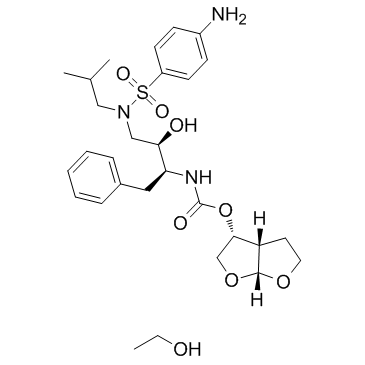
635728-49-3
| Name | [14C]-Darunavir ethanolate |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
DARUNAVIR ETHANOLATE(PREZISTA) TMC114
(3R,3aS,6aR)-Hexahydrofuro[2,3-b]fur-3-yl-[(1S,2R)-3-{[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl](2-methylpropyl)amino}-1-benzyl-2-hydroxypropyl]carbamat-ethanol(1:1) (3R,3aS,6aR)-hexahydrofuro[2,3-b]furan-3-yl [(1S,2R)-3-{[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl](2-methylpropyl)amino}-1-benzyl-2-hydroxypropyl]carbamate - ethanol (1:1) [(1S,2R)-3-{[(4-aminophényl)sulfonyl](2-méthylpropyl)amino}-1-benzyl-2-hydroxypropyl]carbamate de (3R,3aS,6aR)-hexahydrofuro[2,3-b]fur-3-yle - éthanol (1:1) Darunavir Ethanolate (3R,3aS,6aR)-Hexahydrofuro[2,3-b]furan-3-yl [(2S,3R)-4-{[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl](isobutyl)amino}-3-hydroxy-1-phenyl-2-butanyl]carbamate - ethanol (1:1) Carbamic acid, N-[(1S,2R)-3-[[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl](2-methylpropyl)amino]-2-hydroxy-1-(phenylmethyl)propyl]-, (3R,3aS,6aR)-hexahydrofuro[2,3-b]furan-3-yl ester, compd. with ethanol (1:1) carbamic acid, [(1S,2R)-3-[[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl](2-methylpropyl)amino]-2-hydroxy-1-(phenylmethyl)propyl]-, (3R,3aS,6aR)-hexahydrofuro[2,3-b]furan-3-yl ester, compd. with ethanol (1:1) UNII-33O78XF0BW Darunavir Ethanolate(Prezista) Darunavir (Ethanolate) DARUNAVIR THANOLATE |
| Description | Darunavir ethanolate (TMC114 ethanolate) is a potent HIV protease inhibitor used to treat and prevent HIV/AIDS. Darunavir has a Ki of 1 nM for wild type HIV-1 protease. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Ki: 1 nM (WT HIV-1 protease)[1] |
| In Vitro | Darunavir is a broad-spectrum potent inhibitor active against HIV-1 clinical isolates with minimal cytotoxicity. Darunavir forms hydrogen bonds with the conserved main-chain atoms of Asp29 and Asp30 of the protease. These interactions are proposed to be critical for the potency of this compound against HIV isolates that are resistant to multiple protease inhibitors[1]. In an in vitro study in MT-2 cells, the potency of darunavir is greater than that of saquinavir, amprenavir, nelfinavir, indinavir, lopinavir and ritonavir. Darunavir is primarily metabolized by the hepatic cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes, primarily CYP3A. The ‘boosting’ dose of ritonavir acts an an inhibitor of CYP3A, thereby increasing darunavir bioavailability[2]. |
| In Vivo | Darunavir is effective against wild-type and PI-resistant HIV, and has an oral bioavailability of 37%. It needs to be combined with ritonavir, which increases the bioavailability to 82%[3]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C29H43N3O8S |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 593.732 |
| Exact Mass | 593.277100 |
| PSA | 169.03000 |
| LogP | 4.42680 |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |
| HS Code | 29334900 |
|---|
|
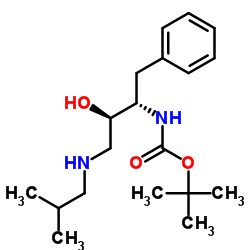
~% 
635728-49-3 |
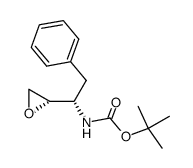
| Literature: Vellanki, Siva Rama Prasad; Sahu, Arabinda; Katukuri, Aravind Kumar; Vanama, Vikram; Kothari, Satishbabu; Ponnekanti, Venkata Suryanarayana; Datta, Debashish Patent: US2012/251826 A1, 2012 ; |
|
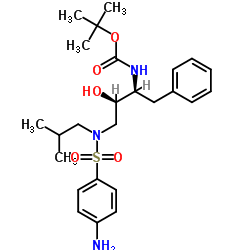
~83% 
635728-49-3 |
| Literature: Vellanki, Siva Rama Prasad; Sahu, Arabinda; Katukuri, Aravind Kumar; Vanama, Vikram; Kothari, Satishbabu; Ponnekanti, Venkata Suryanarayana; Datta, Debashish Patent: US2012/251826 A1, 2012 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 10 ; |
|
~% 
635728-49-3 |
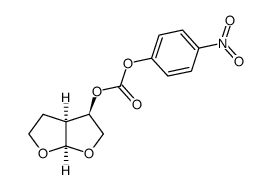
| Literature: US2012/251826 A1, ; |
|
~% 
635728-49-3 |
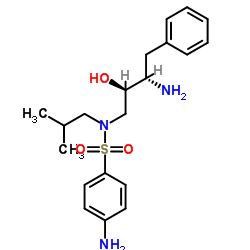
| Literature: US2012/251826 A1, ; |
|
~% 
635728-49-3 |
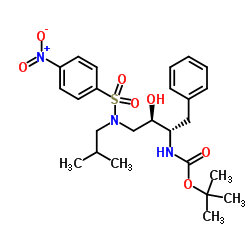
| Literature: US2012/251826 A1, ; |
|
~% 
635728-49-3 |
| Literature: US2012/251826 A1, ; |
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |