16009-13-5
| Name | hemin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Hemin
Chloro(protoporphyrinato)iron(III) MFCD00010726 Chloro[3,3'-(3,7,12,17-tetramethyl-8,13-divinyl-2,18-porphyrindiyl-κN,N)dipropanoato(2-)]iron Ferriprotoporphyrin chloride 7,12-Diethenyl-3,8,13,17-tetramethyl-21H,23H-porphine-2,18-dipropanoic acid Ferriheme chloride Ferriprotoporphyrin IX chloride Chloroprotoporphyrin IX iron(III) EINECS 240-140-1 |
| Description | Hemin is an iron-containing porphyrin. Hemin is an Heme oxygenase (HO)-1 inducer. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Heme oxygenase[1] |
| In Vitro | Hemin and PGJ2, used as positive controls, strongly increase both expression and activity of HMOX after 4 and 12 h, respectively. Indeed, a significant effect is found of 30 μM Hemin on cell proliferation in all used cell lines after 48 h, which is dose-dependent. Hemin treatment decreases cell proliferation to 62±5 %, 51±3 %, and 38±8 % in PA-TU-8902, BxPC-3 and MiaPaCa-2 cancer cells, respectively, with p<0.0001 for all comparisons. Furthermore, enhancement of anti-proliferative effects of statins is observed by Hemin, documented as decreased cell proliferation after 48 h of co-treatment[1]. |
| In Vivo | Following the i.p. administration of Hemin (100 μmol/kg), the HO-1 level in the renal cortex begins to increase gradually. The HO-1 level reaches its peak 24 h after Hemin preconditioning. HO-1 is expressed mainly in the renal tubules. The HO-2 level in the kidney does not change following Hemin preconditioning[2]. |
| Cell Assay | For the cell proliferation assay, cells are seeded into 96 well (5-12.5×104 cells per mL according to the cell line) and kept at 37°C and 5 % CO2. After 24 h, cells are treated with statins or/and Hemin, followed by the MTT test as a general cell proliferation assay[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[2] Eight- to ten-week-old male BABL/c mice are used for the ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) experiments. The animals are divided into five groups as follows: (1) the sham group undergo isolation of the bilateral renal arteries without clamping; (2) the vehicle group receive an intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of 4 mL/kg PBS as a vehicle control (with IRI); (3) the Hemin-preconditioned group receive Hemin, a potent inducer of HO-1, at 100 μmol/kg i.p.; (4) the Hemin plus ZnPP group receive zinc protoporphyrin IX, an inhibitor of HO-1 activity, at 5 mg/kg i.p. 6 h after receiving 100 μmol/kg Hemin i.p.; and (5) the Hemin plus PD98059 group receive PD98059, an inhibitor of ERK1/2 activity, at 10 mg/kg i.p. 6 h after receiving 100 μmol/kg Hemin i.p. Both inhibitors are administered i.p. 2 h before I/R, whereas Hemin was administered 8 h before I/R. |
| References |
| Melting Point | 300 °C |
|---|---|
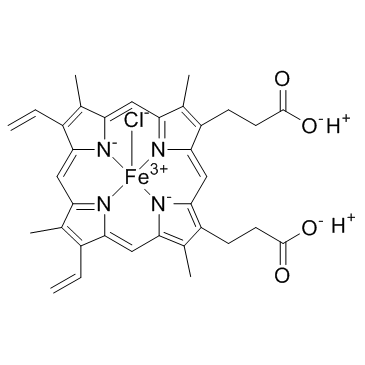
| Molecular Formula | C34H32ClFeN4O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 651.940 |
| Exact Mass | 651.146179 |
| PSA | 109.18000 |
| LogP | 4.29920 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. Combustible. |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | N,Xi |
| Risk Phrases | R10:Flammable. R19:May form explosive peroxides. R50:Very Toxic to aquatic organisms. R36:Irritating to the eyes. |
| Safety Phrases | 24/25-22-36-26 |
| RIDADR | UN 3272 3/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | LJ8080000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 3 |