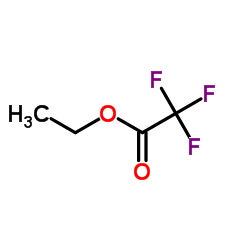
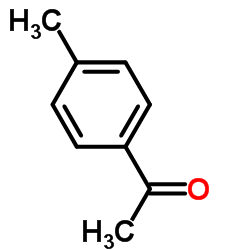
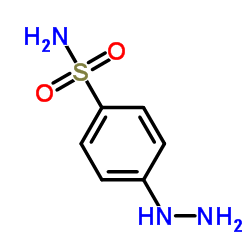
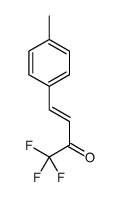
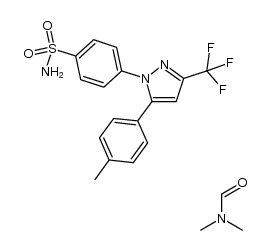
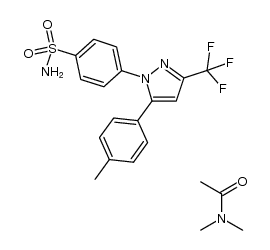
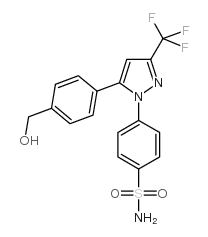
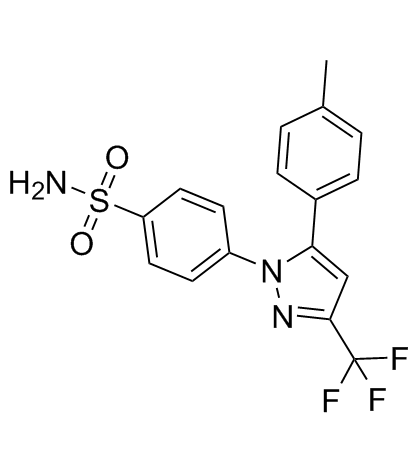
169590-42-5
| Name | celecoxib |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
4-[5-(4-methylphenyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)pyrazol-1-yl]benzenesulfonamide
4-(5-p-tolyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)benzenesulfonamide 4-[5-(4-Methylphenyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl]benzenesulfonamide Celebra Celecoxib 1-(4-sulphamoylphenyl)-3-trifluoromethyl-5-(p-tolyl)-pyrazole MFCD00941298 Celecox YM 177 Solexa 4-[5-(4-methylphenyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl]benzene sulfonamide 4-5-(4-methylphenyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-1-ylbenzenesulfonamide Celocoxib Celebrex N-[4-[5-(4-methylphenyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-1yl]phenylsulfonyl]benzensulfonamide celexicob Celebrex,Celebra |
| Description | Celecoxib is a selective COX-2 inhibitor with an IC50 of 40 nM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
COX-2:40 nM (IC50) COX-1:15 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | The selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitor Celecoxib (10-75 μM) inhibits the proliferation of the NPC cell lines in a dose-dependent manner. Celecoxib (25 and 50 μM) induces apoptosis and cell-cycle arrest at the G0/G1 checkpoint in the NPC cell lines, which is associated with significantly reduced STAT3 phosphorylation. The genes downstream of STAT3 (ie, Survivin, Mcl-1, Bcl-2 and Cyclin D1) are significantly down-regulated after exposure to Celecoxib (25 and 50 μM)[2]. |
| In Vivo | Celecoxib demonstrates potent, oral anti-inflammatory activity. Celecoxib reduces acute inflammation in the carrageenan edema assay with an ED50 of 7.1 mg/kg and reduces chronic inflammation in the adjuvant arthritis model with an ED50 of 0.37 mg/kg/day. In addition, Celecoxib also exhibits analgesic activity in the Hargreaves hyperalgesia model with an ED50 of 34.5 mg/kg. Celecoxib has potency equivalent to that of standard nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), yet shows no acute GI toxicity in rats at doses up to 200 mg/kg. In addition, it displays no chronic GI toxicity in rats at doses up to 600 mg/kg/day over 10 days[1]. In the KpB mice fed a high fat diet (obese) and treated with Celecoxib, tumor weight decreases by 66% when compare with control animals. Among KpB mice fed a low fat diet (non-obese), tumor weight decreases by 46% after treatment with Celecoxib[3]. Rat models are orally administrated with Celecoxib (20 mg/kg) and/or intramuscularly with Fasudil (10 mg/kg) for 2 weeks. Results demonstrates that the combined use of Celecoxib and fasudil significantly decreases COX-2 and Rho kinase II expression surrounding the lesion site in rats with spinal cord injury, improves the pathomorphology of the injured spinal cord, and promoted the recovery of motor function[4]. |
