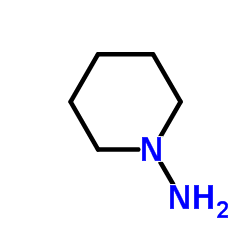
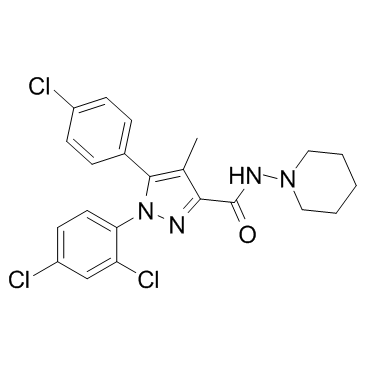
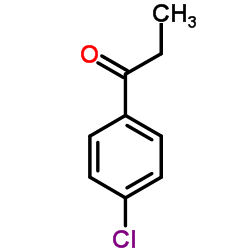
158681-13-1
| Name | Rimonabant Hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
5-(4-Chlorophenyl)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4-methyl-N-(1-piperidinyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide hydrochloride (1:1)
5-(4-Chlorophenyl)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4-methyl-N-(piperidin-1-yl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide hydrochloride (1:1) 1H-Pyrazole-3-carboxamide, 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4-methyl-N-1-piperidinyl-, hydrochloride (1:1) Rimonabant hydrochloride 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4-methyl-N-piperidin-1-ylpyrazole-3-carboxamide,hydrochloride MFCD04034714 Rimonabant (Hydrochloride) |
| Description | Rimonabant hydrochloride is a cannabinoid receptor (CB) antagonist which binds selectively to CB1 with a Ki of 2 nM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Ki: 2 nM (CB1 receptor)[1] |
| In Vitro | Rimonabant hydrochloride (SR 141716A) binds selectively to central cannabinoid receptors (CB1) with high affinity (Ki=2 nM), and blocks the inhibitory effects of cannabinoid receptor agonists in the mouse vas deferens, dopamine-stimulated adenylyl cyclase and WIN 55212-stimulated GTPγS binding[1]. Rimonabant dose-dependently inhibited CO synthesis in Raw 264.7 macrophages, with 1 µM producing a significant (~40%) decrease compared to untreated controls and concentrations ≥ 5 µM producing near complete inhibition. A small, but significant, reduction of TG and DG synthesis is also observed with Rimonabant at concentrations ≥ 10 µM. Inhibition of CO synthesis in Raw 264.7 macrophages by Rimonabant (IC50 value 2.9±0.38 µM) is very similar to that of AM251 and SR144528 (IC50 value 2.6±0.26 µM and 2.5±0.32 µM, respectively), two related compounds previously demonstrated to be potent ACAT inhibitors. Mouse peritoneal macrophages also displayed significantly reduced CO synthesis in response to Rimonabant treatment. Rimonabant at concentrations ≥ 1 µM significantly inhibits CO synthesis in CHO-ACAT1 and CHO-ACAT2 cells in a concentration-dependent manner with similar efficiency (IC50s of 1.5±1.2 µM and 2.2±1.1 µM, respectively)[2]. |
| In Vivo | Pretreatment with Rimonabant hydrochloride (SR 141716A) blocks the antinociceptive, discriminative stimulus, memory impairing and hypolocomotor effects produced by Δ-9-THC. SR 141716A also precipitates a withdrawal syndrome in rats treated chronically with Δ-9-THC[1]. Pretreatment of mice with 0.1 mg/kg of WIN 55212-2 is effective in increasing the CPP induced by MDMA , while 1 mg/kg of Rimonabant specifically blocks CB1 receptors and does not act as an inverse agonist[3]. |
| Kinase Assay | Raw 264.7 cells (2×106/well) in 12-well plates are rinsed with PBS and refed culture media supplemented with varying amounts of Rimonabant 1h prior to supplementation with 7-ketocholesterol (7KC). All wells are adjusted to receive equal amounts of vehicle. Following a 16 h incubation, caspase-3 and caspase 3-like activity is determined[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[3] A total of 250 male mice of the OF1 strain (21 days of age) are used. Animals are injected i.p. with cocaine hydrochloride, WIN 55212-2, or Rimonabant (SR 141716A) in a volume of 0.01 mL/g. Control groups are injected with the physiological saline used to dissolve cocaine (NaCl 0.9%) or with Tween-80, which is used to dissolve WIN 55212-2 and Rimonabant (0.01%, 0.01 mL of Tween dissolved in 100 mL of saline). The doses of cocaine administered are selected on the basis of previous studies showing that 1 mg/kg is a subthreshold dose for inducing CPP in naïve mice, while 6 mg/kg is effective in inducing CPP acquisition but not in producing reinstatement after extinction of CPP. Similarly, the doses of cannabinoid drugs administered are selected on the basis of previous studies on the effects of WIN 55212-2 in the CPP paradigm and on the effects of cannabinoid pretreatment on the CPP induced by other drugs of abuse. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 627.6ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 230-240ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C22H22Cl4N4O |
| Molecular Weight | 500.248 |
| Flash Point | 333.3ºC |
| Exact Mass | 498.054779 |
| PSA | 50.16000 |
| LogP | 7.06940 |
| Storage condition | -20°C Freezer |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301-H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P301 + P310-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Hazard Codes | T,Xi |
| Risk Phrases | 25-36 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-45 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1 / PGIII |
|
~% 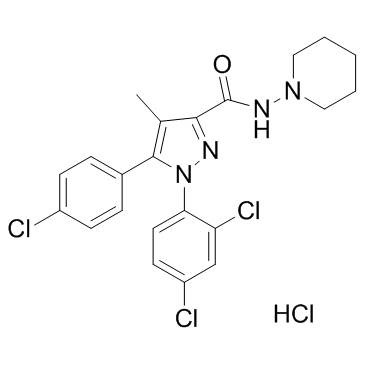
158681-13-1 |
| Literature: WO2008/32330 A2, ; Page/Page column 7 ; |
|
~% 
158681-13-1 |
| Literature: WO2006/87732 A1, ; Page/Page column 6 ; |
|
~% 
158681-13-1 |
| Literature: Organic Preparations and Procedures International, , vol. 44, # 2 p. 164 - 168 |
|
~% 
158681-13-1 |
| Literature: Organic Preparations and Procedures International, , vol. 44, # 2 p. 164 - 168 |
| Precursor 5 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |