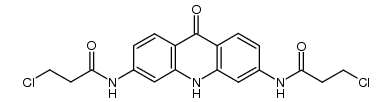
351351-75-2
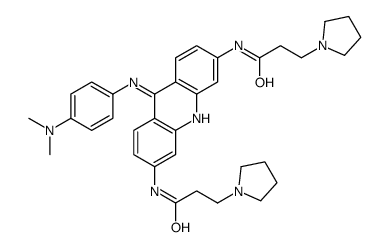
| Name | N-[9-[4-(dimethylamino)anilino]-6-(3-pyrrolidin-1-ylpropanoylamino)acridin-3-yl]-3-pyrrolidin-1-ylpropanamide |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
N-{9-[4'-(N,N-dimethylamino)phenylamino]}-3,6-bis(3-pyrrolidinopropionamido)acridine
UNII-Z7C5CD91WI N,N'-(9-((4-(Dimethylamino)phenyl)amino)-3,6-acridinediyl)bis(1-pyrrolidinepropanamide) BRACO-19 9-[4-(N,N-dimethylamino)phenylamino]-3,6-bis(3-pyrrolodinopropionamido) acridine 1-Pyrrolidinepropanamide,N,N'-(9-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)amino)-3,6-acridinediyl)bis |
| Description | Braco-19 is a potent telomerase/telomere inhibitor, preventing the capping and catalytic action of telomerase. Braco-19 acts as G-quadruplex (GQ) binding ligand, stabilizing G-quadruplexes formation at the 3V telomeric DNA overhang and produce rapid senescence or selective cell death. Braco-19 is also a HAdV virus replication inhibitor[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: telomerase/telomere[1] |
| In Vitro | Braco-19, as a well-known GQ binding ligand, interacts specifically with the HAdV GQs and increases their stability, and blocks the HAdV multiplication[2]. BRACO-19 (1.0-10 μM; 5 day) cause zero growth inhibition is found 1 μM, the IC50 for BRACO-19 in UXF1138L cells is 2.5 μM, the IC100 is 5 μM[1]. BRACO-19 (1 μM; 24 hours) shows dramatically reduced nuclear hTERT expression. However, residual cytoplasmic hTERT staining is observed accompanied by the occurrence of atypical mitoses[1]. BRACO-19 (0-40 μM; 24 hours) decreases the AdV virus growth in a dose-dependent manner in eGFP-transinfected HEK 293 cells[2]. BRACO-19 (0-150 μM; 24 hours) shows a decrease in band intensity in an increasing concentration-dependent manner[2]. Cell Viability Assay[1] Cell Line: HEK 293 cells Concentration: 20 μM; 40 μM Incubation Time: 24 hours Result: Displayed low cytotoxicity and decreased the eGFP fluorescence. |
| In Vivo | BRACO-19 (oral administration or intraperitoneal injection; 2 or 5 mg/kg; 3 weeks) oral dosing regimen are always inactive and the animals have to be sacrificed due to high tumor burden before overall termination of the study, Chronic, i.p. BRACO-19 administration, qdx5 is efficient in inhibiting tumor growth in earlystage xenografts but not advanced-stage xenografts[1]. BRACO-19 (intraperitoneal injection; 2 mg/kg; 3 weeks; starting 6 days after transplantation of UXF1138LX fragments) inhibits tumor growth significantly and under these conditions, marked single-agent antitumor activity is observed, with some animals in the group showing complete regressions (5 of 12 tumors)[1]. Animal Model: Established UXF1138LX Xenografts in nude mice[1] Dosage: 2 mg/kg Administration: Intraperitoneal injection; 3 weeks; starting 6 days after transplantation of UXF1138LX fragments Result: Showed partial tumor regressions with an optimal T/C on day 28 of 4.1%, equal to 95.9% inhibition of tumor growth compared with control. |
| References |
| Density | 1.275g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 854.95ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C35H43N7O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 593.76200 |
| Flash Point | 470.857ºC |
| Exact Mass | 593.34800 |
| PSA | 103.05000 |
| LogP | 6.64310 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.708 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |