56365-38-9
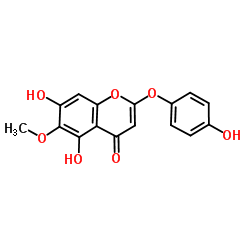
| Name | 5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenoxy)-6-methoxychromen-4-one |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
5,7-Dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenoxy)-6-methoxy-4H-chromen-4-one
Capillarisin X1106 Capillarisine 2-(p-Hydroxyphenoxy)-6-methoxy-5,7-dihydroxychromone |
| Description | Capillarisin, as a constituent from Artemisiae Capillaris herba, is found to exert anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Capillarisin can be used for the research of asthma-mediated complications and can be a potential neuroprotectant against bupivacaine-induced neurotoxicity[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Capillarisin (0~40 μM; 24 hours; SH-SY5Y cells) does not produce any significant changes on the viability of SH-SY5Y cells[3]. .Capillarisin (40 μM; 24 hours; SH-SY5Y cells) induces PI3K/PKB pathway inactivation, which inhibiting apoptosis in bupivacaine-challenged SH-SY5Y cells is overturned by LY294002 treatment and counteracts bupivacaine-induced injury via activating the PI3K/PKB pathway[3]. .Capillarisin antagonizes bupivacaine-induced oxidative stress via activating the PI3K/PKB pathway in SH-SY5Y cells. Capillarisin inhibits bupivacaine-induced mitochondrial injury and endoplasmic reticulum stress via activating PI3K/PKB pathway[3]. Cell Viability Assay[3] Cell Line: SH-SY5Y cells Concentration: 0~40 μM Incubation Time: 24 hours Result: Did not produce any significant changes on the viability of SH-SY5Y cells. Western Blot Analysis[3] Cell Line: SH-SY5Y cells Concentration: 40 μM Incubation Time: 24 hours Result: Induced PI3K/PKB pathway inactivation in SH-SY5Y cells. Apoptosis Analysis[3] Cell Line: SH-SY5Y cells Concentration: 40 μM Incubation Time: 24 hours Result: Induced inhibition of apoptosis in bupivacaine-challenged SH-SY5Y cells was overturned by LY294002 treatment. |
| In Vivo | Capillarisin (20 and 80 mg/kg; i.p.; 1 hour) pretreatment strongly inhibits NF-κB mediated genes (iNOS, COX-2)[4]. Capillarisin significantly reduces the plasma leading nitrite production. Capillarisin markedly suppresses the adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) in plasma and substance P in CFA-induced paw tissue[4]. Animal Model: ICR mice[4] Dosage: 20 and 80 mg/kg Administration: I.p.; 1 hour Result: Pretreatment strongly inhibited NF-κB mediated genes (iNOS, COX-2). |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 582.6±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C16H12O7 |
| Molecular Weight | 316.262 |
| Flash Point | 221.2±23.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 316.058289 |
| PSA | 109.36000 |
| LogP | 2.28 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.695 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|