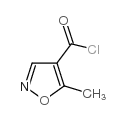
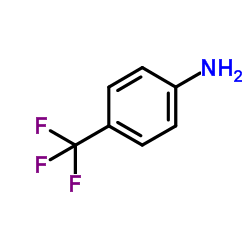
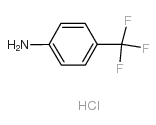
75706-12-6
| Name | leflunomide |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
N-(4-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-5-methylisoxazole-4-carboxamide
Leflunomidum 5-Methyl-N-[4-(trifluormethyl)phenyl]isoxazol-4-carboxamid Leflunomide Leflunomida Arava lefunamide MFCD00867593 5-methyl-N-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]isoxazole-4-carboxamide 5-méthyl-N-[4-(trifluorométhyl)phényl]isoxazole-4-carboxamide 5-Methyl-N-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1,2-oxazole-4-carboxamide HWA 486 Leflunomid |
| Description | Leflunomide is a pyrimidine synthesis inhibitor, inhibiting dihydroorotate dehydrogenase, and acts as a disease-modifying antirheumatic drug. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Leflunomide is actually a prodrug that has been shown to inhibit proliferation of mononuclear and T-cells. Leflunomide is an inhibitor of several protein tyrosine kinases, with IC50 values between 30 mM and 100 mM in vitro cellular and enzymatic assays[1]. Leflunomide is capable of inhibiting anti-CD3- and interleukin-2 (IL-2)-stimulated T cell proliferation. Leflunomide is able to inhibit p59fyn and p56lck activity in in vitro tyrosine kinase assays. Leflunomide also inhibits Ca2+ mobilization in Jurkat cells stimulated by anti-CD3 antibody but not in those stimulated by ionomycin. Leflunomide also inhibits distal events of anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody stimulation, namely, IL-2 production and IL-2 receptor expression on human T lymphocytes. Leflunomide also inhibits tyrosine phosphorylation in CTLL-4 cells stimulated by IL-2[2]. Leflunomide is an immunomodulatory drug that may exert its effects by inhibiting the mitochondrial enzyme dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH), which plays a key role in the de novo synthesis of the pyrimidine ribonucleotide uridine monophosphate (rUMP). Leflunomide prevents the expansion of activated and autoimmune lymphocytes by interfering with the cell cycle progression due to inadequate production of rUMP and utilizing mechanisms involving p53[3]. |
| Kinase Assay | DHODase activity is measured by the DCIP colorimetric assay. This is a coupled assay in which oxidation of DHO and subsequent reduction of ubiquinone are stoichiometrically equivalent to the reduction of DCIP. Reduction of DCIP is accompanied by a loss of absorbance at 610 nm (ε=21500 M/cm). The assay is performed in a 96-well microtiter plate at ambient temperature (ca. 25°C). Stock solutions of 10 mM leflunomide and A771726 are prepared in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and these are diluted with reaction buffer (100 mM Tris and 0.1 % Triton X-100, pH 8.0) to prepare working stocks of the inhibitors at varying concentrations. For each reaction, the well contained 10 nM DHODase, 68 μM DCIP, 0.16 mg/mL gelatin, the stated concentration of ubiquinone, 10 μL of an inhibitor working stock to give the stated final concentration, and reaction buffer. After a 5-min equilibration period, the reaction is initiated by addition of DHO to the stated final concentrations. The total volume of reaction mixture for each assay is 150 μL, and the final DMSO concentration is ≤ 0.01% (v/v). The reaction progress is followed by recording the loss of absorbance at 610 nm over a 10-min period (during which the velocity remained linear). Velocities are reported as the change in absorbance at 610 nm per minute, and each reported value is the average of three replicates. In experiments where the DHO or ubiquinone concentration is varied, the other substrate is held constant at 200 μM. To determine the inhibitor potency of leflunomide and A771726, the effects of varying concentrations of the two compounds on the initial velocity of the DHODase reaction is measured over a concentration range of 0.01−1.0 μM. In these experiments the DHO and ubiquinone concentrations are held constant at 200 and 100 μM, respectively. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 289.3±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 163-168°C |
| Molecular Formula | C12H9F3N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 270.207 |
| Flash Point | 128.8±27.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 270.061615 |
| PSA | 55.13000 |
| LogP | 1.95 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.541 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301-H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P280-P301 + P310 + P330-P305 + P351 + P338-P337 + P313 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-36 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | NY2354200 |
| HS Code | 2934999090 |
|
~93% 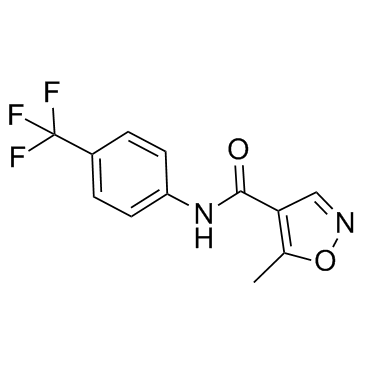
75706-12-6 |
| Literature: Fossa; Menozzi; Schenone; Filipelli; Russo; Lucarelli; Marmo Farmaco, 1991 , vol. 46, # 6 p. 789 - 802 |
|
~64% 
75706-12-6 |
| Literature: UNICHEM LABORATORIES LIMITED Patent: WO2007/86076 A2, 2007 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 5-7 ; |
|
~% 
75706-12-6 |
| Literature: US2002/22646 A1, ; |
|
~% 
75706-12-6 |
| Literature: Farmaco, , vol. 46, # 6 p. 789 - 802 |
|
~% 
75706-12-6 |
| Literature: Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 135, # 23 p. 8436 - 8439 |
|
~% 
75706-12-6 |
| Literature: Chemical Communications, , vol. 48, # 96 p. 11781 - 11783 |
| Precursor 4 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| HS Code | 2934999090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2934999090. other heterocyclic compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |