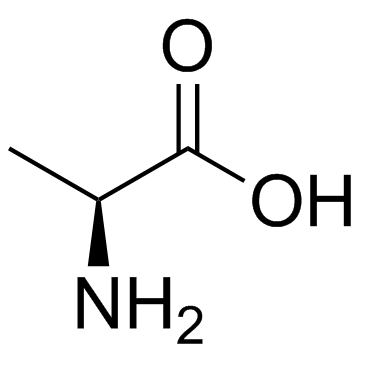
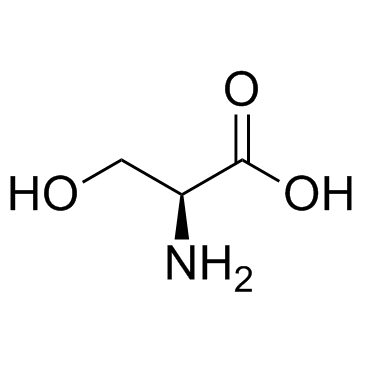
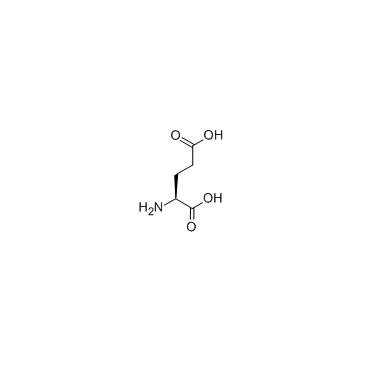
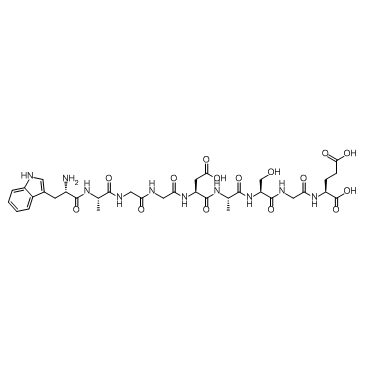
62568-57-4
| Name | dsip |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
trp-ala-gly-gly-asp-ala-ser-gly-glu
UNII:YN28Z5YZ73 trp-ala-gly-gly-asn-ala-ser-gly-glu sleep inducing peptide L-Tryptophyl-L-alanylglycylglycyl-L-a-aspartyl-L-alanyl-L-serylglycyl-L-glutamic Acid emideltide L-Tryptophyl-L-alanylglycylglycyl-L-α-aspartyl-L-alanyl-L-serylglycyl-L-glutamic acid N-(N-(N-(N-(N-(N-(N-(N-L-Tryptophyl-L-alanyl)glycyl)glycyl)-L-a-aspartyl)-L-alanyl)-L-seryl)-glycyl)-L-glutamic Acid waggdasge TRP-ALA-GLY-GLY-ASP-ALA-SER: PO3H2-GLY-GLU [WAGGDA-S: PO3H2-GE] δ-Sleep Inducing Peptide |
| Description | δ-Sleep Inducing Peptide is a neuropeptide, with antioxidant and anxiolytic properties. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vivo | In rabbit infused with δ-Sleep Inducing Peptide (DSIP), the spindle activity is increased, and heart and respiration rate are moderately decreased. δ-Sleep Inducing Peptide (DSIP) may act as a programming modulator at supra-operational level rather than as a transmitter at operational level[1]. δ-Sleep Inducing Peptide (DSIP; 40 μg/kg, i.p.) increases catalase and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activities and malonic dialdehyde (MDA) concentration in the liver homogenate of rats subjected to acute stress, but the opposite effects are observed at 120, and 360 μg/kg[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats[2] Experiments are performed on male Wistar rats (n = 100) weighing 250-280 g. The animals are divided into groups (10 specimens per group). They are maintained under standard vivarium conditions and have free access to water and food (12:12-h light/dark regimen). δ-Sleep Inducing Peptide is dissolved in physiological saline and injected intraperitoneally 60 min before each stress exposure. Control animals receive an equivalent volume of physiological saline (1 mL/kg). The liver is homogenized in ice-cold physiological saline and centrifuged. The content of LPO products and activities of antioxidant enzymes are measured in the supernatant. LPO intensity is evaluated by malonic dialdehyde (MDA) concentration. Activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase are measured spectrophotometrically. The total antioxidant activity (TAA) is evaluated by the method based on inhibition of ascorbate-induced and iron-induced oxidation of Tween-80 to MDA. The assay is conducted on a BTS-330 biochemical analyzer[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 1522.7±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C35H48N10O15 |
| Molecular Weight | 848.814 |
| Flash Point | 874.7±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 848.330078 |
| PSA | 406.74000 |
| LogP | -3.57 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.612 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water at 0.5mg/ml |
| Safety Phrases | 22-24/25 |
|---|---|
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
~% 
62568-57-4 |
| Literature: Synthesis, , # 9 p. 845 - 846 |
|
Detail
|
| Literature: Russian Journal of Bioorganic Chemistry, , vol. 40, # 1 p. 1 - 8 Bioorg. Khim., , vol. 40, # 1 p. 3 - 11,9 |
| Precursor 6 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 4 | |



