1140909-48-3
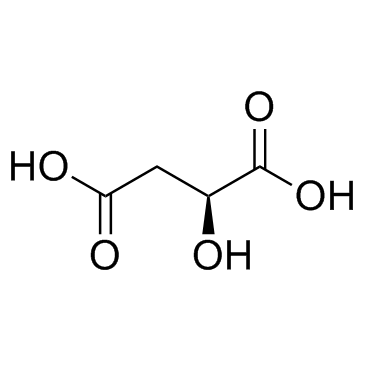
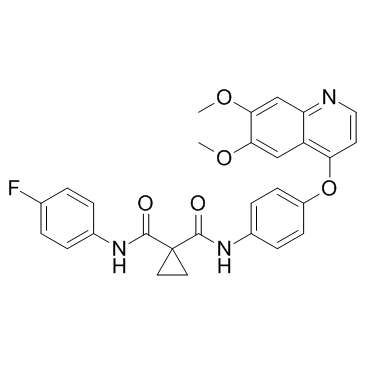
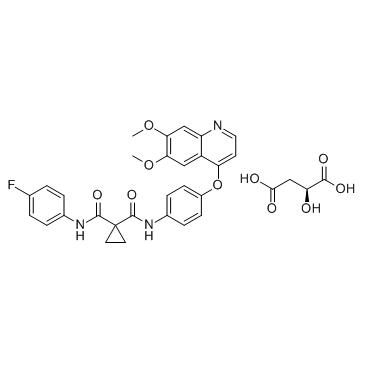
| Name | 1-N-[4-(6,7-dimethoxyquinolin-4-yl)oxyphenyl]-1-N'-(4-fluorophenyl)cyclopropane-1,1-dicarboxamide,(2S)-2-hydroxybutanedioic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Cabozantinib malate (XL184)
Cometriq UNII-DR7ST46X58 N-(4-{[6,7-bis(methyloxy)quinolin-4-yl]oxy}phenyl)-N'-(4-fluorophenyl)cyclopropane-1,1-dicarboxamide (L) malate N-(4-{[6,7-bis(methyloxy)quinolin-4-yl]oxy}phenyl)-N'-(4-fluorophenyl)cyclopropane-1,1-dicarboxamide (L)-malate salt XL 184 Cabozantinib L-Malate Salt Butanedioic acid, 2-hydroxy-, (2S)-, compd. with N-[4-[(6,7-dimethoxy-4- quinolinyl)oxy]phenyl]-N'-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,1-cyclopropanedicarboxamide (1:1) Butanedioic acid, 2-hydroxy-, (2S)-, compd. with N-[4-[(6,7-dimethoxy-4-quinolinyl)oxy]phenyl]-N'-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,1-cyclopropanedicarboxamide (1:1) cabozantinib malate Cabozantinib (XL184) N-{4-[(6,7-dimethoxyquinolin-4-yl)oxy]phenyl}-N'-(4-fluorophenyl)cyclopropane-1,1-dicarboxamide mono[(2S)-2-hydroxybutanedioate] UNII:DR7ST46X58 Cabozantinib s-malate (2S)-2-Hydroxysuccinic acid - N-{4-[(6,7-dimethoxy-4-quinolinyl)oxy]phenyl}-N'-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,1-cyclopropanedicarboxamide (1:1) Cabozantinib s-malate [USAN] Cabozantinib malate salt cyclopropane-1,1-dicarboxylic acid [4-(6,7-dimethoxy-quinoline-4-yloxy)-phenyl]-amide (4-fluoro-phenyl)-amide L-malate cyclopropane-1,1-dicarboxylic acid [4-(6,7-dimethoxyquinoline-4-yloxy)phenyl]amide (4-fluoro-phenyl)amide (L)-malate salt cabozantinib L-malate Cabozantinib (S-malate) |
| Description | Cabozantinib (S-malate) is a potent multiple receptor tyrosine kinases inhibitor that inhibits VEGFR2, c-Met, Kit, Axl and Flt3 with IC50s of 0.035, 1.3, 4.6, 7 and 11.3 nM, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
VEGFR2:0.035 nM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | XL184 (0.1-0.5μM) inhibits the constitutive and inducible MET phosphorylation and its resultant downstream signaling in all MPNST cells. XL184 (> 0.1μM) elicits a significant MPNST cell growth inhibition; higher XL184 doses are needed to inhibit NSC growth. XL184 treatment blocks HGF-induced MPNST motility and invasion (a similar effect of found on NSC)[2]. In cellular assays, cabozantinib inhibits phosphorylation of MET and VEGFR2, as well as KIT, FLT3, and AXL with IC50 values of 7.8, 1.9, 5.0, 7.5, and 42 μM, respectively. Cabozantinib also inhibits tubule formation in response to conditioned media derived from cultures of MDA-MB-231 (IC50=5.1 nM), A431 (IC50=4.1 nM), HT1080 (IC50=7.7 nM), and B16F10 (IC50=4.7 nM) cells[3]. |
| In Vivo | Cabozantinib (60 mg/kg, i.p.) decreases the tumor vascularity with reductions ranging from 67% at 3 mg/kg to 83% at 30 mg/kg for 7 days in animals. Tumors in RIP-Tag2 mice treated for 7 days beginning at age 10 weeks are 40% smaller after XL880 and 35% smaller after XL184, compared to corresponding values for vehicle[1]. XL184 (30 mg/kg) significantly decreases the microvessel density in mice[2]. Cabozantinib (100 mg/kg, p.o.) inhibits in vivo stimulation of MET phosphorylation by HGF in liver hepatocytes and VEGF-stimulated phosphorylation of FLK1 with inhibition of both targets sustained through 8 hours postdose. Cabozantinib (100 mg/kg, p.o.) disrupts tumor vasculature and promotes tumor and endothelial cell death. Cabozantinib (1-60 mg/kg, p.o.) inhibits tumor growth and promotes tumor regression in vivo[3]. |
