| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
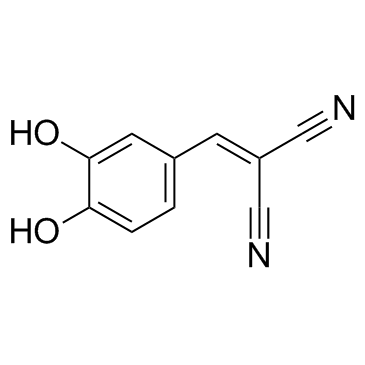 |
AG 18
CAS:118409-57-7 |
|
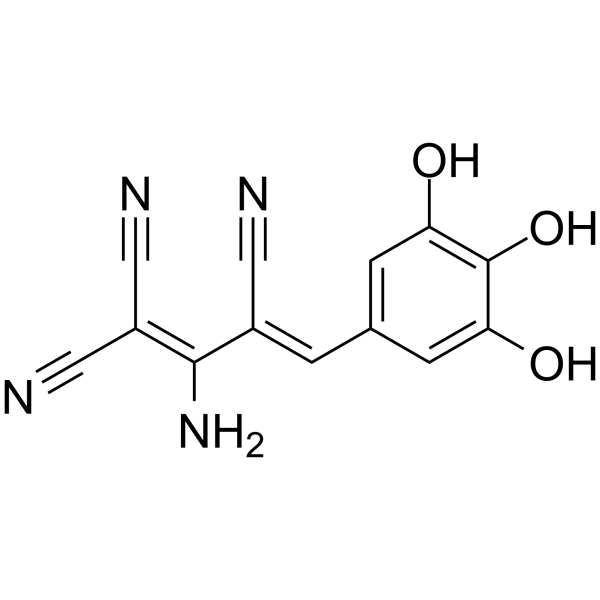 |
Tyrphostin 51
CAS:126433-07-6 |
|
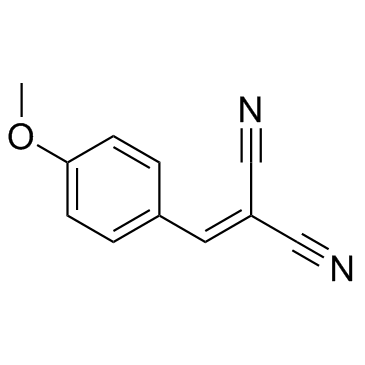 |
Tyrphostin A1
CAS:2826-26-8 |