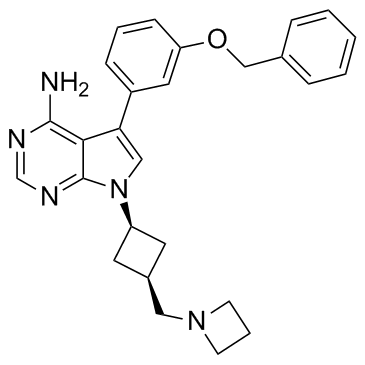
475489-16-8
| Name | [7-[cis-3-[(Azetidin-1-yl)methyl]cyclobutyl]-5-(3-benzyloxyphenyl)-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl]amine |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
avp-aew541
nvp-aew541 7-[cis-3-(1-Azetidinylmethyl)cyclobutyl]-5-[3-(benzyloxy)phenyl]-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-amine nvp-aew541 aew541 |
| Description | NVP-AEW541 is a potent inhibitor of IGF-1R with IC50 of 0.15 μM, also inhibits InsR, with IC50 of 0.14 μM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 0.15 ±0.036 μM (IGF-IR), 0.14±0.039 μM (InsR), 0.42±0.11 μM (Flt-3), 2±0.61 μM (PDGFR), 2.4±0.38 μM (c-Src), 3.3±1.4 μM (c-Kit)[1] |
| In Vitro | NVP-AEW541 inhibits the in vitro kinase activity of the recombinant IGF-IR kinase domain with an IC50 value of 0.15 μM and to be equipotent against the recombinant InsR kinase domain. NVP-AEW541 is confirmed active toward the IGF-IR kinase (IC50=86 nM) and shown to be selective at the cellular level. Indeed, NVP-AEW541 is found to be 27-fold more potent toward the native IGF-IR, as compared to the structurally related native InsR (IC50=2.3 μM). NVP-AEW541 suppresses the IGF-I-mediated survival, soft agar and proliferation of MCF-7 cells with IC50 of 0.162 μM, 0.105 μM and 1.64 μM, respectively[1]. |
| In Vivo | Oral administration of NVP-AEW541 (20, 30, or 50 mg/kg) results in abrogation of basal and IGF-I-induced receptor, and PKB and MAPK phosphorylation in the NWT-21 tumor xenograft[1]. NVP-AEW541 is administered by oral gavage [50 mg/kg in 0.2 mL of 25 mM L-(+)-tartaric acid] twice a day for 14 consecutive days. The control group is similarly treated with 0.2 mL carrier [25 mM L-(+)-tartaric acid] twice a day. Tumor volume and animal weight are measured thrice a week till the end of the treatment. At that time, animals are sacrificed and tumors are collected and formalin fixed for histologic and immunohistochemical analyses. In both cases, NVP-AEW541 treatment causes tumor shrinkage that reached the statistical significance (P=0.0156 and P=0.0111 for HTLA-230 and SK-N-BE2c, respectively)[2]. |
| Kinase Assay | The activities of protein kinases are assayed in the presence or absence of inhibitors by measuring the incorporation of 33P from [γ33P]ATP (1000 Ci/mmol) into appropriate substrates. The protein kinase assays are carried out in 96-well plates at RT under conditions described in details below andterminated by the addition of 20 μL of 125 mM EDTA. Subsequently, 30 μL (c-Abl, c-Src, IGF-1R) or 40 μL (all other kinases) of the reaction mixture are transferred onto Immobilon-PVDF pre-soaked for 5 min with methanol, rinsed with water, then soaked for 5 min with 0.5 % H3PO4 and mounted on vacuum manifold. After spotting all samples, vacuum is connected and each well rinsed with 200 μL 0.5 % H3PO4. Membranes are removed and washed 4× on a shaker with 1% H3PO4, once with ethanol. After drying, mounting in Packard TopCount 96- well frame, and adding of 10 μL/well of Microscint, membranes are counted. IC50 values are calculated by linear regression analysis of the percentage inhibition of each compound in duplicate, at four concentrations (usually 0.01, 0.1, 1, and 10 μM).One unit of protein kinase activity is defined as 1 nmole of 33P transferred from [γ33P]ATP to the substrate protein per minute per mg of protein at 37C[1]. |
| Cell Assay | Between 3000 and 6000 cells/well are seeded in 96-well plates with a total media volume of 100 μL/well. Increasing concentrations of the compound are added 24 hr thereafter in quadruplicate. 72 hr later, cells are fixed by addition of 25 μL/well Glutaraldehyde (20%) and incubation for 10 min at RT. Cells are then washed 2× with 200μL/well H2O and 100μL Methylene Blue (0.05%) is added. After incubation for 10 min at RT, cells are washed 3× with 200 μL/well H2O. 200 μL/well HCl (3%) is added, and following incubation for 30 min at RT on a plate shaker, absorbance is measured at 650 nm[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[1] Female Harlan athymic nude mice are used NWT-21 cells are grown in DMEM (high glucose, 4.5 g/L), 10% FCS, 1% L-glutamine, and 1% Na-pyruvate. 5×106 cells/animal are initially injected s.c. into the right flank of five mice. For the in vivo efficacy experiment, tumors of 500 to 800 mm3 are excised and nonnecrotic areas are cut to fragments of 3×3×3 mm. Tumor fragments are washed in sterile PBS and one tumor fragment per animal is trans- planted s.c. into the right flank. Tumor volumes (length×width ×height×π/6) and body weights are determined three times weekly. At the first day of treatment (day 0), the therapy group (NVP-AEW541) and the control group (vehicle only) are selected by stratification (8 animals per group, average tumor volume of about 95 mm3 per group). Animals are treated p.o. twice daily, 7 days/week either with NVP-AEW541 (20, 30, or 50 mg/kg; 10 mL/kg dissolved in 25 mM L(+)-tartaric acid, therapy group) or with 25 mM L(+)-tartaric acid (control group). Antitumor activity is expressed as T/C%(mean increase of tumor volumes of treated animals divided by the mean increase of tumor volumes of control animals multiplied by 100). The experiment is terminated when the mean tumor volume is about 1500 mm3. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 669.0±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 145℃ |
| Molecular Formula | C27H29N5O |
| Molecular Weight | 439.552 |
| Flash Point | 358.4±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 439.237213 |
| PSA | 69.20000 |
| LogP | 4.66 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.710 |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |