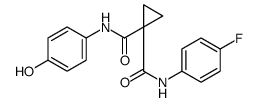
849217-68-1
| Name | cabozantinib |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
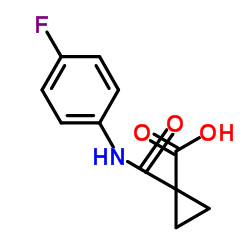
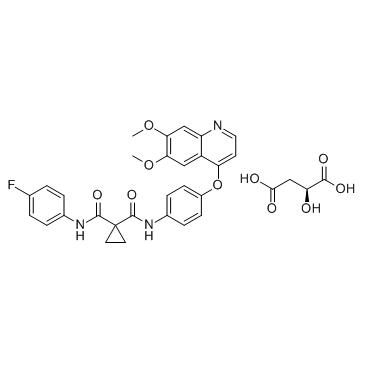
N'-[4-[(6,7-dimethoxy-4-quinolinyl)oxy]phenyl]-N-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,1-cyclopropanedicarboxamide
[14C]-Cabozantinib Cometriq N-{4-[(6,7-dimethoxyquinolin-4-yl)oxy]phenyl}-N'-(4-fluorophenyl)cyclopropane-1,1-dicarboxamide cyclopropane-1,1-dicarboxylic acid [4-(6,7-dimethoxy-quinoline-4-yloxy)-phenyl]-amide (4-fluoro-phenyl)-amide XL 184 UNII-1C39JW444G N-(4-{[6,7-bis(methyloxy)quinolin-4-yl]oxy}phenyl)-N-(4-fluorophenyl)cyclopropane-1,1-dicarboxamide Cabozantinib BMS-907351 1-N-[4-(6,7-dimethoxyquinolin-4-yl)oxyphenyl]-1-N'-(4-fluorophenyl)cyclopropane-1,1-dicarboxamide N-{4-[(6,7-Dimethoxy-4-quinolinyl)oxy]phenyl}-N'-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,1-cyclopropanedicarboxamide XL-184 XL184 |
| Description | Cabozantinib is a potent multiple receptor tyrosine kinases inhibitor that inhibits VEGFR2, c-Met, Kit, Axl and Flt3 with IC50s of 0.035, 1.3, 4.6, 7 and 11.3 nM, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
VEGFR2:0.035 nM (IC50) Flt-1:12 nM (IC50) Flt-4:6 nM (IC50) FLT3:11.3 nM (IC50) c-Met:1.3 nM (IC50) c-Kit:4 nM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Cabozantinib is a potent inhibitor of MET and VEGFR2 with IC50 values of 1.3 and 0.035 nM, respectively. MET-activating kinase domain mutations Y1248H, D1246N, or K1262R are also inhibited by Cabozantinib (IC50=3.8, 11.8, and 14.6 nM, respectively). Cabozantinib displays strong inhibition of several kinases that have also been implicated in tumor pathobiology, including KIT, RET, AXL, TIE2, and FLT3 (IC50=4.6, 5.2, 7, 14.3, and 11.3 nM, respectively). In cellular assays, Cabozantinib inhibits phosphorylation of MET and VEGFR2, as well as KIT, FLT3, and AXL with IC50 values of 7.8, 1.9, 5.0, 7.5, and 42 μM, respectively. The effect of Cabozantinib on proliferation is evaluated in a number of human tumor cell lines. SNU-5 and Hs746T cells harboring amplified MET are the most sensitive to Cabozantinib (IC50=19 and 9.9 nM, respectively); however, SNU-1 and SNU-16 cells lacking MET amplification are more resistant (IC50=5,223 and 1,149 nM, respectively). MDA-MB-231 and U87MG cells exhibit comparable levels of sensitivity to Cabozantinib (IC50=6,421 and 1,851 nM, respectively), whereas H441, H69, and PC3 cell lines are the least sensitive to Cabozantinib with IC50 values of 21,700, 20,200, and 10,800 nM, respectively. In addition, BaF3 cells expressing human FLT3-ITD, an activating mutation in acute myelogenous leukemia, are sensitive to Cabozantinib (IC50=15 nM) when compared with wild-type BaF3 cells (IC50=9,641 nM)[2]. |
| In Vivo | Tumor vascularity decreases after Cabozantinib (XL184), with reductions ranging from 67% at 3 mg/kg to 83% at 30 mg/kg for 7 days[1]. In mouse models, Cabozantinib dramatically alters tumor pathology, resulting in decreased tumor and endothelial cell proliferation coupled with increased apoptosis and dose-dependent inhibition of tumor growth in breast, lung, and glioma tumor models. Importantly, treatment with Cabozantinib does not increase lung tumor burden in an experimental model of metastasis, which has been observed with inhibitors of VEGF signaling that do not target MET. On a body weight dosage basis, Cabozantinib plasma exposures range from 6- to 10-fold higher in rats than in mice, which accounts for lower doses inducing tumor growth inhibition/regression in rats than in mice. Subchronic administration of Cabozantinib is well tolerated in mice and rats with no signs of toxicity, as determined by stable and/or increasing body weights during the treatment period[2]. |
| Kinase Assay | The inhibition profile of Cabozantinib against a broad panel of 270 human kinases is determined using luciferase-coupled chemiluminescence, 33P-phosphoryl transfer, or AlphaScreen technology. Recombinant human full-length, glutathione S-transferase tag, or histidine tag fusion proteins are used, and IC50 values are determined by measuring phosphorylation of peptide substrate poly(Glu, Tyr) at ATP concentrations at or below the Km for each respective kinase. The mechanism of kinase inhibition is evaluated using the AlphaScreen Assay by determining the IC50 values over a range of ATP concentrations[2]. |
