The metabolism of thioacetanilide in the rat.
P N Trennery, R H Waring
Index: Xenobiotica 13(8) , 475-82, (1983)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The metabolism and acute toxicity of thioacetanilide was studied in the rat. Following intragastric dosage (100 mg/kg), over 90% dose was excreted in urine, predominantly as conjugated metabolites: less than 7% was recovered in the faeces, consisting of unchanged thioacetanilide. N-Acetyl-4-aminophenol sulphate was the major urinary metabolite, with smaller amounts of conjugated 4-hydroxythioacetanilide and unmetabolized thioacetanilide. Biliary excretion amounted to only 3.4% and was N-acetyl-4-aminophenol glucuronide. Although desulphuration was a major metabolic pathway in the rat, no hepatic toxicity (shown by serum enzymes, plasma bilirubin, hepatic glutathione and cytochrome P-450 levels) occurred up to doses of 500 mg/kg. Combination of rapid 4-hydroxylation, absence of sulphoxide formation, and the structural tautomerism exhibited by thioacetanilide may be, in part, responsible for these findings.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
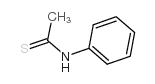 |
Thioacetanilide
CAS:637-53-6 |
C8H9NS |
|
1,2,3-Selenadiazole thioacetanilides: synthesis and anti-HIV...
2009-09-01 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17(17) , 6374-9, (2009)] |
|
Synthesis and biological evaluation of imidazole thioacetani...
2009-08-15 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17(16) , 5775-81, (2009)] |
|
Effects from filtration, capping agents, and presence/absenc...
2010-12-01 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. 20(18) , 5527-36, (2012)] |
|
[Substantiation of maximum permissible levels of thioacylani...
1986-07-01 [Gig. Tr. Prof. Zabol. (7) , 51-2, (1986)] |
|
Application of beta-(2-chloroaroyl) thioacetanilides in synt...
2008-03-07 [J. Org. Chem. 73(5) , 1852-63, (2008)] |