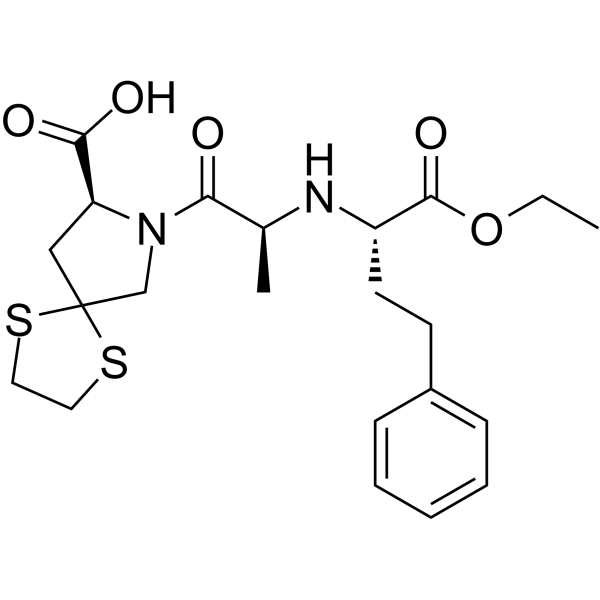
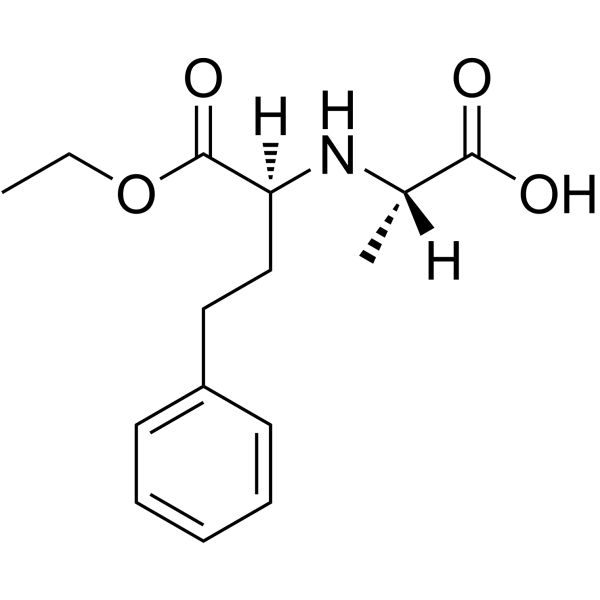
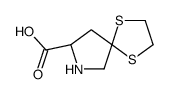
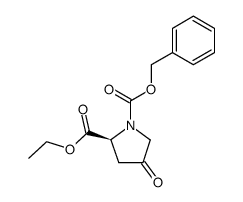
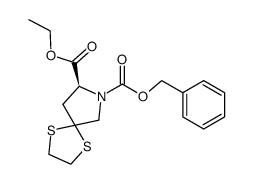
94841-17-5
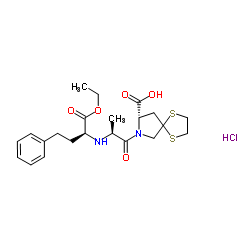
| Name | (8S)-7-[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-1-ethoxy-1-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-yl]amino]propanoyl]-1,4-dithia-7-azaspiro[4.4]nonane-8-carboxylic acid,hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
TI 211-950
Sandopril (8S-(7(R*(R*)),8R*))-7-(2-((1-(ethoxycarbonyl)-3-phenylpropyl)amino)-1-oxopropyl)-1,4-Dithia-7-azaspiro[4.4]nonane-8-carboxylic acid monohydrochloride (8S)-7-[(2S)-2-{[(2S)-1-ethoxy-1-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-yl]amino}propanoyl]-1,4-dithia-7-azaspiro[4.4]nonane-8-carboxylic acid hydrochloride (1:1) (non-preferred name) Renormax Spirapril HCl spiprapril hydrochloride (8S)-7-[(2S)-2-{[(2S)-1-Ethoxy-1-oxo-4-phenyl-2-butanyl]amino}propanoyl]-1,4-dithia-7-azaspiro[4.4]nonane-8-carboxylic acid hydrochloride (1:1) (8S)-7((S)-N-((S)-1-Carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)alanyl)-1,4-dithia-7-azaspiro[4.4]nonane-8-carboxylic acid 1-ethyl ester monohydrochloride spirapril hydrochloride |
| Description | Spirapril (SCH 33844) hydrochloride is a potent angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor with antihypertensive activity. Spirapril competitively binds to ACE and prevents the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II. Spirapril is an orally active prodrug of Spiraprilat and can be used for the research of hypertension, congestive heart failure[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: angiotensin converting enzyme[1] |
| In Vivo | Spirapril (feeding needle; 10 mg/kg; 3 weeks) decreases alcohol intake in TGM123 mice and dose not reduce the alcohol consumption in TLM mice. Spirapril shows a 40.2% reduction in ACE activity in brain membrane from treated-mice. It crosses the blood-brain barrier and suppresses the transgene effect in the experiments.[2] Animal Model: TGM123 mice (expressing a rat angiotensinogen transgene) and TLM ( lacking the angiotensinogen gene) mice[2] Dosage: 10 mg/kg Administration: Feeding needle; 10 mg/kg; 3 weeks Result: Alter voluntary alcohol consumption in animals. Crossed the blood-brain barrier and may influences alcohol consumption mainly by decreasing central angiotensin II (AII) levels. |
| References |
[1]. Spirapril. Drugbank. [2]. B Maul, et al. Alcohol consumption is controlled by angiotensin II. FASEB J |
| Boiling Point | 697.8ºC at 760mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 192-194ºC (dec.) |
| Molecular Formula | C22H31ClN2O5S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 503.07500 |
| Flash Point | 375.8ºC |
| Exact Mass | 502.13600 |
| PSA | 146.54000 |
| LogP | 3.52160 |
|
~% 
94841-17-5 |
| Literature: Smith, Elizabeth M.; Swiss, Gerald F.; Neustadt, Bernard R.; McNamara, Paul; Gold, Elijah H.; et al. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 1989 , vol. 32, # 7 p. 1600 - 1606 |
|
~% 
94841-17-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 32, # 7 p. 1600 - 1606 |
|
~% 
94841-17-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 32, # 7 p. 1600 - 1606 |
|
~% 
94841-17-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 32, # 7 p. 1600 - 1606 |
|
~% 
94841-17-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 32, # 7 p. 1600 - 1606 |
|
~% 
94841-17-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 32, # 7 p. 1600 - 1606 |
|
~% 
94841-17-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 32, # 7 p. 1600 - 1606 |
| Precursor 6 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |