97682-44-5
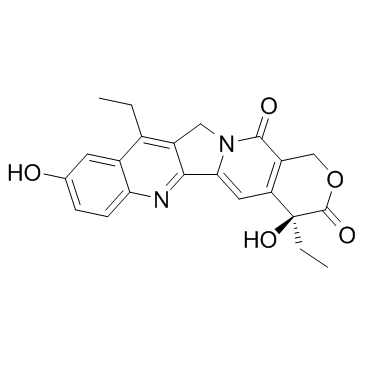
| Name | Irinotecan |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Irinotecan
7-ethoxyxanthone-3-carboxylic acid Campto (+)-Irinotecan 9H-Xanthene-3-carboxylic acid,7-ethoxy-9-oxo MFCD01862255 (4S)-4,11-Diethyl-4-hydroxy-3,14-dioxo-3,4,12,14-tetrahydro-1H-pyrano[3',4':6,7]indolizino[1,2-b]quinolin-9-yl 1,4'-bipiperidine-1'-carboxylate [1,4'-Bipiperidine]-1'-carboxylic acid, (4S)-4,11-diethyl-3,4,12,14-tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-3,14-dioxo-1H-pyrano[3',4':6,7]indolizino[1,2-b]quinolin-9-yl ester |
| Description | Irinotecan is a water soluble topoisomerase I inhibitor, preventing religation of the DNA strand by binding to topoisomerase I-DNA complex. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Topoisomerase I |
| In Vitro | Irinotecan is a topoisomerase I inhibitor. Irinotecan inhibits the growth of LoVo and HT-29 cells, with IC50s of 15.8 ± 5.1 and 5.17 ± 1.4 μM, respectively, and induces similar amounts of cleavable complexes in both in LoVo and HT-29 cells[2]. Irinotecan suppresses the proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC), with an IC50 of 1.3 μM[3]. |
| In Vivo | Irinotecan (CPT-11, 5 mg/kg) significantly inhibits the growth of tumors by intratumoral injection daily for 5 days, on two consecutive weeks in rats, and such effects also occur via continuous intraperitoneal infusion by osmotic minipump into mice. However, Irinotecan (10 mg/kg) shows no effect on the growth of tumor by i.p[1]. Irinotecan (CPT-11, 100-300 mg/kg, i.p.) apparently suppresses tumor growth of HT-29 xenografts in athymic female mice by day 21. The two groups of Irinotecan (125 mg/kg) plus TSP-1 (10 mg/kg per day) or Irinotecan (150 mg/kg) in combination TSP-1 (20 mg/kg per day) are nearly equally effective and inhibit tumor growth 84% and 89%, respectively, and both are more effective than Irinotecan alone at doses of 250 and 300 mg/kg[3]. |
| Cell Assay | Exponentially growing cells are seeded in 20 cm2 dishes with an optimal cell number for each cell line (20,000 for LoVo cells, 100,000 for HT-29 cells). They are treated 2 days later with increasing concentrations of irinotecan or SN-38 for one cell doubling time (24 h for LoVo cells, 40 h for HT-29 cells). After washing with 0.15 M NaCl, the cells are further grown for two doubling times in normal medium, detached from the support with trypsin-EDTA and counted in a hemocytometer. The IC50 values are then estimated as the drug concentrations responsible for 50% growth inhibition as compared with cells incubated without drug[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Irinotecan has been administered by intratumoral injection at 0.1 cc volume of the appropriate solution, for a doses of 5 mg/kg daily for 5 days, on two consecutive weeks, followed by a 7-days rest period, referred to as one cycle of therapy. Rats receive three cycles over a period of 8 weeks. Control animals receive 0.1 cc of sterile 0.9% sodium chloride solution by intratumoral injection in the same rule of administration as that of animals of group II[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 873.4±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C33H38N4O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 586.678 |
| Flash Point | 482.0±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 586.279114 |
| PSA | 114.20000 |
| LogP | 4.35 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.689 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Precursor 6 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 3 | |