Removal of tetrafluoroborate ion from aqueous solution using magnesium-aluminum oxide produced by the thermal decomposition of a hydrotalcite-like compound.
Toshiaki Yoshioka, Tomohito Kameda, Motoya Miyahara, Miho Uchida, Tadaaki Mizoguchi, Akitsugu Okuwaki
Index: Chemosphere 69(5) , 832-5, (2007)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Magnesium-aluminum oxide (Mg-Al oxide) prepared by the thermal decomposition of a hydrotalcite-like compound was found to have potential for treating NaBF(4) wastewater. The Mg-Al oxide removed the BF(4)(-) and F(-) and H(3)BO(3) from the NaBF(4) solution. With increasing Mg-Al oxide quantity and time, the BF(4)(-) concentration decreased and the degree of BF(4)(-), F(-), and boron removal increased. The decrease in the BF(4)(-) concentration resulted from uptake by the Mg-Al oxide and not hydrolysis. The Mg-Al oxide took up F(-) from the solution preferentially. The Mg-Al oxide also converted the H(3)BO(3) in the aqueous solution into H(2)BO(3)(-), which it took up.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
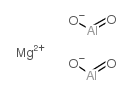 |
magnesium aluminate
CAS:12068-51-8 |
Al2H2MgO4 |
|
Epitaxially driven formation of intricate supported gold nan...
2009-12-01 [Nano Lett. 9(12) , 4258-63, (2009)] |
|
Removal of HCl, SO₂, and NO by treatment of acid gas with Mg...
2011-01-01 [Chemosphere 82(4) , 587-91, (2011)] |
|
Study on adsorption of glyphosate (N-phosphonomethyl glycine...
2005-10-17 [J. Hazard. Mater. 125(1-3) , 89-95, (2005)] |
|
Spectrophotometric evaluation of the optical influence of co...
2009-01-01 [Dent. Mater. 25(2) , 158-65, (2009)] |
|
Removal of hydrogen chloride from gaseous streams using magn...
2008-10-01 [Chemosphere 73(5) , 844-7, (2008)] |