| Kinase Assay | The inhibition profile of cabozantinib against a broad panel of 270 human kinases is determined using luciferase-coupled chemiluminescence, 33P-phosphoryl transfer, or AlphaScreen technology. Recombinant human full-length, glutathione S-transferase tag, or histidine tag fusion proteins are used, and half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values are determined by measuring phosphorylation of peptide substrate poly (Glu, Tyr) at ATP concentrations at or below the Km for each respective kinase. The mechanism of kinase inhibition is evaluated using the AlphaScreen Assay by determining the IC50 values over a range of ATP concentrations. |
| Cell Assay | Cells are seeded in triplicate overnight in media containing 10% FBS. The next day, cells are treated with serial dilutions of cabozantinib for 48 hours, followed by analysis of proliferation using Cell Proliferation ELISA, BrdUrd. |
| Animal Admin | H441 cells (3×106) are implanted intradermally into the hind flank and when tumors reach approximately 150 mg, tumor weight is calculated using the formula: (tumor volume=length (mm) × width2 (mm2)]/2, mice are randomized (n=5 per group) and orally administered a single 100 mg/kg dose of cabozantinib or vehicle. Tumors are collected at the indicated time points. Pooled tumor lysates are subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-MET (SC161) and Western blotting with anti-phosphotyrosine MET (pY1230/34/35). After blot stripping, total MET is quantitated as a loading control. In a separate experiment, naive mice (n=5 per group) are administered a single 100 mg/kg dose of cabozantinib or vehicle, followed by intravenous administration of HGF (10 μg per mouse) 10 minutes before liver collection. Analysis of MET phosphorylation in liver lysates is as described above. In a separate experiment, naive mice (n=5 per group) are administered a single 100 mg/kg dose of cabozantinib or vehicle, followed by intravenous administration of VEGF (10 μg per mouse) 30 minutes before lung collection. Pooled lung lysates are subjected to immunoprecipitation with FLK1 (SC6251) and Western blotting with anti-phosphotyrosine (4G10). After blot stripping, total FLK1 is quantitated as a loading control. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C32H30FN3O10 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 635.593 |
| Exact Mass | 635.191528 |
| PSA | 193.61000 |
| LogP | 4.59340 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|
|
~% 
1140909-48-3 |
| Literature: WO2010/83414 A1, ; Page/Page column 26 - 27 ; |
|
~% 
1140909-48-3 |
| Literature: WO2012/109510 A1, ; |
|
~% 
1140909-48-3 |
| Literature: WO2012/109510 A1, ; |
|
~% 
1140909-48-3 |
| Literature: WO2012/109510 A1, ; |
|
~% 
1140909-48-3 |
| Literature: WO2012/109510 A1, ; |
|
~% 
1140909-48-3 |
| Literature: WO2012/109510 A1, ; |
|
~% 
1140909-48-3 |
| Literature: WO2013/166296 A1, ; |
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |