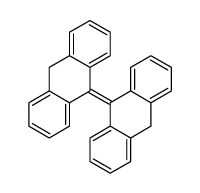
434-85-5
| Name | Bianthrone |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
EINECS 207-106-8
9,9'-Bianthracene-10,10'-dione dianthraquinone 10,10'-bianthrone MFCD00001238 Dehydroxydianthrone 10-(10-Oxoanthracen-9(10H)-yliden)anthracen-9(10H)-on 10H,10'H-[9,9'-Bianthracenylidene]-10,10'-dione 10-(10-Oxo-9(10H)-anthracenylidene)-9(10H)-anthracenone Bianthron Dianthrone Dehydrodianthrone Bisanthrone 10-(10-oxoanthracen-9(10H)-ylidene)anthracen-9(10H)-one Bianthvone 10,10'-Dianthrone 10-[10-oxoanthracen-9(10H)-ylidene]anthracen-9(10H)-one |
| Description | Bianthrone (Dianthrone) is a natural product that can be isolated from Rheum officinale Baill. Bianthrone is a potential toxic marker of Polygonum multiflorum Thunb[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 570.8±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 300 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C28H16O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 384.425 |
| Flash Point | 208.4±27.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 384.115021 |
| PSA | 34.14000 |
| LogP | 3.71 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.728 |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. Combustible. |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 7 | |
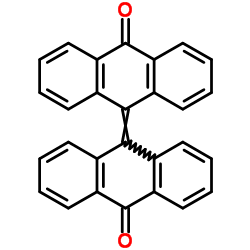
![[9,9'-Bianthracene]-10,10'(9H,9'H)-dione structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/191/434-84-4.png)
![9,9'-Bi[anthracen-10-ol] structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/367/16014-05-4.png)
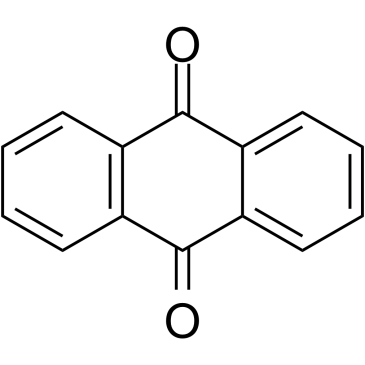
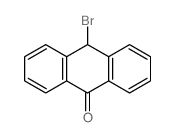
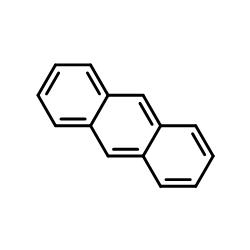
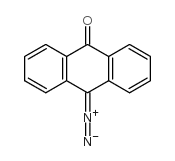
![Phenanthro[1,10,9,8-opqra]perylene-7,14-dione structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/193/475-64-9.png)