3-Chloroaniline
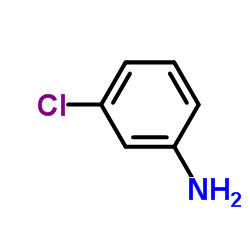
3-Chloroaniline structure
|
Common Name | 3-Chloroaniline | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 108-42-9 | Molecular Weight | 127.572 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 227.8±13.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H6ClN | Melting Point | −11-−9 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 123.9±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | 3-Chloroaniline |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 227.8±13.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | −11-−9 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C6H6ClN |
| Molecular Weight | 127.572 |
| Flash Point | 123.9±0.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 127.018875 |
| PSA | 26.02000 |
| LogP | 1.81 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.1±0.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.598 |
| InChIKey | PNPCRKVUWYDDST-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | Nc1cccc(Cl)c1 |
| Water Solubility | 6.8 g/L (20 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |



GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301-H311-H331-H373-H410 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P273-P280-P301 + P310-P311-P501 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | T:Toxic |
| Risk Phrases | R23/24/25;R33;R50/53 |
| Safety Phrases | S28-S36/37-S45-S60-S61-S28A |
| RIDADR | UN 2019 6.1/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | BX0350000 |
| Packaging Group | II |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| HS Code | 2902909090 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2902909090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2902909090 other aromatic hydrocarbons。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:2.0%。General tariff:30.0% |
|
cIEF for rapid pKa determination of small molecules: a proof of concept.
Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 63 , 14-21, (2014) A capillary isoelectric focusing (cIEF) method was developed for the determination of the ionization constants (pKa) of small molecules. Two approaches used to decrease the electroosmotic flow (EOF) w... |
|
|
Calculating virtual log P in the alkane/water system (log P(N)(alk)) and its derived parameters deltalog P(N)(oct-alk) and log D(pH)(alk).
J. Med. Chem. 48 , 3269-79, (2005) Growing interest in the use of both the logarithm of the partition coefficient of the neutral species in the alkane/water system (log P(N)(alk)) and the difference between log P(N)(oct) (the logarithm... |
|
|
QSAR study on permeability of hydrophobic compounds with artificial membranes.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 15 , 3756-67, (2007) We previously reported a classical quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) equation for permeability coefficients (P(app-pampa)) by parallel artificial membrane permeation assay (PAMPA) of... |
| Orange GC Base |
| m-Aminochlorobenzene |
| Benzenamine,3-chloro |
| 1-Chloro-3-aminobenzene |
| Aniline, m-chloro- |
| 3-chlorobenzenamine |
| m-chloraniline |
| MFCD00007765 |
| m-Chloroaniline |
| 1-Amino-3-chlorobenzene |
| aniline, 3-chloro- |
| m-Chlorophenylamine |
| 3-Chlorophenylamine |
| 6-amino-2-chlorobenzene |
| Chloroaniline |
| Benzenamine, 3-chloro- |
| m-Chloroaminobenzene |
| 3-chloro-aniline |
| EINECS 203-581-0 |
 CAS#:121-73-3
CAS#:121-73-3 CAS#:625-99-0
CAS#:625-99-0 CAS#:108-37-2
CAS#:108-37-2 CAS#:63503-60-6
CAS#:63503-60-6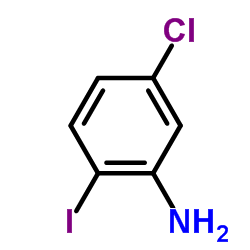 CAS#:6828-35-9
CAS#:6828-35-9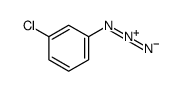 CAS#:3296-06-8
CAS#:3296-06-8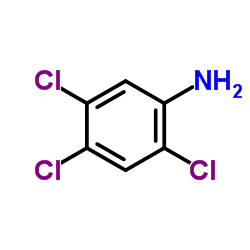 CAS#:636-30-6
CAS#:636-30-6 CAS#:7440-05-3
CAS#:7440-05-3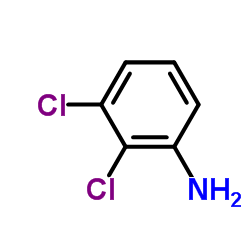 CAS#:608-27-5
CAS#:608-27-5 CAS#:95-50-1
CAS#:95-50-1 CAS#:112069-52-0
CAS#:112069-52-0![Benzenamine,3-chloro-N-[(3-nitrophenyl)methylene]- structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/372/10480-27-0.png) CAS#:10480-27-0
CAS#:10480-27-0 CAS#:111609-82-6
CAS#:111609-82-6 CAS#:10468-17-4
CAS#:10468-17-4![2-[4-(3-chlorophenyl)-3-oxo-1,4-benzothiazin-2-yl]acetamide structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/378/106691-40-1.png) CAS#:106691-40-1
CAS#:106691-40-1 CAS#:10286-92-7
CAS#:10286-92-7 CAS#:141-85-5
CAS#:141-85-5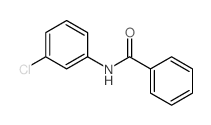 CAS#:6004-21-3
CAS#:6004-21-3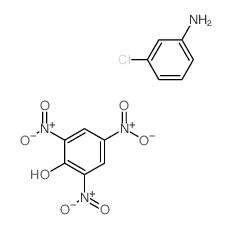 CAS#:10530-56-0
CAS#:10530-56-0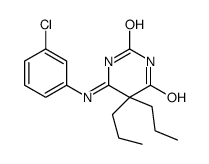 CAS#:105891-82-5
CAS#:105891-82-5
