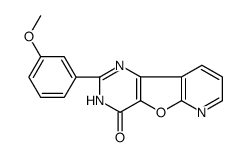
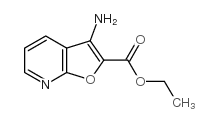
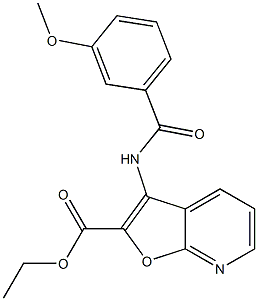
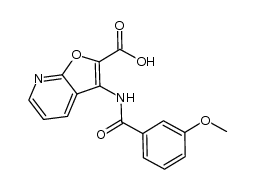
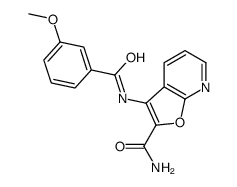
371935-74-9
| Name | 3-(4-morpholin-4-ylpyrido[2,3]furo[2,4-b]pyrimidin-2-yl)phenol |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
3-[4-(4-Morpholinyl)pyrido[3',2':4,5]furo[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl]phenol hydrochloride (1:1)
PI103 Phenol, 3-[4-(4-morpholinyl)pyrido[3',2':4,5]furo[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl]-, hydrochloride (1:1) 3-[4-(Morpholin-4-yl)pyrido[3',2':4,5]furo[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl]phenol hydrochloride (1:1) S1038_Selleck X6K PI-103 |
| Description | PI-103 is a potent PI3K and mTOR inhibitor with IC50s of 8 nM, 88 nM, 48 nM, 150 nM, 20 nM, and 83 nM for p110α, p110β, p110δ, p110γ, mTORC1, and mTORC2. PI-103 also inhibits DNA-PK with an IC50 of 2 nM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
p110α:8 nM (IC50) p110β:88 nM (IC50) p110δ:48 nM (IC50) p110γ:150 nM (IC50) PI3KC2β:26 nM (IC50) PI3KC2α:1 μM (IC50) hsVPS34:2.3 μM (IC50) mTORC1:20 nM (IC50) mTORC2:83 nM (IC50) DNA-PK:2 nM (IC50) ATR:850 nM (IC50) ATM:920 nM (IC50) PI4KIIIβ:50 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | PI-103 exhibits antiproliferative properties in a panel of human cancer cell lines[1]. PI-103 is essentially cytostatic for cell lines and induced cell cycle arrest in the G1 phase. In blast cells, PI-103 inhibits leukemic proliferation, the clonogenicity of leukemic progenitors and induces mitochondrial apoptosis, especially in the compartment containing leukemic stem cells [2]. PI-103 potently inhibits both the rapamycin-sensitive (mTORC1, IC50=20 nM) and rapamycin-insensitive (mTORC2, IC50=83 nM) complexes of the protein kinase mTOR[4]. |
| In Vivo | PI-103 shows therapeutic activity against a range of human tumor xenografts, exhibiting inhibition of angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis, as well as direct antiproliferative effects[1]. PI-103 induces immunosuppression promoting in vivo tumor growth and inhibiting apoptosis. Tumors from PI-103-treated mice shows higher levels of cyclin D1 and more proliferating cells[3]. |
| Kinase Assay | IC50 values are measured using either a standard thin-layer chromatography (TLC) assay for lipid kinase activity or a high-throughput membrane capture assay. Kinase reactions are performed by preparing a reaction mixture containing kinase, inhibitor (2% DMSO final concentration), buffer (25 mM HEPES, pH 7.4, 10 mM MgCl2), and freshly sonicated phosphatidylinositol (100 μg/mL). Reactions are initiated by the addition of ATP containing 10 μCi of γ-32P-ATP to a final concentration 10 or 100 μM, and allowed to proceed for 20 minutes at room temperature. For TLC analysis, reactions are then terminated by the addition of 105 μL 1N HCl followed by 160 μL CHCl3:MeOH (1:1). The biphasic mixture is vortexed, briefly centrifuged, and the organic phase transferred to a new tube using a gel loading pipette tip precoated with CHCl3. This extract is spotted on TLC plates and developed for 3-4 hours in a 65:35 solution of n-propanol:1M acetic acid. The TLC plates are then dried, exposed to a phosphorimager screen, and quantitated. For each compound, kinase activity is typically measured at 10-12 inhibitor concentrations representing two-fold dilutions from the highest concentration tested (100 μM). For compounds showing significant activity, IC50 determinations are repeated two to four times, and the reported value is the average of these independent measurements[4]. |
| Cell Assay | For proliferation assays, MOLM14, OCI-AmL3 and MV4-11 cells are cultured during 48 h at 105 cells/mL, in triplicate, in 10% FCS, without or with 0.1 or 1 μM PI-103, and then pulsed 6 h with 1μCi (37 kBq) [4H]-thymidine. The amounts oadioactivity are determined after trichloracetic acid precipitation[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[3] Five to six month old males of either FVB/N strain or nude BALB/c strain are injected subcutaneously with one million cells in PBS. When tumor reaches between 50 and 100 mm3, mice are treated with 10 mg/kg or 70 mg/kg of PI-103 and/or 50 mg/kg Sorafenib by IP injection daily. Control mice are treated with the same volume of DMSO. Tumor size and mice weight is monitored every 2 days. When mice are sacrificed, tumors are dissected and processed[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.409 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 520.25ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C19H16N4O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 348.36 |
| PSA | 84.51000 |
| LogP | 3.84720 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.712 |
| Storage condition | Desiccate at +4°C |
|
~% 
371935-74-9 |
| Literature: Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters, , vol. 17, # 9 p. 2438 - 2442 |
|
~% 
371935-74-9 |
| Literature: Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters, , vol. 17, # 9 p. 2438 - 2442 |
|
~% 
371935-74-9 |
| Literature: Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters, , vol. 17, # 9 p. 2438 - 2442 |
|
~% 
371935-74-9 |
| Literature: Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters, , vol. 17, # 9 p. 2438 - 2442 |
|
~% 
371935-74-9 |
| Literature: Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters, , vol. 17, # 9 p. 2438 - 2442 |
|
~% 
371935-74-9 |
| Literature: Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters, , vol. 17, # 9 p. 2438 - 2442 |
|
~% 
371935-74-9 |
| Literature: Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters, , vol. 17, # 9 p. 2438 - 2442 |
| Precursor 6 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |