| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
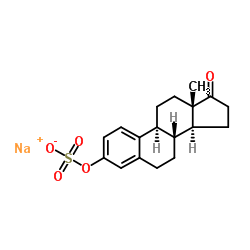 |
Estrone sulfate sodium
CAS:438-67-5 |
|
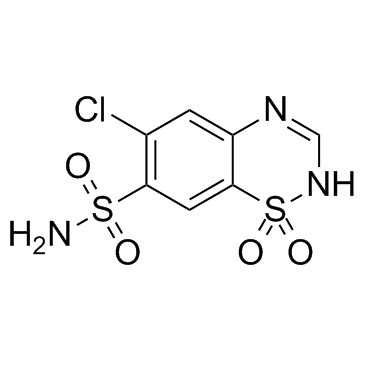 |
Chlorothiazide
CAS:58-94-6 |
|
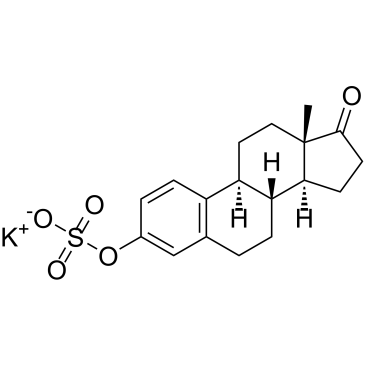 |
Estrone sulfate potassium
CAS:1240-04-6 |