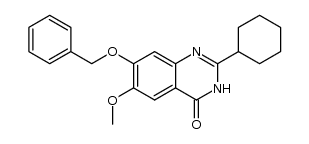
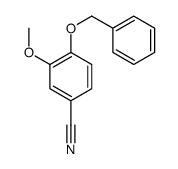
1255580-76-7
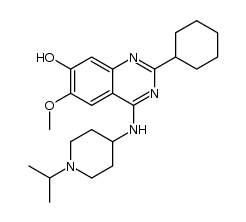
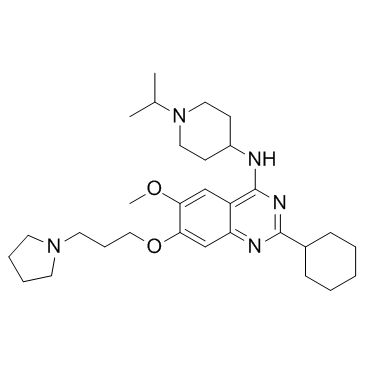
| Name | 2-cyclohexyl-6-methoxy-N-(1-propan-2-ylpiperidin-4-yl)-7-(3-pyrrolidin-1-ylpropoxy)quinazolin-4-amine |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
cc-643
UNC 0638 2-Cyclohexyl-N-(1-isopropyl-4-piperidinyl)-6-methoxy-7-[3-(1-pyrrolidinyl)propoxy]-4-quinazolinamine UNII-26A103L2FO 2-Cyclohexyl-N-(1-isopropylpiperidin-4-yl)-6-methoxy-7-(3-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)propoxy)quinazolin-4-amine UNC-0638 UNC0638 2-Cyclohexyl-6-methoxy-N-[1-(1-methylethyl)-4-piperidinyl]-7-[3-(1-pyrrolidinyl)propoxy]-4-quinazolinamine |
| Description | UNC0638 selectively inhibits G9a and GLP histone methyltransferase activity with IC50s of less than 15 nM and 19 nM, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: <15 nM (G9a), 19±1 nM (GLP)[1] |
| In Vitro | UNC0638, an inhibitor of G9a and GLP with excellent potency and selectivity over a wide range of epigenetic and non-epigenetic targets.The Ki of UNC0638 is determined to be 3.0±0.05 nM (n=2). Consistent with this, the Morrison Ki for UNC0638 is 3.7±0.2 nM (n=3). The selectivity of UNC0638 over a wide range of epigenetic targets is evaluated. Notably, UNC0638 is inactive against other H3K9 (SUV39H1 and SUV39H2), H3K27 (EZH2), H3K4 (SETD7, MLL and SMYD3), H3K79 (DOT1L) and H4K20 (SETD8) methyltransferases, as well as PRDM1, PRDM10 and PRDM12. In addition, UNC0638 is inactive against protein arginine methyltransferases PRMT1 and PRMT3, and HTATIP, a histone acetyltransferase. Of note, UNC0638 has weak but measurable activity against JMJD2E (IC50=4,500±1,100 nM), a Jumonji protein demethylase and DNA methyltransferase DNMT1 (IC50=107,000±6,000 nM). Nevertheless, the selectivity of UNC0638 for G9a and GLP over JMJD2E is >200-fold, and selectivity for G9a and GLP over DNMT1 is >5,000-fold[1]. UNC0638 is a type of small molecule that can specifically inhibit the enzyme activity of histone methyltransferase EHMT and reduce the H3K9 dimethylation (H3K9me2) levels in cells[2]. |
| Kinase Assay | The enzymatic reactions are conducted in duplicate at room temperature for 1 hour in a 50 μL mixture containing PKMT assay buffer, substrate coated plate, 10 M SAM, a HMT enzyme (EZH2 (800 ng/reaction), MLL (300 ng/reaction), PRMT1 (0.5 ng/reaction), SUV39H1 (75 ng/reaction) and UNC0638 (0-1.25 μM). After enzymatic reactions, 100 μL of first antibody is added to each well and the plate is incubated at room temperature for an additional 1 h. 100 μL of secondary antibody is added to each well and the plate is incubated at room temperature for an additional 30 min. 100 μL of developer reagents are added to wells and luminescence is measured using a BioTek SynergyTM 2 microplate reader. Enzyme activity assays are performed in duplicates at each concentration. The luminescence data are analyzed using the computer software, Graphpad Prism[1]. |
| Cell Assay | MDA-MB-231, PC3, HCT116 cells are cultured in RPMI with 10% FBS, 22RV1 cells in alphaMEM and 10% FBS, MCF7 and IMR90 cells in DMEM with 10% FBS. Cells are grown in the presence or absence of UNC0638 (10 nM, 100 nM, 1 μM, 10 μM, and 100 μM ) for stated amount of time. The media is removed and replaced with DMEM 10% FBS without phenol red supplemented with 1mg/mL of MTT and incubated for 1-2 h. Live cells reduce yellow MTT to purple formazan. The resulting formazan is solubilized in acidified isopropanol and 1% Triton and absorbance measured at 570 nm, corrected for 650 nm background[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[1] Standard DMPK studies in male Swiss albino mice (3 animals per data point) are conducted, following intravenous (IV, 1 mg/kg), oral (PO, 3 mg/kg), and intraperitoneal (IP, 2.5 mg/kg) administration of UNC0638. |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 563.9±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 93-94 ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C30H47N5O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 509.727 |
| Flash Point | 294.8±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 509.372986 |
| PSA | 62.75000 |
| LogP | 5.75 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.587 |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |
| Water Solubility | Practically insoluble (0.012 g/L) (25 ºC) |
|
~% 
1255580-76-7 |
| Literature: Liu, Feng; Barsyte-Lovejoy, Dalia; Allali-Hassani, Abdellah; He, Yunlong; Herold, J. Martin; Chen, Xin; Yates, Christopher M.; Frye, Stephen V.; Brown, Peter J.; Huang, Jing; Vedadi, Masoud; Arrowsmith, Cheryl H.; Jin, Jian Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2011 , vol. 54, # 17 p. 6139 - 6150 |
|
~% 
1255580-76-7 |
| Literature: Liu, Feng; Barsyte-Lovejoy, Dalia; Allali-Hassani, Abdellah; He, Yunlong; Herold, J. Martin; Chen, Xin; Yates, Christopher M.; Frye, Stephen V.; Brown, Peter J.; Huang, Jing; Vedadi, Masoud; Arrowsmith, Cheryl H.; Jin, Jian Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2011 , vol. 54, # 17 p. 6139 - 6150 |
|
~% 
1255580-76-7 |
| Literature: Liu, Feng; Barsyte-Lovejoy, Dalia; Allali-Hassani, Abdellah; He, Yunlong; Herold, J. Martin; Chen, Xin; Yates, Christopher M.; Frye, Stephen V.; Brown, Peter J.; Huang, Jing; Vedadi, Masoud; Arrowsmith, Cheryl H.; Jin, Jian Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2011 , vol. 54, # 17 p. 6139 - 6150 |
|
~% 
1255580-76-7 |
| Literature: Liu, Feng; Barsyte-Lovejoy, Dalia; Allali-Hassani, Abdellah; He, Yunlong; Herold, J. Martin; Chen, Xin; Yates, Christopher M.; Frye, Stephen V.; Brown, Peter J.; Huang, Jing; Vedadi, Masoud; Arrowsmith, Cheryl H.; Jin, Jian Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2011 , vol. 54, # 17 p. 6139 - 6150 |
|
~% 
1255580-76-7 |
| Literature: Liu, Feng; Barsyte-Lovejoy, Dalia; Allali-Hassani, Abdellah; He, Yunlong; Herold, J. Martin; Chen, Xin; Yates, Christopher M.; Frye, Stephen V.; Brown, Peter J.; Huang, Jing; Vedadi, Masoud; Arrowsmith, Cheryl H.; Jin, Jian Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2011 , vol. 54, # 17 p. 6139 - 6150 |
|
~% 
1255580-76-7 |
| Literature: Liu, Feng; Barsyte-Lovejoy, Dalia; Allali-Hassani, Abdellah; He, Yunlong; Herold, J. Martin; Chen, Xin; Yates, Christopher M.; Frye, Stephen V.; Brown, Peter J.; Huang, Jing; Vedadi, Masoud; Arrowsmith, Cheryl H.; Jin, Jian Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2011 , vol. 54, # 17 p. 6139 - 6150 |
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |