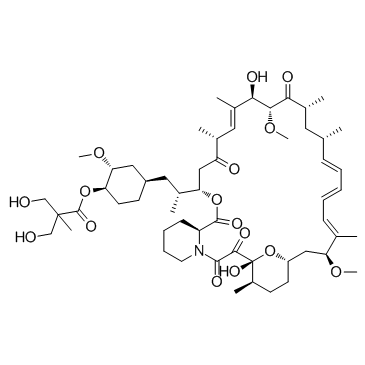
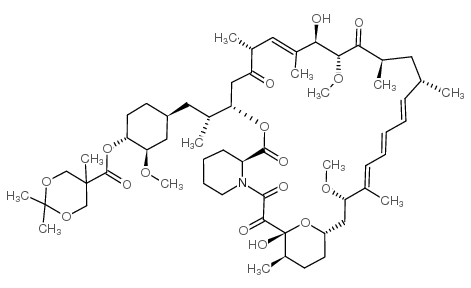
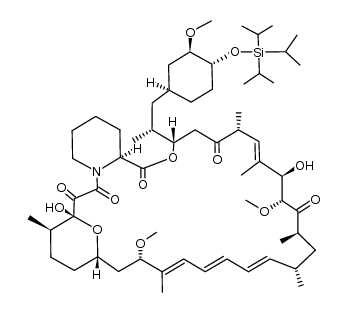
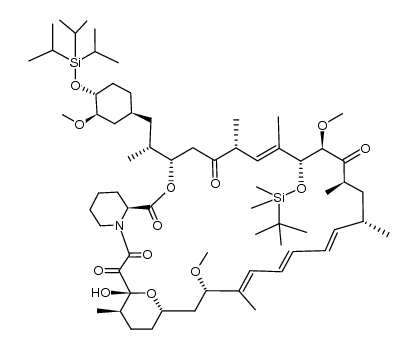
53123-88-9
| Name | sirolimus |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
sila9268a
23,27-Epoxy-3H-pyrido[2,1-c][1,4]oxaazacyclohentriacontine AY 22989 EINECS 262-640-9 RAPA Rapamycin RPM RAPAMUNE MFCD00867594 Sirolimus Rapamicin |
| Description | Rapamycin (Sirolimus) is a potent and specific mTOR inhibitor with an IC50 of 0.1 nM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
mTOR:0.1 nM (IC50) Autophagy |
| In Vitro | Rapamycin inhibits endogenous mTOR activity in HEK293 cells with IC50 of 0.1 nM, more potently than iRap and AP21967 with IC50 of 5 nM and 10 nM, respectively[1]. Rapamycin exerts its antitumor effect on malignant glioma cells by inducing autophagy and suggest that in malignant glioma cells a disruption of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway could greatly enhance the effectiveness of mTOR inhibitors. Rapamycin inhibits cell viability in all three cell lines in a dose-dependent manner, but their sensitivities varied. The IC50 levels of T98G, U87-MG, and U373-MG cells are 2 nM, 1 μM, and >25 μM, respectively[3]. |
| In Vivo | Treatment with Rapamycin (i.p, 1.5 mg/kg) almost completely prevents the hypertrophic increases in plantaris muscle weight and fibre size at 7 and 14 days[4]. WT or LS/+ mice are treated daily Rapamycin (2 mg/kg body weight i.p.) for 4 weeks, follows by an additional 4 weeks of weekly injections of the same dose. There is significant reversal of the abnormal fetal gene expression profile of hearts from Rapamycin-treated LS/+ mice[5]. |
| Kinase Assay | HEK293 cells are plated at 2-2.5×105 cells per well of a 12-well plate and serum-starved for 24 h in DMEM only. Cells are mock-treated or treated with Rapamycin (0.05-50 nM), iRap (0.5-500 nM), or AP21967 (0.5-500 nM) for 15 minutes at 37°C. Serum is added to a final concentration of 20% for 30 minutes at 37°C. Cells are lysed and cell lysates are separated by SDS-PAGE. Resolved proteins are transferred to a PVDF membrane and immunoblotted with a phosphospecific primary antibody against Thr389 of p70 S6 kinase. Data are analyzed using ImageQuant and KaleidaGraph[1]. |
| Cell Assay | HL-60, NB4, U937, KG-1, and K562 cells are passaged routinely in RPMI-1640 supplemented with 10% heat- inactivated FBS, 2 mM L-glutamine, 50 U/mL penicillin and 50 μg/mL streptomycin in a 5% CO2 humidified atmosphere at 37°C. For the experiments, exponentially growing cells are harvested by centrifugation, and resuspended in fresh medium containing 10% FBS. The cells are seeded at an initial cell density of 2×105/mL in BD Falcon six-well plates in the presence of various concentrations of DMSO or 1 μM ATRA. Rapamycin (20 nM) is added 20 min prior to the differentiation agents. At day 2, 0.3 mL of fresh medium is added to each well. The viable cells are determined by trypan blue exclusion and quantified using a hemocytometer[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats[4] Female Sprague-Dawley rats (250-275 g), the adult female SD rats (225-250 g) are randomized to treatment or vehicle groups so that the mean starting body weights of each group are equal. Drug treatment began on the day of surgery or on the first day of reloading after the 14-day suspension. Rapamycin is delivered once daily by intraperitoneal injection at a dose of 1.5 mg/kg, dissolved in 2% carboxymethylcellulose. CsA is delivered once daily by subcutaneous injection at a dose of 15 mg/kg, dissolved in 10% methanol and olive oil. FK506 is delivered once daily via subcutaneous injection at a dose of 3 mg/kg, dissolved in 10% ethanol, 10% cremophor and saline. Mice[5] Rapamycin is dissolved in ethanol at a concentration of 20 mg/mL, filter sterilized, resuspended in vehicle (0.25% PEG, 0.25% Tween-80) at a concentration of 1 mg/mL, and injected i.p. (2 mg/kg body weight), either daily for 4 weeks or daily for 4 weeks followed by weekly injections for an additional 4 weeks. Injections began at either 8 weeks (prior to onset of hypertrophy) or 12 weeks (after established hypertrophy is indicated) of age, and mice are assessed after 4 weeks of treatment or after 8 weeks of treatment, as detailed in the Results and figure legends. As controls, WT and LS/+ mice are treated with vehicle alone. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 973.0±75.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 183-185°C |
| Molecular Formula | C51H79NO13 |
| Molecular Weight | 914.172 |
| Flash Point | 542.3±37.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 913.555115 |
| PSA | 195.43000 |
| LogP | 3.54 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.551 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS02, GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H225-H302 + H312 + H332-H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P280-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | UN 1648 3 / PGII |
| RTECS | VE6250000 |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
| Precursor 4 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
|---|



![[chloro(methyl)phosphoryl]methane structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/069/1111-92-8.png)