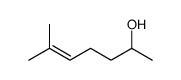
6147-11-1
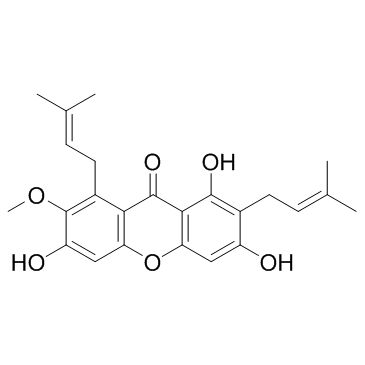
| Name | α-mangostin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
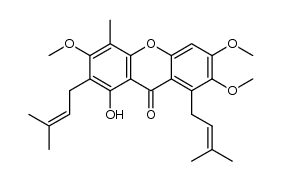
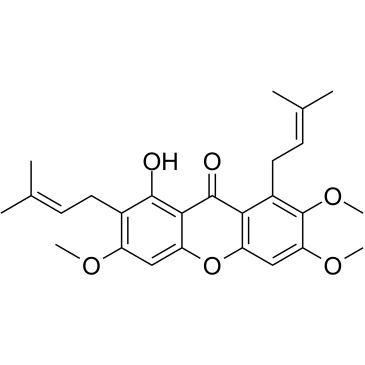
1,3,6-Trihydroxy-7-methoxy-2,8-di(3-methyl-2-butenyl)xanthone
Mangostin 1,3,6-trihydroxy-7-methoxy-2,8-bis(3-methylbut-2-enyl)xanthen-9-one alpha-mangostin EINECS 448-420-7 a-Mangostin 1,3,6-Trihydroxy-7-methoxy-2,8-bis(3-methyl-2-butenyl)-9H-xanthen-9-one 1,3,6-Trihydroxy-7-méthoxy-2,8-bis(3-méthyl-2-butèn-1-yl)-9H-xanthén-9-one 1,3,6-Trihydroxy-7-methoxy-2,8-bis(3-methyl-2-buten-1-yl)-9H-xanthen-9-one 1,3,6-Trihydroxy-7-methoxy-2,8-bis(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)-9H-xanthen-9-one MFCD00135200 |
| Description | Alpha-mangostin is a dietary xanthone with broad biological activities, such as antioxidant, anti-allergic, antiviral, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and anticancer effects. It is an inhibitor of mutant IDH1 (IDH1-R132H) with a Ki of 2.85 μM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 2.85 μM (IDH1-R132H)[1] |
| In Vitro | Alpha-mangostin exhibits a selective inhibitory effect on IDH1-R132H, but not on IDH1. Alpha-mangostin competitively inhibits the binding of alpha-mangostin (α-KG) to IDH1-R132H. The structure–relationship study reveals that alpha-mangostin exhibits the strongest core inhibitor structure. Alpha-mangostin selectively promotes demethylation of 5-methylcytosine (5mC) and histone H3 trimethylated lysine residues in IDH1 (+/R132H) MCF10A cells[1]. Cell proliferation significantly decreases in a dose-dependent manner in the cells treated with alpha-mangostin. Alpha-mangostin also increases the levels of Bax (pro-apoptotic), cleaved caspase-3, cleaved caspase-9 and cleaved-poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP)[2]. Alpha-mangostin significantly inhibits light-induced degeneration of photoreceptors and 200 μM H2O2-induced apoptosis of RPE cells. 200 μM H2O2-induced generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and light-induced generation of malondialdehyde (MDA) are suppressed by alpha-mangostin[3]. |
| In Vivo | Alpha-mangostin reduces risk of liver fibrosis through the decrease in p53 expression as compared to the TAA_DMSO treatment. The serum levels of the liver enzymes AST and ALT after treatment with α-mangostin decrease as compared to DMSO alone[4]. |
| Cell Assay | IDH1+/+ and IDH1 MCF10A cells are grown in DMEM/F-12 media, supplemented with 5% horse serum, 20 ng/mL EGF, 0.5 μg/mL hydrocortisone, 10 μg/mL insulin. IDH1+/+ and IDH1 MCF10A cells are seeded in 6 well plates. After an exposure to 5 μM alpha-mangostin. cells are collected after indicated times and the viable cell number is calculated, using hemacytometer counting[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats: Male Wistar rats are divided into 3 groups and treated with intraperitoneal injections of TAA (200 mg/kg). One subgroup is left untreated whereas the other two are treated either with 100 mg/kg alpha-mangostin or vehicle alone (80% DMSO, 20% water), which are administered intraperitoneally 3 times per weekfor a total of4 weeks. The incidence offibrotic nodules on the liver and the serum levels of the liver enzymes aspartate transaminase (AST) and alanine transaminase (ALT) are measured[4]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 640.1±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 182ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C24H26O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 410.460 |
| Flash Point | 220.3±25.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 410.172943 |
| PSA | 100.13000 |
| LogP | 5.45 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.624 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301 |
| Precautionary Statements | P301 + P310 |
| Hazard Codes | T |
| Risk Phrases | 25 |
| Safety Phrases | 45 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1 / PGIII |
| RTECS | ZD6122420 |
| HS Code | 2932999099 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
| HS Code | 2932999099 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2932999099. other heterocyclic compounds with oxygen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |



![2-[3-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-4-oxoquinazolin-2-yl]sulfanyl-N-ethyl-N-(3-methylphenyl)acetamide structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/389/6195-80-8.png)

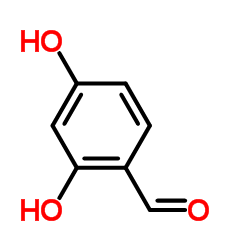
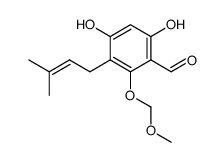
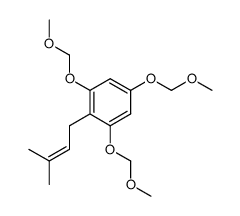
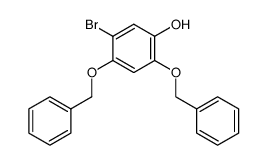

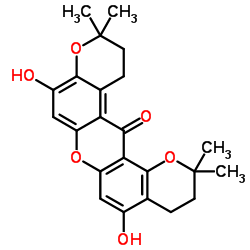
![5,9-Dihydroxy-8-methoxy-2,2-dimethyl-7-(3-methyl-2-buten-1-yl)-3,4-dihydro-2H,6H-pyrano[3,2-b]xanthen-6-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/218/19275-46-8.png)

![3,4-dihydro-5,9-dihydroxy-8-methoxy-7-(3-methoxy-3-methylbutyl)-2,2-dimethyl-2H,6H-pyrano-[3,2-b]xanthen-6-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/259/112649-47-5.png)