DL-β-Hydroxybutyryl coenzyme A lithium
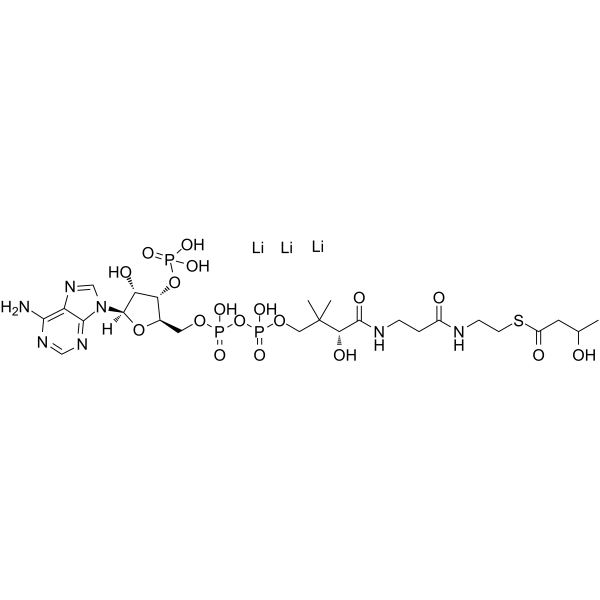
DL-β-Hydroxybutyryl coenzyme A lithium structure
|
Common Name | DL-β-Hydroxybutyryl coenzyme A lithium | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 103404-51-9 | Molecular Weight | 859.55600 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C25H41LiN7O18P3S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of DL-β-Hydroxybutyryl coenzyme A lithiumDL-β-Hydroxybutyryl coenzyme A lithium is an intermediate in the fermentation of butyric acid and the metabolism of lysine and tryptophan, and is produced from β-hydroxybutyric acid by short-chain-CoA synthase[1][2]. |
| Name | DL-β-Hydroxybutyryl coenzyme A lithium salt |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | DL-β-Hydroxybutyryl coenzyme A lithium is an intermediate in the fermentation of butyric acid and the metabolism of lysine and tryptophan, and is produced from β-hydroxybutyric acid by short-chain-CoA synthase[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | DL-β-Hydroxybutyryl coenzyme A lithium (β-Hydroxybutyryl-CoA) can be produced as an intermediate metabolite via the mitochondrial pathway, where impaired mitochondrial function in cancer cells leads to the accumulation of it. At the same time, DL-β-Hydroxybutyryl coenzyme A lithium can also be produced via the fatty acid β-oxidation, which is accelerated by starvation and fasting, leading to the accumulation of it and thus to diseases caused by certain metabolic adaptations[1]. DL-β-Hydroxybutyryl coenzyme A lithium (β-Hydroxybutyryl-CoA) can act as a cofactor for lysine β-hydroxybutyrylation (Kbhb), with elevated levels of histone Kbhb in a streptozotocin (STZ)-induced type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) mouse model[2]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C25H41LiN7O18P3S |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 859.55600 |
| Exact Mass | 859.16000 |
| PSA | 441.42000 |
| LogP | 0.23680 |
| InChIKey | OVAWKNZLRFPNGG-JFVJNUAZSA-K |
| SMILES | CC(O)CC(=O)SCCNC(=O)CCNC(=O)C(O)C(C)(C)COP(=O)([O-])OP(=O)(O)OCC1OC(n2cnc3c(N)ncnc32)C(O)C1OP(=O)([O-])[O-].[Li+].[Li+].[Li+] |
| Storage condition | 20°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
Characterization of the highly active polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase of Chromobacterium sp. strain USM2.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77 , 2926-2933, (2011) The synthesis of bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) is very much dependent on the expression and activity of a key enzyme, PHA synthase (PhaC). Many efforts are being pursued to enhance the activit... |
|
|
A quantitative cytochemical method for the measurement of beta-hydroxyacyl CoA dehydrogenase activity in rat heart muscle.
Histochemistry 75 , 67, (1982) Although cytochemical methods exist for measuring dehydrogenases that act on substrates involved in the production of chemical energy from sugars, virtually no methods exist for measuring the dehydrog... |
|
|
Detection of covalent and noncovalent intermediates in the polymerization reaction catalyzed by a C149S class III polyhydroxybutyrate synthase.
Biochemistry 48 , 9202-9211, (2009) Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) synthases catalyze the conversion of 3-hydroxybutyryl coenzyme A (HBCoA) to PHB with a molecular mass of 1.5 MDa. The class III synthase from Allochromatium vinosum is a tetr... |
| S-[2-[3-[[4-[[[5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-phosphonooxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-2-hydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutanoyl]amino]propanoylamino]ethyl] 3-hydroxybutanethioate,lithium |