14116-68-8
| Name | lacto-n-tetraose |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
fromhumanmilk
GAL-BETA1,3GLCNAC-BETA1,3GAL-BETA1,4GLC LNT-GEL LNT LACTO-N-TETRAOSE FROM HUMAN MILK LCOSE4 LNT-KLH |
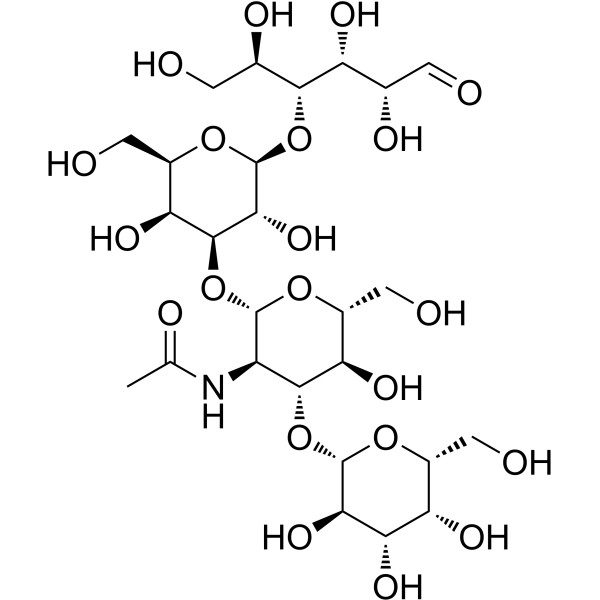
| Description | Lacto-N-tetraose is the significant core structure of human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs) naturally existing in human milk. Lacto-N-tetraose is consist of galactose, N-acetylglucosamine, and glucose moieties. Lacto-N-tetraose has prebiotic effect, immune regulatory effect, anti-inflammatory effects, intestinal cell responses regulatory effect, antibacterial activity and antiviral activity. Lacto-N-tetraose has been widely added to infant formula[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | HMOs exhibits antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity against Streptococcus agalactiae, antibiofilm activity against Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), and antimicrobial activity against both Acinetobacter baumannii and Clostridium difficile[2]. Lacto-N-tetraose (500-2000 μg/mL) does not cause clastogenic or aneugenic signs in human peripheral blood lymphocytes, nor increase the percentage of micronucleated cells[3]. |
| In Vivo | Lacto-N-tetraose (1000-4000 mg/kg; p.o.; daily for 90 days) does not show toxicity in neonatal SD rats[3]. Animal Model: Female neonatal SD rats (housed together with dam until weaning after 21 days)[3] Dosage: 1000, 25000 and 4000 mg/kg Administration: p.o.; daily for 90 days Result: Did not show toxicity on clinical observations, body weight, food consumption, development and maturation, clinical pathology, organ weights or histopathology. |
| References |
| Density | 1.76g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 1116.1ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C26H45NO21 |
| Molecular Weight | 707.63000 |
| Flash Point | 628.8ºC |
| Exact Mass | 707.24800 |
| PSA | 356.70000 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.668 |
| Safety Phrases | 24/25 |
|---|