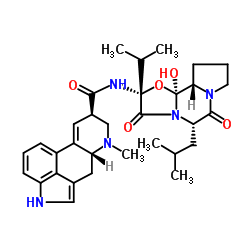
25614-03-3
| Name | bromocriptine |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Bromocryptine
MFCD00870213 Bromoergocryptine Bromergocryptine Bromoergocriptine Bromocriptinum Ergoset EINECS 247-128-5 Bromocriptin |
| Description | Bromocriptine is a potent dopamine D2/D3 receptor agonist, which binds D2 dopamine receptor with pKi of 8.05±0.2. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
pKi: 8.05±0.2 (dopamine D2 receptor)[1] |
| In Vitro | Bromocriptine stimulates [35S]-GTPγS binding at D2 dopamine receptor expressed in CHO cells with pEC50 of 8.15±0.05[1]. Bromocriptine also is a strong inhibitor of brain nitric oxide synthase. The ergot alkaloid Bromocriptine (BKT) is found to act as a strong inhibitor of purified neuronal nitric oxide synthase (NOS) (IC50=10±2 μM) whereas it is poorly active towards inducible macrophage NOS (IC50>100 μM) [2]. Bromocriptine is found to inhibit the activity of at least one human cytochrome P450 enzyme. Bromocriptine is a potent inhibitor of CYP3A4 with a calculated IC50 value for the interaction of 1.69 μM[3]. |
| In Vivo | Bromocriptine (a dopamine agonist) treatment (2 mg/kg, i.p.) group shows significant anti-immobility action as compared to control. When Bromocriptine administered 30 min after the last dose of 7 days MPE treatment and subjected to FST, this dopaminergic agonist produces significant and dose dependent potentiation of anti-immobility action of MPE (200 mg/kg, p.o.) as compared to MPE treatment alone. Bromocriptine (a dopamine agonist) treatment (2 mg/kg, i.p.) group shows a significant reduction of immobility time as compared to control. Bromocriptine administration after 7 days pretreatment with MPE (100 and 200 mg/kg, p.o.) shows significant and dose dependent potentiation of anti-immobility action of MPE as compared to MPE treatment alone[4]. Intraperitoneal administration of Bromocriptine induces a significant, dose dependent (0.1 mg and 1 mg/Kg) decrease in pain scores in CCI-IoN group when compared to sham and its effect lasted for 6 h. The highest dose induces the highest score decrease, (P<0.01). As a positive control SKF8129 (DR1 agonist) is used. Its intraperitoneal administration induces a non-significant increase in the SMA score when compared to sham (saline-injected). Intracisternal administration of Bromocriptine decreases significantly the SMA score when compared to sham (saline-injected). Bromocriptine effect lasted for 20 min. Intraperitoneal administration of Bromocriptine induces a significant dose dependent decrease in SMA score in CCI-IoN?+?6-OHDA lesioned group compared to that of sham. Its effect lasted for 6 h. SKF81297 administration increases the allodynic score. Intracisternal administration of Bromocriptine decreases significantly the SMA score compared to that of sham (saline-injected rats) and its effect lasted for 30 min[5]. |
| Kinase Assay | The [35S]-GTPγS binding assay is carried out. Cell membranes (25 ±75 ug) are incubated in Buffer B containing 0.1 mM dithiothreitol (DTT) and 1 uM GDP and drugs in a volumeof 0.9 mL for 30 min at 30°C. This preincubation ensures that the agonists tested are at equilibrium when the [35S]-GTPγS (50±150 pM, final concentration) is added (in 100 uL ofBuffer B) to initiate the reaction. The assay mixture is incubated for a further 20 min unless otherwise stated. The assays are terminated by rapid filtration and bound radio-activity determined as described for the radio-ligand binding assays above. The total binding of [35S]-GTPγS is less than 20% of that added[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[4] Swiss mice (20-25 g) of either sex (total 150) are used. Bromocriptine mesylate is used as dopamine receptor (D2) agonist. Haloperidol is diluted in distilled water which is used for a vehicle of injection. Bromocriptine mesylate is dissolved in one drop of glacial acetic acid and made up to volume in distilled water. Imipramine is dissolved in 0.9% normal saline. Haloperidol (0.1 mg/kg, i.p.) and Bromocriptine mesylate (2 mg/kg, i.p.) are administered for 7 days in groups of mice in Forced Swimming Test (FST) and Tail Suspension Test (TST). Imipramine (10 mg/kg, p.o.) as a standard is administered in positive control groups for 7 days. Rats[5] Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats (N=112, 275-325 g) are used. Two weeks after the 6-OHDA injection, the animals are briefly (<3 min) anesthetized with 2 % halothane using a mask and received for intracisternal administration Bromocriptine (7 μg/kg dissolved in 5 μL vehicle) or the vehicle alone (5 μL of 0.9 % saline). For i.p. injection we used Bromocriptine (1 mg/kg) and SKF81297 (3 mg/kg dissolved in 0.9 % saline) concentrations. Following a recovery period (<2 min), the rats are placed in the observation field for 40 min period-test by a blind-experimenter. |
| References |
| Density | 1.52 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 891.3ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C32H40BrN5O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 654.59400 |
| Flash Point | 492.8ºC |
| Exact Mass | 653.22100 |
| PSA | 118.21000 |
| LogP | 3.39740 |
| Vapour Pressure | 4.15E-34mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.696 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Hazard Codes | Xn,Xi |
|---|---|
| Risk Phrases | R20/21/22:Harmful by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed . |
| Safety Phrases | S45 |
|
~91% 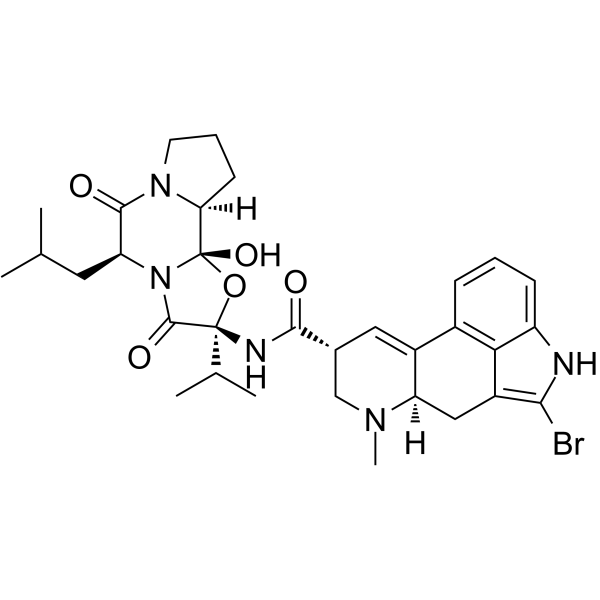
25614-03-3 |
| Literature: Megyeri, Gabor; Keve, Tibor Synthetic Communications, 1989 , vol. 19, # 20 p. 3415 - 3430 |
|
~% 
25614-03-3 |
| Literature: US4816587 A1, ; |