Nateglinide
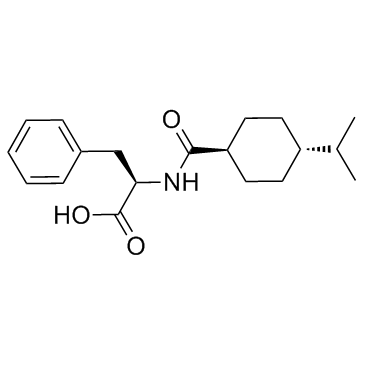
Nateglinide structure
|
Common Name | Nateglinide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 105816-04-4 | Molecular Weight | 317.423 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 527.6±39.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H27NO3 | Melting Point | 137-141ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 272.9±27.1 °C | |
Use of NateglinideNateglinide is an insulin secretagog agent used for the treatment of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM).Target: OthersNateglinide is an oral antihyperglycemic agent used for the treatment of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM). It belongs to the meglitinide class of short-acting insulin secretagogues, which act by binding to β cells of the pancreas to stimulate insulin release. Nateglinide is an amino acid derivative that induces an early insulin response to meals decreasing postprandial blood glucose levels. It should only be taken with meals and meal-time doses should be skipped with any skipped meal. Approximately one month of therapy is required before a decrease in fasting blood glucose is seen. Meglitnides may have a neutral effect on weight or cause a slight increase in weight. The average weight gain caused by meglitinides appears to be lower than that caused by sulfonylureas and insulin and appears to occur only in those na?ve to oral antidiabetic agents. Due to their mechanism of action, meglitinides may cause hypoglycemia although the risk is thought to be lower than that of sulfonylureas since their action is dependent on the presence of glucose. In addition to reducing postprandial and fasting blood glucose, meglitnides have been shown to decrease glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels, which are reflective of the last 8-10 weeks of glucose control. Meglitinides appear to be more effective at lowering postprandial blood glucose than metformin, sulfonylureas and thiazolidinediones. Nateglinide is extensively metabolized in the liver and excreted in urine (83%) and feces (10%). The major metabolites possess less activity than the parent compound. One minor metabolite, the isoprene, has the same potency as its parent compound [1-3]. |
| Name | nateglinide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Nateglinide is an insulin secretagog agent used for the treatment of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM).Target: OthersNateglinide is an oral antihyperglycemic agent used for the treatment of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM). It belongs to the meglitinide class of short-acting insulin secretagogues, which act by binding to β cells of the pancreas to stimulate insulin release. Nateglinide is an amino acid derivative that induces an early insulin response to meals decreasing postprandial blood glucose levels. It should only be taken with meals and meal-time doses should be skipped with any skipped meal. Approximately one month of therapy is required before a decrease in fasting blood glucose is seen. Meglitnides may have a neutral effect on weight or cause a slight increase in weight. The average weight gain caused by meglitinides appears to be lower than that caused by sulfonylureas and insulin and appears to occur only in those na?ve to oral antidiabetic agents. Due to their mechanism of action, meglitinides may cause hypoglycemia although the risk is thought to be lower than that of sulfonylureas since their action is dependent on the presence of glucose. In addition to reducing postprandial and fasting blood glucose, meglitnides have been shown to decrease glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels, which are reflective of the last 8-10 weeks of glucose control. Meglitinides appear to be more effective at lowering postprandial blood glucose than metformin, sulfonylureas and thiazolidinediones. Nateglinide is extensively metabolized in the liver and excreted in urine (83%) and feces (10%). The major metabolites possess less activity than the parent compound. One minor metabolite, the isoprene, has the same potency as its parent compound [1-3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
[1]. http://205.193.93.51/dpdonline/searchRequest.dodin=2245439 |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 527.6±39.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 137-141ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C19H27NO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 317.423 |
| Flash Point | 272.9±27.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 317.199097 |
| PSA | 66.40000 |
| LogP | 4.21 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.536 |
| Storage condition | Room temp |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R22 |
| Safety Phrases | 24/25-36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| RTECS | SQ7318950 |
| HS Code | 2924299090 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |
| HS Code | 2924299090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924299090. other cyclic amides (including cyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Formulation and in vitro evaluation of nateglinide microspheres using HPMC and carbopol-940 polymers by ionic gelation method.
Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 26(6) , 1229-35, (2013) This study involves the design and characterization of Nateglinide (NAT) microspheres to enhance patient compliance. Ionic gelation technique was used to prepare Nateglinide Microspheres by using rate... |
|
|
From evidence assessments to coverage decisions?: the case example of glinides in Germany.
Health Policy 104(1) , 27-31, (2012) In Germany, coverage decisions in the statutory health insurance (SHI) system are based on the principles of evidence-based medicine. Recently, an evidence assessment by the Institute for Quality and ... |
|
|
Nateglinide--current and future role in the treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Int. J. Clin. Pract. 59(10) , 1218-28, (2005) Therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus should aim to control not only fasting, but also postprandial glucose levels. Nateglinide, a d-phenylalanine derivative, restores postprandial early phase insulin ... |
| Glinate |
| Starsis |
| SDZ DJN 608 |
| Starlix |
| (2R)-2-{[(trans-4-Isopropylcyclohexyl)carbonyl]amino}-3-phenylpropanoic acid |
| N-{[trans-4-(1-methylethyl)cyclohexyl]carbonyl}-D-phenylalanine |
| (-)-N-(trans-4-Isopropylcyclohexanecarbonyl)-D-phenylalanine |
| (2R)-2-({[trans-4-(1-methylethyl)cyclohexyl]carbonyl}amino)-3-phenylpropanoic acid |
| DJN 608 |
| Natelide |
| N-[[trans-4-(1-Methylethyl)cyclohexyl]carbonyl]-D-phenylalanine |
| N-{[trans-4-(Propan-2-yl)cyclohexyl]carbonyl}-D-phenylalanin |
| MFCD00875706 |
| ay4166 |
| Starlix DS |
| Fastic-d5 |
| A-4166 |
| Fastic |
| D-Phenylalanine, N-[[trans-4-(1-methylethyl)cyclohexyl]carbonyl]- |
| N-[(trans-4-Isopropylcyclohexyl)carbonyl]-D-phenylalanine |
| (-)-N-(trans-4-Isopropylcyclohexyl-1-carbonyl)-D-phenylalanine |
| Nateglinide |
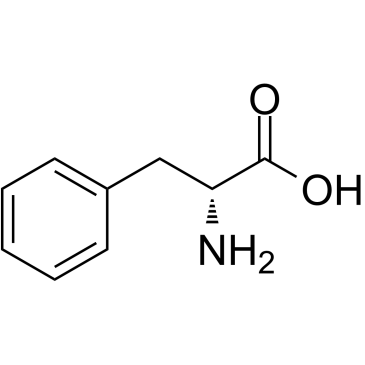 CAS#:673-06-3
CAS#:673-06-3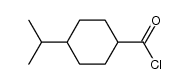 CAS#:100597-38-4
CAS#:100597-38-4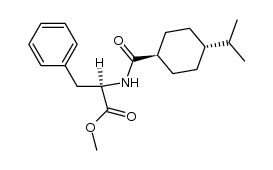 CAS#:105746-47-2
CAS#:105746-47-2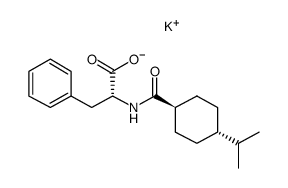 CAS#:594837-86-2
CAS#:594837-86-2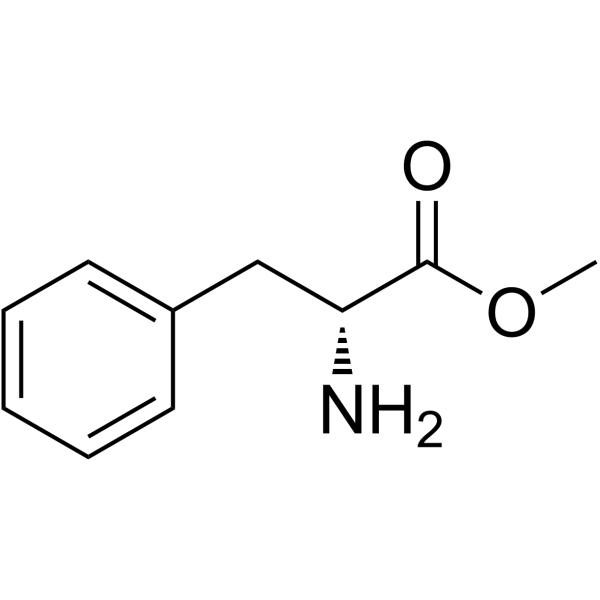 CAS#:21685-51-8
CAS#:21685-51-8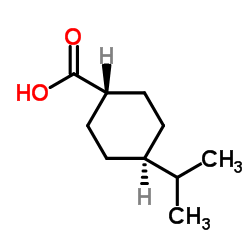 CAS#:7077-05-6
CAS#:7077-05-6 CAS#:594837-85-1
CAS#:594837-85-1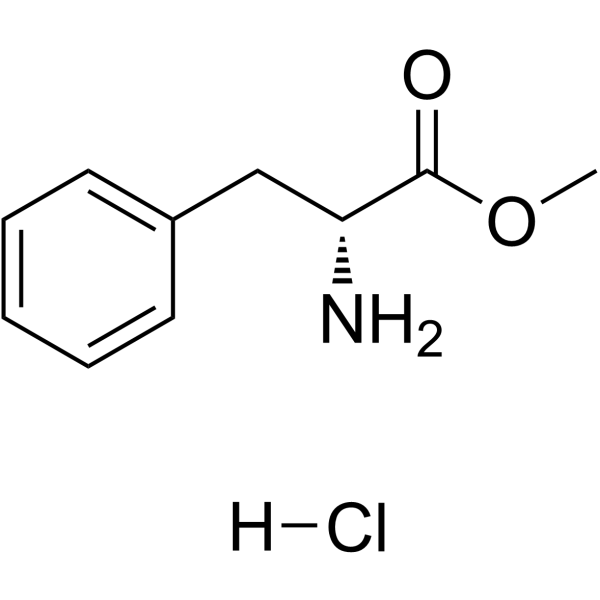 CAS#:13033-84-6
CAS#:13033-84-6 CAS#:187728-85-4
CAS#:187728-85-4
