Covalent aspartylation of aspartyl-tRNA synthetase from bakers' yeast by its cognate aspartyl adenylate: identification of the labeled residues.
H Mejdoub, D Kern, R Giegé, J P Ebel, Y Boulanger, J Reinbolt
Index: Biochemistry 26(7) , 2054-9, (1987)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Aspartyl-tRNA synthetase from bakers' yeast gives an unstable complex with the cognate adenylate, which reacts after dissociation with amino acid side chains of the protein. This leads to a covalent incorporation of aspartic acid into aspartyl-tRNA synthetase via amide or ester bonds formed between the alpha-carboxyl group of activated aspartic acid and accessible lysines, serines, and threonines. This property is used to label the peptides at the surface of the enzyme. The main labeled residues have been identified, and their location in the primary structure is discussed in relation to structural properties of aspartyl-tRNA synthetase.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
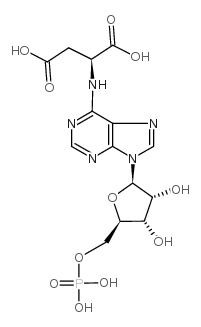 |
Adenylosuccinic acid
CAS:19046-78-7 |
C14H18N5O11P |
|
The RimL transacetylase provides resistance to translation i...
2014-10-01 [J. Bacteriol. 196(19) , 3377-85, (2014)] |
|
Synthesis and aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase inhibitory activity ...
2005-01-03 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. 13(1) , 69-75, (2005)] |
|
MccE provides resistance to protein synthesis inhibitor micr...
2010-04-23 [J. Biol. Chem. 285(17) , 12662-9, (2010)] |
|
[Aspartyladenylate analog--effective inhibitor of asparagine...
1988-07-01 [Bioorg. Khim. 14(7) , 969-72, (1988)] |
|
Escherichia coli peptidase A, B, or N can process translatio...
2008-04-01 [J. Bacteriol. 190(7) , 2607-10, (2008)] |