52-0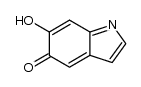 CAS#:59719-88-9
CAS#:59719-88-9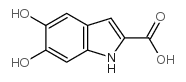 CAS#:4790-08-3
CAS#:4790-08-3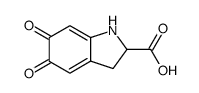 CAS#:89762-39-0
CAS#:89762-39-0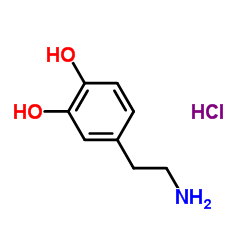 CAS#:51-61-6
CAS#:51-61-6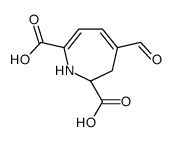 CAS#:12624-18-9
CAS#:12624-18-9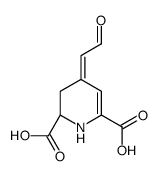 CAS#:18766-66-0
CAS#:18766-66-0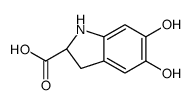 CAS#:18766-67-1
CAS#:18766-67-1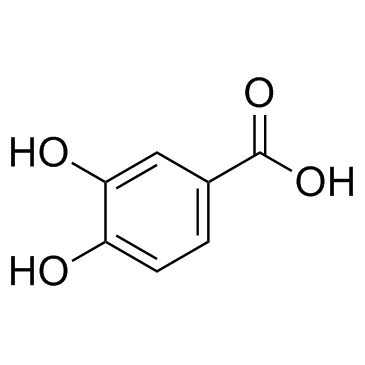 CAS#:99-50-3
CAS#:99-50-3
