| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
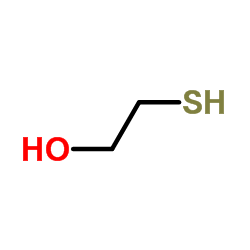 |
mercaptoethanol
CAS:60-24-2 |
|
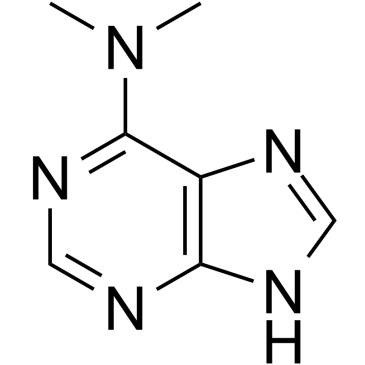 |
N6,N6-dimethyladenine
CAS:938-55-6 |