| Cell Assay | The antiproliferative effect of Celecoxib on NPC cells is assessed using an MTT assay. Cells are seeded into 96-well plates and allowed to attach for 24 h. The cells are then treated with increasing concentrations of Celecoxib (0, 5, 10, 25, 50 or 75 μM) dissolved in DMSO (final concentration ≤0.1%) and incubated for up to 48 h. After the incubation, 20 μL of MTT dye (5 mg/mL) are added to each well and cells are incubated at 37°C for 4 h. After removing the supernatants, the crystals are dissolved in DMSO and the absorbance is measured at 490 nm. The percentage growth inhibition is calculated as (ODcontrol−ODdrug)/ODcontrol×100%. The half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values and the 95% confidence intervals are calculated using probit regression using SPSS 15.0 software. The experiment is performed in triplicate and repeated at least three times[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[3] The KpB mice are monitored weekly by palpation for tumor growth. Celecoxib and placebo treatment is initiated after palpation of a 1 cm tumor in mice on the HFD (obese group) and LFD (non-obese group) (N=15 mice per group). Celecoxib is dissolved in DMSO at 5 mg/mL, further diluted 10 times in 0.5% methylcellulose with 0.025% Tween 80 and injected (IP) daily at a dose of 5 mg/kg body weight for 4 weeks. The tumor sizes are measured once a week by palpation. Tumor volume is calculated using the following equation: volume (mm3)=a×b2/2, where is the largest diameter and b is the smallest diameter. The animals are weighed weekly throughout the study. At sacrifice, mice are weighed and blood samples are taken. Half of the ovarian tumor is snap-frozen and stored at −80°C, and the other half is fixed in 10% neutral-buffered formalin and paraffin embedded. Mouse heart, lungs and kidneys are also harvested, fixed in formalin and grossly examined for any suspicious lesions before paraffin embedding. Rats[4] Forty adult, clean, female, Sprague-Dawley rats aged 3 months and weighing 280-330 g, are used. Forty rats are randomized to five groups as follows: sham surgery, model, Celecoxib, fasudil and combination groups, with eight rats in each group. Rats in the Celecoxib group are intragastrically administrated with a suspension of Celecoxib (20 mg/kg), and a suspension of Celecoxib containing 0.5% sodium carboxymethylcellulose is made from the capsules. Rats in the fasudil group are intramuscularly administrated with fasudil hydrochloride injection (10 mg/kg) via the dorsal muscle. Rats in the combination group are administrated with both a suspension of Celecoxib (20 mg/kg) and fasudil hydrochloride (10 mg/kg). The fasudil and Celecoxib doses are based on doses administered to adults and these are adjusted in a pre-study. Administration is once every day for 2 weeks. Subsequently, all rats are treated normally for another 2 weeks, and then sacrificed either for histological examination or for western blot assay. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 529.0±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 157-159ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C17H14F3N3O2S |
| Molecular Weight | 381.372 |
| Flash Point | 273.7±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 381.075867 |
| PSA | 86.36000 |
| LogP | 4.21 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.606 |
| Storage condition | Store at RT |
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H360D |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P308 + P313 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Phrases | R20/21/22 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25-S28-S37/39 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 |
| RTECS | DB2944937 |
| HS Code | 2935009090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |
| HS Code | 2935009090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2935009090 other sulphonamides VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:35.0% |



![N,N-dibenzyl-4-[5-(4-methylphenyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl]benzenesulfonamide structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/224/853793-24-5.png)