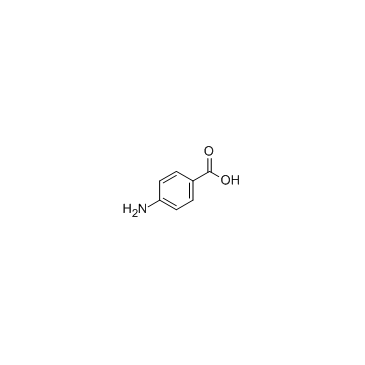
94-09-7
| Name | benzocaine |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
ORTHESIN
Americaine Ora-jel ethyl 4-aminobenzene carboxylate Anaesthesin AETHOFORM Benzocainum Ethyl 4-aminobenzoate ethyl ester of p-aminobenzoic acid Benzocaine Ethoform 4-Aminobenzoic acid ethyl ester Topcaine Benzoic acid, 4-amino-, ethyl ester Solu H MFCD00007892 Euphagin EINECS 202-303-5 4-ethoxycarbonylaniline Norcaine 4-amino-benzoic acid ethyl ester Norcain Anaesthin Anbesol ethyl 4-amino-benzoate p-aminobenzoic acid ethyl ester Ethyl4-aminobenzoate |
| Description | Benzocaine shares a common receptor with all other local anesthetics (LAs) in the voltage-gated Na+ channel, with an IC50 of 0.8 mM tested with a potential of +30 mV. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 0.8 mM (Na+ channel)[1]. |
| In Vitro | Benzocaine blocks μ1 wild-type Na+ currents in a dose-dependent Manner. The Benzocaine concentration that inhibits 50% of Na+ currents (IC50) is estimated to be about 0.8 mM when a test potential of +30 mV is applied. The slope of the h∞ curve is also significantly reduced by benzocaine (from 6.6 to 9.9 mV). Mutation of μ1-N1584A also significantly increases the potency of Benzocaine. At 1 mM, Benzocaine blocks about 55% of wild-type Na+ current but about 95% of μ1-N1584A mutant current. Benzocaine also appears to bind more strongly to its LA receptor in the N1584A mutant than in the wild type[1]. The inhibition of Ca2+ uptake occurres at lower Benzocaine concentration (IC50=40.3±1.2mM) than that affecting the enzymatic activity[2]. |
| In Vivo | A common Benzocaine-containing anesthetic is topically applied to the following species: dogs, domestic shorthair cats, Long-Evans rats, Sprague-Dawley rats, ferrets, rhesus monkeys, cynomolgus monkeys, owl monkeys, New Zealand White rabbits, miniature pigs, ICR mice, C3H mice, and C57BL/10SnJ mice. All animals, except mice and rats, receive a 2-second spray to the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx for an estimated dose of 56 mg. A 2-second spray to rodents' oral mucous membranes delivers too great a volume of fluid for these animals. The study is repeated in dogs several months later to confirm low response. Response to Benzocaine spray is observed in most animals tested, with response peaking between 15 and 30 minutes after dosing[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 310.7±15.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 88-90 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C9H11NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 165.189 |
| Flash Point | 164.2±17.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 165.078979 |
| PSA | 52.32000 |
| LogP | 1.95 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.555 |
| Storage condition | 0-6°C |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38;R43 |
| Safety Phrases | 22-24/25-37/39-26-24 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | DG2450000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| HS Code | 2922499990 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2922499990 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS:2922499990 other amino-acids, other than those containing more than one kind of oxygen function, and their esters; salts thereof VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward) MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |






![ethyl 4-[(4-nitrophenyl)methylideneamino]benzoate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/411/108529-41-5.png)


![Benzoic acid,4-[(1,3-dioxobutyl)amino]-, ethyl ester structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/274/30764-23-9.png)