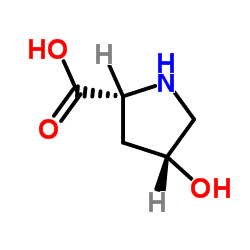
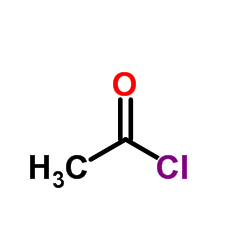
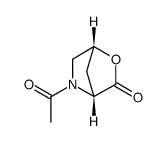
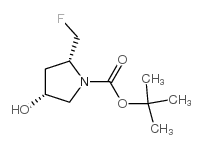
114676-59-4
| Name | D-Proline, 4-hydroxy-, methyl ester, (Hydrochloride) (1:1), (4R) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
D-Proline, 4-hydroxy-, methyl ester, (4R)-, hydrochloride (1:1)
Trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline methyl ester hydrochloride Methyl (4R)-4-hydroxy-L-prolinate hydrochloride (1:1) Methyl (4R)-4-hydroxy-D-prolinate hydrochloride (1:1) CIS-4-HYDROXY-D-PROLINE METHYL ESTER L-Proline, 4-hydroxy-, methyl ester, (4R)-, hydrochloride (1:1) cis-4-hydroxy-D-proline methyl ester hydrochloride methyl cis 4-hydroxyl-D-proline (2R,4R)-4-Hydroxypyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester hydrochloride (2R,4R)-Methyl 4-hydroxypyrrolidine-2-carboxylate hydrochloride |
| Description | D-Proline, 4-hydroxy-, methyl ester hydrochloride is a non-cleavable ADC linker used in the synthesis of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). D-Proline, 4-hydroxy-, methyl ester hydrochloride is also a alkyl chain-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs[1][2 |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Non-cleavable |
| In Vitro | ADCs are comprised of an antibody to which is attached an ADC cytotoxin through an ADC linker[1]. PROTACs contain two different ligands connected by a linker; one is a ligand for an E3 ubiquitin ligase and the other is for the target protein. PROTACs exploit the intracellular ubiquitin-proteasome system to selectively degrade target proteins[2]. |
| References |
| Melting Point | 121-123 ºC |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C6H12ClNO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 181.617 |
| Exact Mass | 181.050568 |
| PSA | 58.56000 |
| LogP | 0.01300 |
|
~99% 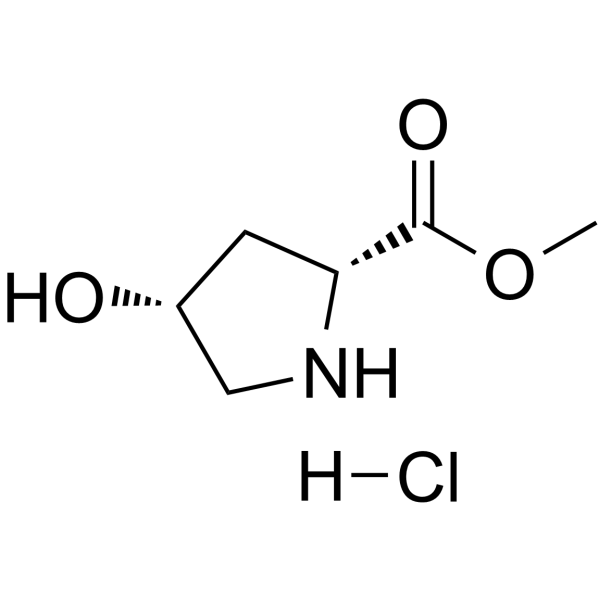
114676-59-4 |
| Literature: VICURON PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. Patent: WO2004/7444 A2, 2004 ; Location in patent: Page 135 ; |
|
~91% 
114676-59-4 |
| Literature: Peng, Jianbiao; Clive, Derrick L. J. Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2009 , vol. 74, # 2 p. 513 - 519 |
|
~99% 
114676-59-4 |
| Literature: Shionogi Seiyaku Kabushiki Kaisha Patent: US5317016 A1, 1994 ; |
|
~98% 
114676-59-4 |
| Literature: Rosen; Fesik; Chu; Pernet Synthesis, 1988 , # 1 p. 40 - 44 |
|
~% 
114676-59-4 |
| Literature: WO2005/108358 A2, ; Page/Page column 35 ; WO 2005/108358 A2 |
|
~% 
114676-59-4 |
| Literature: WO2014/32 A1, ; |
|
~% 
114676-59-4 |
| Literature: WO2014/32 A1, ; |
| Precursor 5 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 4 | |