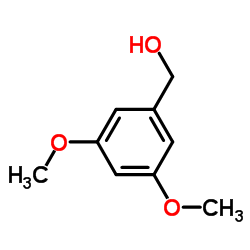
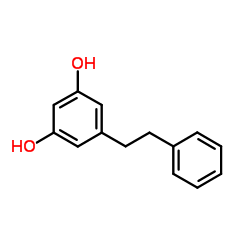
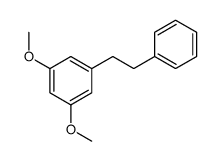
22139-77-1
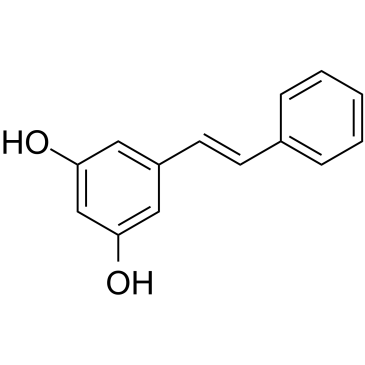
| Name | pinosylvin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
3,5-dihydroxystilbene
E-3,5-Stilbenediol 5-Styrylresorcinol 3,5-TRANS-DIHYDROXYSTILBENE 5-[(E)-2-Phenylvinyl]-1,3-benzenediol Pisylvin 5-[(E)-2-Phényléthènyl]-1,3-benzènediol 5-[(E)-2-phenylethenyl]benzene-1,3-diol 5-[(E)-2-Phenylvinyl]benzene-1,3-diol trans-3,5-Dihydroxystilbene 5-(2-phenylethenyl)benzene-1,3-diol (trans)-3,5-stilbenediol 5-(2-phenylvinyl)benzene-1,3-diol 5-(2-phenylethenyl)-1,3-benzenediol Pinosylvin |
| Description | Pinosylvin is a pre-infectious stilbenoid toxin isolated from the heartwood of Pinus spp, has anti-bacterial activities[1]. Pinosylvin is a resveratrol analogue, can induce cell apoptosis and autophapy in leukemia cells[2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Pinosylvin (0-100 μM; 24 hours) is cytotoxic to THP‐1 and U937 cells, exhibits an IC50 value of 20-30 μM in leukemia cells, the maximal cytotoxic effect occurred at 100 μM following incubation for 24 hr[3]. Pinosylvin (0-100 μM; 24 hours) enhances the number of annexin V+ and PI+ cells in the U937 population at 50 μM, increases annexin V+ and PI+ cells in the THP‐1 population at 100 μM[3]. Pinosylvin (0-100 μM; 24 hours) promotes autophagy in leukemia cells by enhancing the level of LC3‐II and p62/SQSTM1 degradation in leukemia cells[3]. Cell Viability Assay[3] Cell Line: Leukemia cells Concentration: 0 μM; 0.1 μM; 1 μM; 10 μM; 50 μM; 100 μM Incubation Time: 24 hours Result: Was cytotoxic to leukemia cells at high concentrations. Apoptosis Analysis[3] Cell Line: U937 and THP‐1 cells Concentration: 0 μM; 0.1 μM; 1 μM; 10 μM; 50 μM; 100 μM Incubation Time: 24 hours Result: Induced apoptosis cell number in U937 and THP‐1 cells. Western Blot Analysis[3] Cell Line: U937 and THP‐1 cells Concentration: 0 μM; 0.1 μM; 1 μM; 10 μM; 50 μM; 100 μM Incubation Time: 24 hours Result: Induced autophagy in leukemia cells. |
| In Vivo | Pinosylvin (intravenous injection; 10 mg/kg) yields the plasma AUC, urine t , CL and Vd values of 5.23 ± 1.20 mgh mL-1, 13.13 ± 2.05 h, 1.84 ± 0.44 Lh-1kg-1 and 2.29 Lkg-1, respectively in male Sprague-Dawley rats, in a PK study[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 397.6±17.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 155.5-156° |
| Molecular Formula | C14H12O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 212.244 |
| Flash Point | 194.9±15.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 212.083725 |
| PSA | 40.46000 |
| LogP | 3.68 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.727 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Hazard Codes | Xn,N |
|---|---|
| Risk Phrases | 22-36-51/53 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-61 |
| RIDADR | UN 3077 9 / PGIII |
| RTECS | WJ5580000 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 2 | |


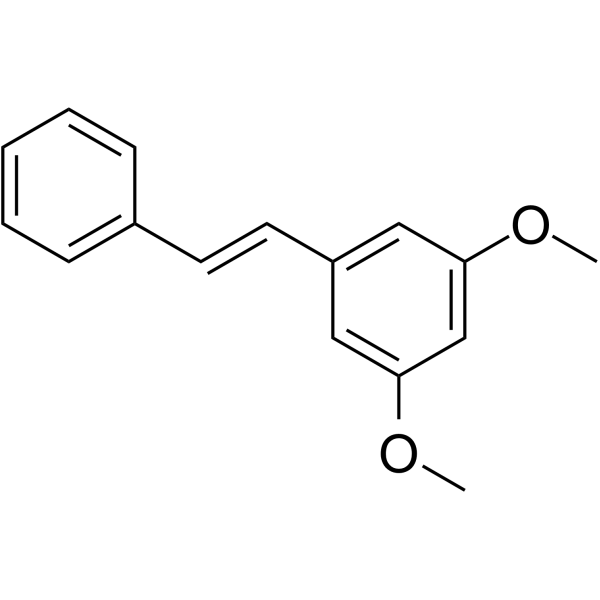
![(E)-1-[3,5-bis(benzyloxy)phenyl]-2-phenylethene structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/214/133156-35-1.png)
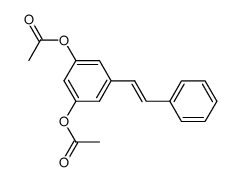
![5-[(Z)-2-phenylethenyl]benzene-1,3-diol structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/162/106325-78-4.png)
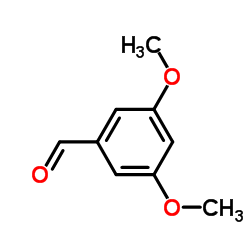

![diethyl [3,5-bis(benzyloxy)benzyl]phosphonate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/030/33617-49-1.png)