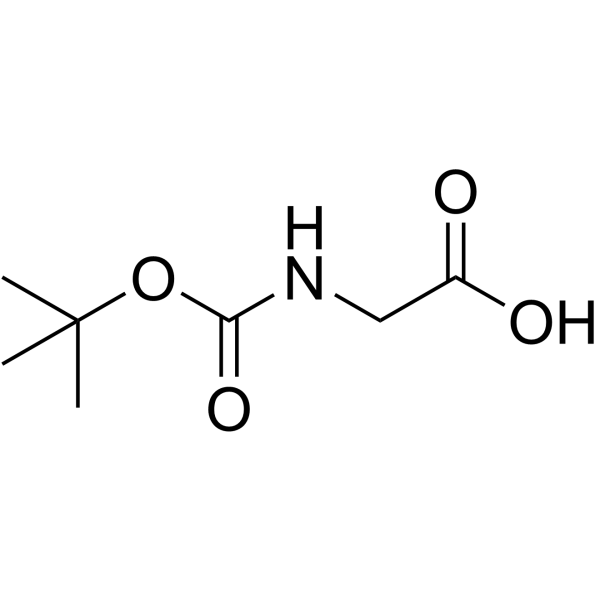
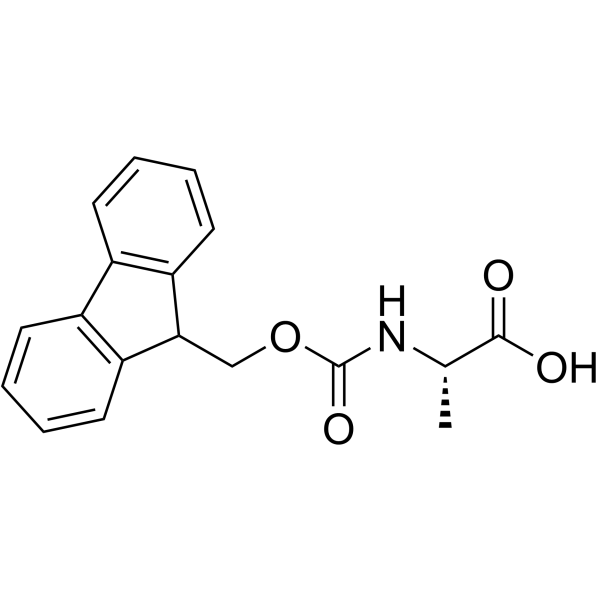

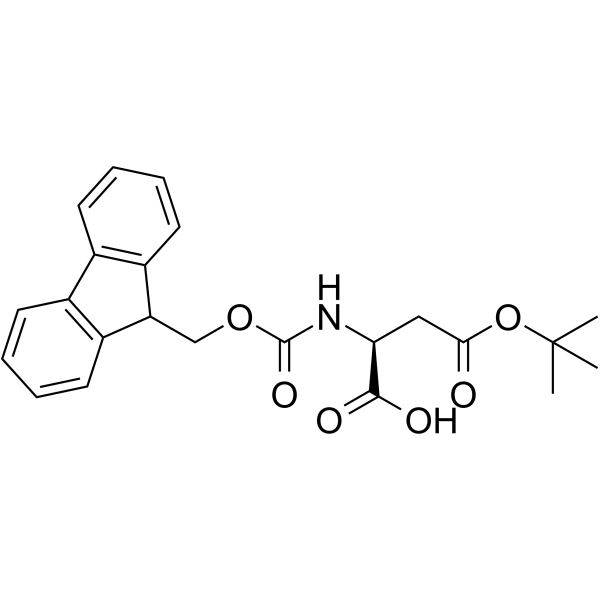

![N-[(tert-Butoxy)carbonyl]-L-tryptophan structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/447/13139-14-5.png)