7085-55-4
| Name | troxerutin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
7,3',4'-Tris[O-(2-hydroxyethyl)]rutin
Posorutin Venoruton P-4 Rufen P-4 Tri(hydroxyethyl)rutoside Venoruton P4 Trioxyethylrutin 2-[3,4-Bis(2-hydroxyethoxy)phenyl]-3-[[6-O-(6-deoxy-a-L-mannopyranosyl)-b-D-glucopyranosyl]oxy]-5-hydroxy-7-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one Venoruton VASTRIBIL MFCD00893813 Z-6000 Vitamin P4 7,3',4'-trihydroxyethyl rutin Troxerutin Troxerutine Factor-P-zyma T66 BO EVJ CR CO2Q DO2Q& GQ IO2Q DO- BT6OTJ CQ DQ EQ F1O-BT6OTJ CQ DQ EQ FQ &&Stereoisomer 2-[3,4-Bis(2-hydroxyethoxy)phenyl]-5-hydroxy-7-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl 6-O-(6-deoxy-α-L-mannopyranosyl)-β-D-glucopyranoside RUVEN EINECS 230-389-4 troxerutina |
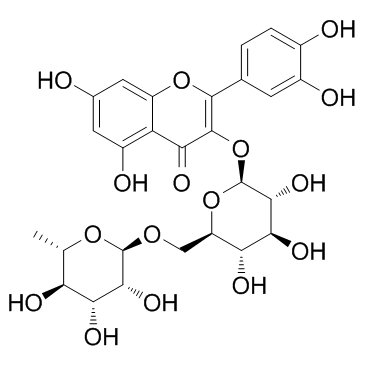
| Description | Troxerutin, also known as vitamin P4, is a tri-hydroxyethylated derivative of natural bioflavonoid rutins which can inhibit the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and depress ER stress-mediated NOD activation. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
ROS[1], NOD[2] |
| In Vitro | The results reveal that the maximum protective effect against ROS induced cell damage in the HDP cells occurs following pretreatment with 10 μM Troxerutin. Treatment with H2O2 alone decreases cell viability to 77.33±2.44%; however, pretreatment with 10 μM Troxerutin maintains cell viability at 90.88±2.24% following H2O2 exposure (P<0.05). At concentrations of 5 and 10 μM, pretreatment with Troxerutin causes a decrease in the number of cells in the sub G1 phase, indicative of cell death. In the control and Troxerutin-only-treated cells, 3.58±0.15 and 0.89±0.11% are 2′7′-dichlorofluorescein (DCF)-positive (P<0.05), whereas treatment with H2O2 alone increases the level of ROS to 46.36±2.33%. The cells pretreated with Troxerutin are 19.92±1.95% DCF-positive following H2O2 treatment, indicating that Troxerutin reduces the H2O2-induced production of ROS in the HDP cells[1] . |
| In Vivo | Troxerutin effectively lowers body weight and obesity-related metabolic parameters in high-fat diet (HFD)-treated mice. Oral administration of Troxerutin notably inhibits those liver injuries in HFD-treated mice, restores glucose intolerance and insulin signaling, and diminishes hepatic gluconeogenesis in HFD-treated mice. Troxerutin remarkably inhibits the nuclear translocation of NF-κB p65, as well as the expressions of its target genes, in the livers of HFD-treated mice. Troxerutin also depresses endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-mediated Nucleotide oligomerization domain (NOD) activation in HFD-treated mouse livers[2]. Lipid depositions in tunica intimae and tunica media are attenuated in Troxerutin-treated diabetic rats compare with untreated diabetic rats. Structural disarrangement and deformity of smooth muscle cells in aortic tissue of Troxerutin-treated diabetic rats are considerably lower than histology of untreated diabetic aorta. Administration of Troxerutin for four weeks to diabetic rats significantly reduces the level of malondialdehyde (MDA) compare to that of untreated diabetic rats (P<0.01)[3]. |
| Cell Assay | The cells are plated at a density of 4×103/well in a 96-well plate. At 70 to 80% confluence, the cells are treated with Troxerutin at concentrations ranging between 0 and 60 μM for 24 h at 37°C. Subsequently, 10 μL water soluble tetrazolium salt assay solution is added to each well and, following incubation for 30 min at 37°C, the optical density is measured at 490 nm using a reader. To examine Troxerutin mediated ROS protection, the cells are pretreated with Troxerutin at the following concentrations: 0, 5, 10 and 15 μM for 8 h. Subsequently, 750 μM H2O2 is added to each well. Following incubation for 24 h at 37°C, cell viability is evaluated using an Cell Viability Assay kit. The level of cell viability (%) is normalized to that of 0.1% dimethyl-sulfoxide (DMSO)-treated cells. Each experiment is repeated at least three times[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Thirty two adult male Wistar rats weighing 250 to 300 grams are used in this study. The animals are randomly divided into four groups (n=8/each) as: group I: control (C), group II: control with Troxerutin (C+TXR), group III: diabetic (D), and group IV: diabetic with Troxerutin (D+TXR). The control rats are received the same amount of citrate buffer alone. Development of diabetes is confirmed by measuring blood glucose levels, 72 hours later. Animals with blood glucose levels higher than 16.65 mM (300 mg/dL) are considered diabetic and those with blood glucose levels lower than this value are excluded from the experiment. Troxerutin (150 mg/kg/day) is administered orally, once daily for four weeks. After 10 weeks of induction of diabetes, diabetic animals as well as the time-matched controls are killed and aortic samples are collected[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 1058.4±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 168 - 176ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C33H42O19 |
| Molecular Weight | 742.675 |
| Flash Point | 332.0±27.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 742.232056 |
| PSA | 297.12000 |
| LogP | -0.32 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.690 |
| Storage condition | Refrigerator |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | LK8331500 |
| HS Code | 2932999099 |
|
~% 
7085-55-4 |
| Literature: Chinese Chemical Letters, , vol. 24, # 3 p. 223 - 226 |
|
~% 
7085-55-4 |
| Literature: Archiv der Pharmazie, , vol. 318, # 8 p. 747 - 753 |
| Precursor 3 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |
| HS Code | 2932999099 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2932999099. other heterocyclic compounds with oxygen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |


![2-[3,4-dihydroxy-3,4-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)cyclohexa-1,5-dien-1-yl]-3,5,7-trihydroxy-7-(2-hydroxyethyl)-8H-chromen-4-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/410/23077-88-5.png)