91396-88-2
| Name | N'-phenylpyridine-4-carbohydrazide |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
1-Isonicotinoyl-2-phenyl-hydrazin
PluriSln 1 N'-Phenylisonicotinohydrazide Isonicotinsaeure-phenylhydrazid Isonicotinsaeure-(2-phenyl-hydrazid) 4-Pyridinecarboxylic acid, 2-phenylhydrazide Isonicotinsaeure-(N'-phenyl-hydrazid) isonicotinic acid N'-phenylhydrazide NSC 14613 |
| Description | PluriSln 1 is an inhibitor of stearoyl-coA desaturase (SCD), and is a pluripotent cell-specific inhibitor. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
SCD[1] |
| In Vitro | PluriSln 1, a small-molecule inhibitor of stearoyl-coA desaturase (SCD), on induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS)-derived cardiomyocytes (CM). PluriSln 1 treatment significantly decreases the mRNA and protein level of Nanog, a marker for both cell pluripotency and tumor progression; importantly, we provide evidence that PluriSln 1 treatment at 20 µM for 1 day significantly induces the apoptosis of Nanog-positive iPS derivates (iPSD). In addition, PluriSln 1 treatment at 20 µM for 4 days diminished Nanog-positive stem cells in cultured iPSD while not increasing apoptosis of iPS-derived CM. To investigate whether PluriSln 1 treatment prevents tumorigenicity of iPSD after cell transplantation, we intramyocardially injected PluriSln 1- or DMSO-treated iPSD in a mouse model of myocardial infarction (MI). DMSO-treated iPSD readily formed Nanog-expressing tumors 2 weeks after injection, which is prevented by treatment with PluriSln 1. Moreover, treatment with PluriSln 1 does not change the expression of cTnI, α-MHC, or MLC-2v, markers of cardiac differentiation (P>0.05, n=4). Importantly, PluriSln 1-treated iPS-derived CM exhibits the ability to engraft and survive in the infarcted myocardium[1]. |
| Cell Assay | The differentiation of iPS cells to cardiomyocytes (CM) is induced by embryoid body (EB) formation. When iPS cells reached 70% confluency in 10-cm dishes, cells are digested using 0.25% trypsin/EDTA. Cell pellets are re-suspended in differentiation medium (DMEM with 20% FBS and 10 ng/mL BMP4) to a final concentration of 200,000 cells/mL. Cell suspensions are added to 6-well plates with Ulta-Low Attachment surfaces for 4 d to initiate EB formation. On day 5, EBs are cultured on 0.1% gelatin-coated dishes for 14 d using CF culture medium for the outgrowth of cardiac structures. At this stage, iPS cells undergoing EB formation are termed iPS derivates (iPSD)[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 335.7±15.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 177-178℃ |
| Molecular Formula | C12H11N3O |
| Molecular Weight | 213.235 |
| Flash Point | 156.9±20.4 °C |
| Exact Mass | 213.090210 |
| PSA | 54.02000 |
| LogP | 1.34 |
| Appearance | white to beige |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.655 |
| Storage condition | ?20°C |
| Water Solubility | DMSO: soluble15mg/mL, clear |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Phrases | 22-36 |
| Safety Phrases | 26 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
~% 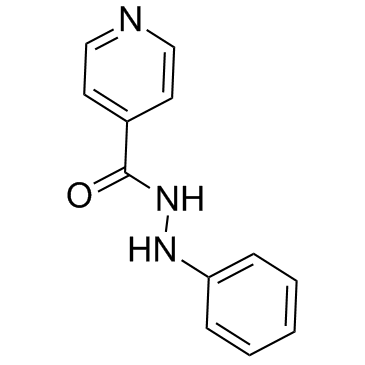
91396-88-2 |
| Literature: Yale et al. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1953 , vol. 75, p. 1933,1934 |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |