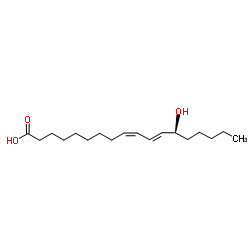
29623-28-7
| Name | 13(s)-hode |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
(9Z,11E,13S)-13-hydroxyoctadeca-9,11-dienoic acid
13-Hydroxy-9c,11t-octadecadienoic acid (9Z,11E,13S)-13-Hydroxy-9,11-octadecadienoic acid 13(S)-HYDROXYOCTADECA-9Z,11E-DIENOIC ACID (13S,9Z,11E)-13-Hydroxy-9,11-octadecadienoic acid 13(S)-HODE |
| Description | (S)-Coriolic acid (13(S)-HODE), the product of 15-lipoxygenase (15-LOX) metabolism of linoleic acid, functions as the endogenous ligand to activate PPARγ. (S)-Coriolic acid is an important intracellular signal agent and is involved in cell proliferation and differentiation in various biological systems. (S)-Coriolic acid induces mitochondrial dysfunction and airway epithelial injury[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | (S)-Coriolic acid (25μM) causes mitochondrial structural alterations and injury in bronchial epithelium[2]. (S)-Coriolic acid (30 nM; 6 hours; E-FABP-/- keratinocytes) induces K1 expression through NF-κB activation. (S)-Coriolic acid increases the phosphorylation of IκBαat serine 32, which induces IκB degradation and thereby activates NF-κB. (S)-Coriolic acid also increases the phosphorylation of Ikkinase-bat tyrosine 199, which promotes IκBα phosphorylation and subsequent NF-kB activation[3]. |
| In Vivo | (S)-Coriolic acid (0-0.6 mg per mouse; Intranasally once a day for 3 consecutive days) causes severe airway dysfunction, airway neutrophilia, mitochondrial dysfunction and epithelial injury[2]. Animal Model: BALB/c mice (6-8 weeks)[2] Dosage: 0-0.6 mg per mouse Administration: Intranasally once a day for 3 consecutive days Result: BALB/c mice developed features of mitochondrial dysfunction such as reduction in mitochondrial membrane potential, reduction in complex IV activity in lung mitochondria, and increase in the levels of cytochrome c in lung cytosol. |
| References |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 422.7±20.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C18H32O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 296.445 |
| Flash Point | 223.6±18.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 296.235138 |
| PSA | 57.53000 |
| LogP | 5.32 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.492 |
| Symbol |


GHS02, GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H225-H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P280-P305 + P351 + P338-P337 + P313-P403 + P235 |
| Hazard Codes | F: Flammable; |
| Risk Phrases | 11 |
| RIDADR | UN 1170 3/PG 2 |
| HS Code | 2918199090 |
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |
| HS Code | 2918199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2918199090 other carboxylic acids with alcohol function but without other oxygen function, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides, peroxyacids and their derivatives。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:6.5%。General tariff:30.0% |