7488-99-5
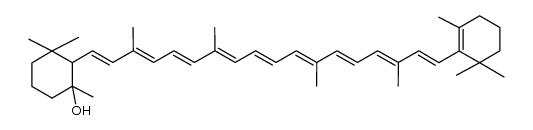
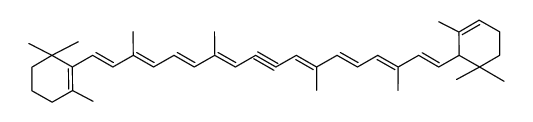
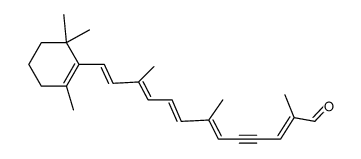
| Name | (6'R)-β,ε-carotene |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
1,3,3-Triméthyl-2-[(1E,3E,5E,7E,9E,11E,13E,15E,17E)-3,7,12,16-tétraméthyl-18-(2,6,6-triméthyl-2-cyclohexén-1-yl)-1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17-octadécanonaèn-1-yl]cyclohexène
CISALPHA-CAROTENE Carotene 1,3,3-Trimethyl-2-[(1E,3E,5E,7E,9E,11E,13E,15E,17E)-3,7,12,16-tetramethyl-18-(2,6,6-trimethyl-2-cyclohexen-1-yl)-1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17-octadecanonaen-1-yl]cyclohexen Renieratene (6'R)-beta,epsilon-carotene Isorenieratene A-CAROTENE MFCD00136012 CAROTENE,A α-Carotene 1,3,3-Trimethyl-2-[(1E,3E,5E,7E,9E,11E,13E,15E,17E)-3,7,12,16-tetramethyl-18-(2,6,6-trimethyl-2-cyclohexen-1-yl)-1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17-octadecanonaen-1-yl]cyclohexene all-trans-α-carotene 4,5-Didehydro-5,6-dihydro-β,β-carotene (+)-α-Carotene |
| Description | α-Carotene, a precursor of vitamin A, is used as an anti-metastatic agent or as an adjuvant for anti-cancer drugs. α-Carotene is isolated from yellow-orange and dark-green vegetables[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | α-Carotene (0.5-2.5 μM; 24 hours) significantly increases protein expression of TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 in a concentration-dependent manner in LLC cells. AC (0.5-2.5 μM) significantly increases PAI-1 protein expression. α-Carotene (2.5 μM) also significantly inhibits integrin β1-mediated phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) which then decreased the phosphorylation of MAPK family[2]. α-Carotene (0.5, 1, 2.5 μM; 48 hours) significantly and concentration-dependently inhibits invasion of LLC during 48 h of incubation[2]. α-Carotene (0.5, 1, 2.5 μM; 24 hours) significantly decreases activities of MMP-9, -2 and uPA in concentration-dependent manner in LLC cells[2]. α-Carotene (2, 5, 10 μM; 7 days) inhibits the proliferation of the human neuroblastoma cell line GOTO in a dose- and time-dependent manner. α-Carotene (5 μM; 48 hours) halts the cell cycle at the G0/G1 phase concomitantly with a reduction in the mRNA expression of the protooncogene N-Myc[3]. Western Blot Analysis[2] Cell Line: Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC) cells Concentration: 0.5, 1, 2.5 μM Incubation Time: 24 hours Result: Significantly increased protein expression of TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 in a concentration-dependent manner in LLC cells. |
| In Vivo | α-Carotene (5 mg/kg; oral; twice a week; for additional 3 weeks) alone significantly decreases lung metastasis without affecting primary tumor growth[2]. Animal Model: C57BL/6 male mice (4 weeks old; 20-25 g) with LLC cells[2] Dosage: 5 mg/kg Administration: Oral; twice a week; for additional 3 weeks Result: Significantly decreased lung metastasis. |
| References |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 644.9±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 185ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C40H56 |
| Molecular Weight | 536.873 |
| Flash Point | 341.2±20.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 536.438232 |
| LogP | 15.45 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.563 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
|---|---|
| Risk Phrases | 40 |
| Safety Phrases | S36/37 |
| RIDADR | UN 1593 6.1/PG 3 |
| Packaging Group | II; III |
| Hazard Class | 4.1 |
|
~% 
7488-99-5 |
| Literature: Phytochemistry (Elsevier), , vol. 6, p. 1119 - 1126 |
|
~% 
7488-99-5 |
| Literature: Phytochemistry (Elsevier), , vol. 6, p. 1119 - 1126 |
|
~% 
7488-99-5 |
| Literature: Helvetica Chimica Acta, , vol. 38, p. 610 |
|
~% 
7488-99-5 |
| Literature: Helvetica Chimica Acta, , vol. 44, p. 985 - 993 |
|
~% 
7488-99-5 |
| Literature: Helvetica Chimica Acta, , vol. 44, p. 985 - 993 |
|
~% 
7488-99-5 |
| Literature: Helvetica Chimica Acta, , vol. 44, p. 985 - 993 |
|
~% 
7488-99-5 |
| Literature: Helvetica Chimica Acta, , vol. 44, p. 985 - 993 |
|
~% 
7488-99-5 |
| Literature: Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie, , vol. 588, p. 117,123 |
|
~% 
7488-99-5 |
| Literature: Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie, , vol. 588, p. 117,123 |
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |