RVX-208
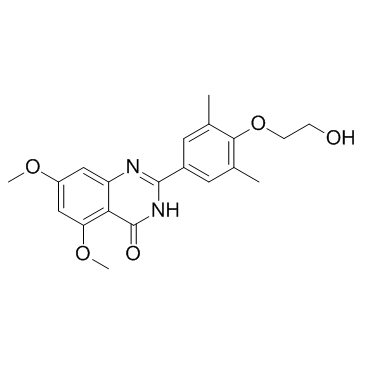
RVX-208 structure
|
Common Name | RVX-208 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1044870-39-4 | Molecular Weight | 370.399 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H22N2O5 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of RVX-208Apabetalone (RVX-208) is an inhibitor of BET transcriptional regulators with selectivity for the second bromodomain. The IC50s are 87±10 μM and 0.51±0.041 μM for BD1 and BD2, respectively. |
| Name | 2-(4-(2-Hydroxyethoxy)-3,5-dimethylphenyl)-5,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-4(3H)-one |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Apabetalone (RVX-208) is an inhibitor of BET transcriptional regulators with selectivity for the second bromodomain. The IC50s are 87±10 μM and 0.51±0.041 μM for BD1 and BD2, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 510±41 nM (BD2), 87±10 μM (BD1)[1] |
| In Vitro | Apabetalone (RVX-208) competes with binding of an acetylated histone peptide to tandem BD1 BD2 protein constructs of the four BET proteins, with IC50s between 0.5 and 1.8 µM. Apabetalone increases the production of ApoA-I in hepatocytes in vitro, which results in increased high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C). Apabetalone selectively binds to bromodomains of the BET (Bromodomain and Extra Terminal) family, competing for a site bound by the endogenous ligand, acetylated lysine, and that this accounts for its pharmacological activity. Apabetalone increases Apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA-I) production through an epigenetic mechanism and suggests that BET inhibition may be a promising new approach to the treatment of atherosclerosis. Apabetalone increases ApoA-I expression in liver cells[2]. |
| In Vivo | In the atherosclerosis prophylactic treatment study design, mice are fed a Western diet concurrent with the treatment with 150 mg/kg/dose b.i.d. for 12 weeks. Mice are sacrificed at 12 weeks after treatment. There is a progressive increase in body weight in both the vehicle treated as well as the Apabetalone (RVX-208) treated groups. However, there is only an increase of 4 g (from 24 g to 28 g) body weight after 12 weeks on Western diet in the Apabetalone treated group whereas this increase is found to be 9 g (25 g-34 g) in the vehicle treated group. The significant decrease in body weight gain in Apabetalone treated mice is not due to decreased feed consumption, suggesting a positive attribute of the molecule. Plasma lipid measurements are done at 6 weeks and 12 weeks of treatment with either the vehicle or Apabetalone. Compared to the vehicle control animals, Apabetalone treated mice show significant increase (~200%) in the levels of HDL-C at 6 weeks of treatment, which is sustained until end of the study (12 weeks)[3]. |
| Cell Assay | Huh7 cells are plated at 23,000/well in a 96 well plate in DMEM+10% FBS before allowing to grow overnight. Cells are treated with compounds for 48 h in 0.1% DMSO with or without 5 µM Actinomycin D. U937 cells are differentiated for 3 days in 60 ng/mL PMA, 32,000 cells/well in 96-well format. Cells are then treated with compound in 0.1% DMSO in RPMI media+10% FBS, and after 1 h, lipopolysaccharide is added to the cells at 1 µg/mL for 3 hours[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[3] Seven to eight week old male ApoE-/- mice are used. Based on the body weight and lipid values, mice are divided into 2 groups (n=12): group 1, vehicle; and group 2, test agent, Apabetalone. Mice are then switched to Western diet (0.15% cholesterol and 42% calories from fat) and concurrently treated orally by gavage with either vehicle or the test agent, Apabetalone (150 mg/kg/dose b.i.d) for 12 weeks. After 6 week of treatment, an interim blood draw is done to monitor serum lipid levels. After 12 weeks of treatment mice are sacrificed to measure blood lipid parameters, aortic lesion, and liver and aortic RNA. Eight mice are used for enface (aortic plaque) analysis, 4 mice for tissue collection for mRNA and all 12 mice used for aortic sinus lesion area measurement. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C20H22N2O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 370.399 |
| Exact Mass | 370.152863 |
| PSA | 93.67000 |
| LogP | 2.04 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.596 |
| InChIKey | NETXMUIMUZJUTB-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | COc1cc(OC)c2c(=O)[nH]c(-c3cc(C)c(OCCO)c(C)c3)nc2c1 |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|
|
~78% 
RVX-208 CAS#:1044870-39-4 |
| Literature: WO2009/158404 A1, ; Page/Page column 16-17 ; WO 2009/158404 A1 |
|
~39% 
RVX-208 CAS#:1044870-39-4 |
| Literature: US2008/188467 A1, ; Page/Page column 33 ; US 20080188467 A1 |
|
~% 
RVX-208 CAS#:1044870-39-4 |
| Literature: US2013/281397 A1, ; |
|
~% 
RVX-208 CAS#:1044870-39-4 |
| Literature: US2013/281397 A1, ; |
|
~% 
RVX-208 CAS#:1044870-39-4 |
| Literature: US2013/281397 A1, ; |
|
~% 
RVX-208 CAS#:1044870-39-4 |
| Literature: US2013/281397 A1, ; |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
| UNII:8R4A7GDZ1D |
| 2-[4-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-3,5-dimethylphenyl]-5,7-dimethoxy-1H-quinazolin-4-one |
| 4(3H)-Quinazolinone, 2-[4-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-3,5-dimethylphenyl]-5,7-dimethoxy- |
| 2-[4-(2-Hydroxyethoxy)-3,5-dimethylphenyl]-5,7-dimethoxy-4(1H)-quinazolinone |
| Apabetalone |
| RVX-208 |