| Cell Assay | The effect of Cabozantinib on proliferation is evaluated in a number of human tumor cell lines, including SNU-5 and Hs746T cells harboring amplified MET, SNU-1 and SNU-16 cells, MDA-MB-231 and U87MG cells, H441, H69, and PC3 cell lines, and BaF3 cells. Cells are seeded in triplicate overnight in media containing 10% FBS. The next day, cells are treated with serial dilutions of Cabozantinib for 48 hours, followed by analysis of proliferation using Cell Proliferation ELISA, BrdUrd[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[1] RIP-Tag2 mice in a C57BL/6 background are used as the tumor model. RIP-Tag2 mice are 10 weeks old at the onset of treatment unless otherwise indicated. Cabozantinib is suspended at a concentration of 5 mg/mL in sterile saline or water and administered by gavage daily for 7 days. Dose-dependent effects are studied in mice treated by gavage daily for 7 days: XL880 (1, 10, 20, 40 or 60 mg/kg), Cabozantinib (3, 10, 30, 40 or 60 mg/kg), or XL999 (25, 40, 50, 60 or 75 mg/kg). The time course of effects is studied in mice treated with XL880 (40 mg/kg) for 6 hr, 1, 4, 7 or 14 days. Effects of withdrawal are studied in mice treated with XL880 (40 mg/kg) for 7 days followed by no treatment for 0, 2, 7 or 14 days. Each group contain 4-6 mice. Mice[2] Female nu/nu mice are used. H441 cells (3×106) are implanted intradermally into the hind flank and when tumors reach approximately 150 mg, tumor weight is calculated using the formula: (tumor volume=length (mm)×width2(mm2)]/2, mice are randomized (n=5 per group) and orally administered a single 100 mg/kg dose of Cabozantinib or vehicle. Tumors are collected at the indicated time points. Pooled tumor lysates are subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-MET and Western blotting with anti-phosphotyrosine MET. After blot stripping, total MET is quantitated as a loading control. Rats[2] On day 0 in female Wistar rats, C6 cells (5×106) are inoculated subcutaneously into the hind flank. When the tumors reach approximately 250 mg (3-4 days postimplantation), rats are randomized (n=8 per group) and treated orally once daily for 12 days with Cabozantinib or water vehicle. Cabozantinib administered via oral gavage at 2 mL/kg. Body weights are collected daily, and tumor weights are collected twice weekly. Percentage of tumor growth inhibition/regression values are expressed as follows: 1−[(mean treated tumor weight on the final day−mean tumor weight on day 0)/(mean vehicle tumor weight on the final day−mean tumor weight on day 0)]×100. Statistical analysis of Cabozantinib-treated tumors versus vehicle-treated tumors or versus predose tumors is done by one-way ANOVA with significance defined as P<0.05. Blood is collected 4 hours after the final dose, and plasma is prepared to determine Cabozantinib concentrations. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 758.1±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C28H24FN3O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 501.506 |
| Flash Point | 412.3±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 501.170013 |
| PSA | 98.78000 |
| LogP | 4.84 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.688 |
| HS Code | 2933499090 |
|---|
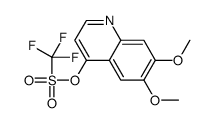
|
~43% 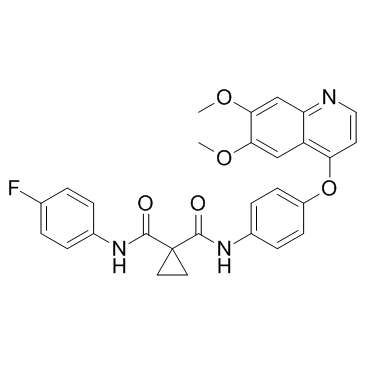
849217-68-1 |
| Literature: WO2005/30140 A2, ; Page/Page column 212 ; WO 2005/030140 A2 |
|
~% 
849217-68-1 |
| Literature: US2012/70368 A1, ; US 20120070368 A1 US2012/252840 A1, ; US 20120252840 A1 |
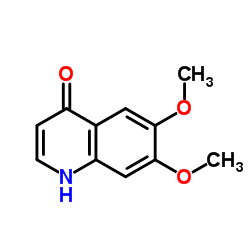
|
~% 
849217-68-1 |
| Literature: US2012/70368 A1, ; US 20120070368 A1 US2012/252840 A1, ; US 20120252840 A1 |
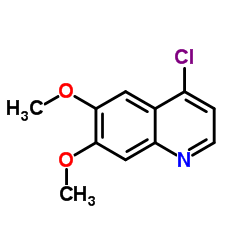
|
~% 
849217-68-1 |
| Literature: WO2012/109510 A1, ; |
|
~% 
849217-68-1 |
| Literature: WO2012/109510 A1, ; |
|
~% 
849217-68-1 |
| Literature: US2012/252840 A1, ; US 20120252840 A1 |
|
~% 
849217-68-1 |
| Literature: US2012/70368 A1, ; US 20120070368 A1 US2012/252840 A1, ; US 20120252840 A1 |
|
~% 
849217-68-1 |
| Literature: WO2013/166296 A1, ; |
|
~% 
849217-68-1 |
| Literature: US2012/252840 A1, ; US 20120252840 A1 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |
| HS Code | 2933499090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933499090. other compounds containing in the structure a quinoline or isoquinoline ring-system (whether or not hydrogenated), not further fused. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |