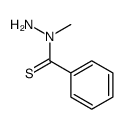
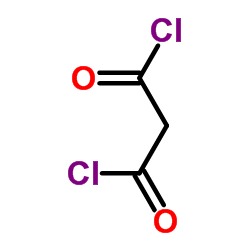
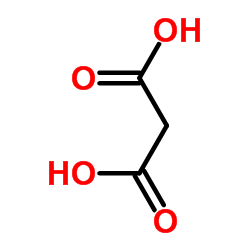
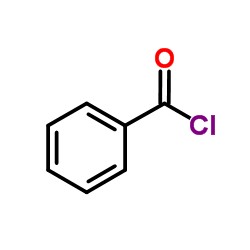
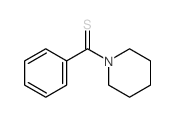
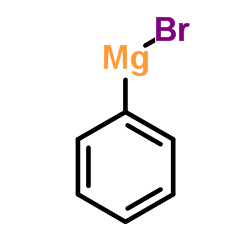
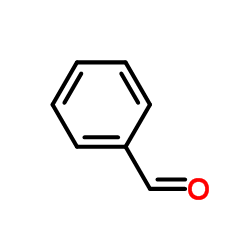
488832-69-5
| Name | elesclomol |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
STA-4783
S1052_Selleck Elesclomol 1-N',3-N'-bis(benzenecarbonothioyl)-1-N',3-N'-dimethylpropanedihydrazide N-malonyl-bis(N'-thiobenzoyl-N'-methyl hydrazide) N',N'-Dimethyl-N',N'-bis(phenylcarbonothioyl)malonohydrazide Propanedioic acid, bis[2-methyl-2-(phenylthioxomethyl)hydrazide] |
| Description | Elesclomol is an oxidative stress inducer that induces cancer cell apoptosis. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Elesclomol significantly induces the expression of heat shock stress response genes and metallothionein genes, a signature transcription profile indicative of oxidative stress in Hs294T cells. Elesclomol (100 nM) rapidly induces Hsp70 RNA levels with a 4.8-fold increase at 1 hour and a 160-fold increase at 6 hours in Ramos Burkitt's lymphoma B cells in consistent with the intracellular ROS content which increases by 20% as early as 0.5 hour and 385% at 6 hours, and the induction of Hsp70 can be blocked by antioxidants N-acetylcysteine (NAC) and Tiron pretreatment. Elesclomol increases the number of early and late apoptotic cells with 3.7- and 11-fold through the induction of oxidative stress, which can be completely blocked by NAC, while having little effect on normal cells[1]. Elesclomol significantly inhibits the cell viability of SK-MEL-5, MCF-7, and HL-60 with IC50 of 110 nM, 24 nM and 9 nM, respectively[2]. Elesclomol induces copper-dependent ROS generation and cytoxicity in yeast. Instead of working through a specific cellular protein target, elesclomol interacts with the electron transport chain (ETC), a biologically coherent set of processes occurring in the mitochondrion, to generate high levels of ROS within the organelle and consequently cell death[3]. |
| In Vivo | Although elesclomol (25-100 mg/kg) shows no antitumor activity in nude mouse xenograft models of human breast cancers (MDA435, MCF7 and ZR-75-1), lung cancer (RER) or lymphoma (U937). Elesclomol substantially enhances the efficacy of chemotherapeutic agents such as paclitaxel in these models, both in terms of tumor regression and extended survival of mice[4]. |
| Cell Assay | For viability assays, HBL and HBL-ρ0 cells are incubated with 300 nM elesclomol-Cu or Cu for 24 h. Cell death is determined using propidium iodide (5 µg/mL in PBS) staining and FACS analysis. Inner mitochondrial transmembrane potential is measured by incubating cells (25×104/mL) with 40 nM DIOC6(3) for 15 minutes at 37°C immediately prior to flow cytometry. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C19H20N4O2S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 400.518 |
| Exact Mass | 400.102753 |
| PSA | 128.86000 |
| LogP | 1.98 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.668 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
|
~65% 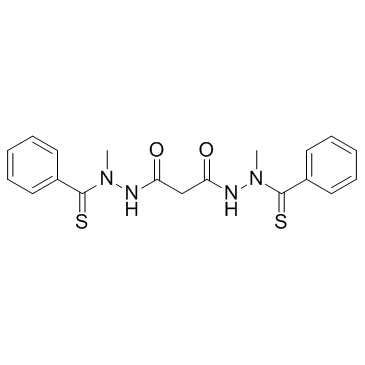
488832-69-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry, , vol. 126, p. 1 - 6 |
|
~83% 
488832-69-5 |
| Literature: WO2009/73147 A2, ; Page/Page column 36-37 ; |
|
~% 
488832-69-5 |
| Literature: Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters, , vol. 23, # 18 p. 5070 - 5076 |
|
~% 
488832-69-5 |
| Literature: Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters, , vol. 23, # 18 p. 5070 - 5076 |
|
~% 
488832-69-5 |
| Literature: Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters, , vol. 23, # 18 p. 5070 - 5076 |
|
~% 
488832-69-5 |
| Literature: Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters, , vol. 23, # 18 p. 5070 - 5076 |
|
~% 
488832-69-5 |
| Literature: Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters, , vol. 23, # 18 p. 5070 - 5076 |
|
~% 
488832-69-5 |
| Literature: Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters, , vol. 23, # 18 p. 5070 - 5076 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |