2096-10-8
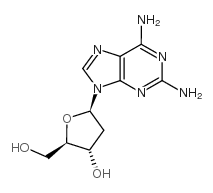
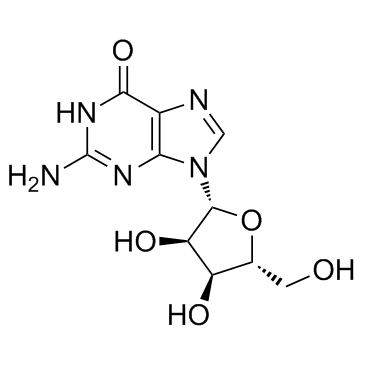
| Name | 9H-Purine-2,6-diamine, 9-.β.-D-ribofuranosyl |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Aminoadenosine
2,6-DiaMinopurinosine 9-Pentofuranosyl-9H-purine-2,6-diamine 2-AMINO-ADENOSINE 2,6-DIAMINOPURINE RIBOSIDE (2R,3R,4S,5R)-2-(2,6-Diamino-9H-purin-9-yl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-3,4-furandiol 2-Amino-adenoside 2-AMINE ADENOSINE 2,6-Diamino-9-(β-D-ribofuranosyl)purine MFCD00053556 2-Aminoadenosine 2,6-Diamino-9-(beta-D-ribofuranosyl)purine 9-(β-D-Ribofuranosyl)-9H-purin-2,6-diamin EINECS 209-610-8 2,6-DiaMinonebularine 2-AMinoadenosin purine-2,6-diamine ribonucleoside 2-NH2-A 2,6-DIAMINOPURINE-RIBOSIDE |
| Description | 2-Aminoadenosine is an adenosine analog. Adenosine analogs mostly act as smooth muscle vasodilators and have also been shown to inhibit cancer progression. Its popular products are adenosine phosphate, Acadesine (HY-13417), Clofarabine (HY-A0005), Fludarabine phosphate (HY-B0028) and Vidarabine (HY-B0277)[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 2.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 798.5±70.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 241-243°C (dec.) |
| Molecular Formula | C10H14N6O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 282.26 |
| Flash Point | 436.7±35.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 282.107666 |
| PSA | 165.56000 |
| LogP | -1.08 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.986 |
| Storage condition | 2~8℃ |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
|---|
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
|---|





![6,6-diacetylamino-9-[(2,3,5-tri-O-acetyl)-β-D-ribofuranosyl]purine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/133/62420-34-2.png)