73-49-4
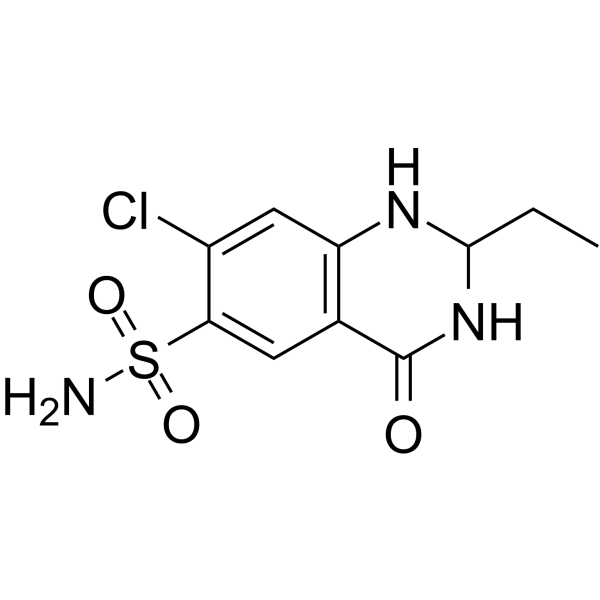
| Name | 7-chloro-2-ethyl-4-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-quinazoline-6-sulfonamide |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Quimethazin
Quinethazonum Hydromox Quinetazona Quinethazon Chinethazonum 7-Chlor-6-sulfamoyl-2-aethyl-4-oxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-chinazolin UNII:455E0S048W 7-Chlor-2-aethyl-6-sulfamoyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-4-chinazolinon quinethazone 7-chloro-2-ethyl-4-oxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-quinazoline-6-sulfonic acid amide 7-chloro-2-ethyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-4-oxo-6-quinazolinesulfonamide Aquamox 7-Chloro-2-ethyl-4-oxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6-quinazolinesulfonamide 7-Chloro-2-ethyl-4-oxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinazoline-6-sulfonamide Idrokin |
| Description | Quinethazone is an orally active diuretic agent and is also a weak inhibitor of carbonic anhydrase. Quinethazone can be used for hypertension research[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vivo | Quinethazone (50 mg/kg; p.o.; daily for 2 weeks) lowers blood pressure of renal hypertensive rats in association with a decrease in potassium but no change in water or sodium contents of aorta wall[1]. Animal Model: Five- to 6-week-old Long Evans male rats, hypertension model[1] Dosage: 50 mg/kg Administration: Oral, daily for 2 weeks Result: Had no significant effect on sodium or water distribution in arterial tissue of hypertensive rats, but decreased approximate 20% intra-cellular content of potassium |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 250 - 252ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C10H12ClN3O3S |
| Molecular Weight | 289.739 |
| Exact Mass | 289.028778 |
| PSA | 109.67000 |
| LogP | 0.49 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.582 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|