Misoprostol acid
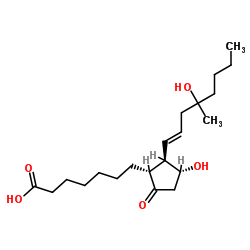
Misoprostol acid structure
|
Common Name | Misoprostol acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 112137-89-0 | Molecular Weight | 368.508 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 538.3±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C21H36O5 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 293.4±26.6 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Misoprostol acidMisoprostol acid is an active metabolite of Misoprostol. Misoprostol is a synthetic analogue of prostaglandin E1 (PGE1), extensively absorbed, and undergoes rapid de-esterification to Misoprostol acid in the gastrointestinal tract after oral administration. Misoprostol can be used for non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced (NSAID) gastric ulcers[1]. Misoprostol is an oral agent used to induce labor[2]. |
| Name | (+/-)-15-deoxy-[16rs]-16-hydroxy-16-methylprostaglandin e1 |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Misoprostol acid is an active metabolite of Misoprostol. Misoprostol is a synthetic analogue of prostaglandin E1 (PGE1), extensively absorbed, and undergoes rapid de-esterification to Misoprostol acid in the gastrointestinal tract after oral administration. Misoprostol can be used for non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced (NSAID) gastric ulcers[1]. Misoprostol is an oral agent used to induce labor[2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Prostaglandin E1 (PGE1)[1] |
| In Vivo | Unlike the Misoprostol, Misoprostol acid is detectable in plasma. Misoprostol is a lipophilic methyl ester prodrug and is readily metabolized to the free acid, which is the biologically active form. Misoprostol is used worldwide for a variety of indications in obstetrics and gynecology. Misoprostol has both gastric antisecretory and mucosal protective effects[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 538.3±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C21H36O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 368.508 |
| Flash Point | 293.4±26.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 368.256287 |
| PSA | 94.83000 |
| LogP | 2.45 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.543 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301-H315-H319-H335-H361 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P281-P301 + P310-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Hazard Codes | T: Toxic; |
| Risk Phrases | R45 |
| Safety Phrases | 53-22-36/37/39-45 |
| RIDADR | UN 2810 6 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
|
Active management of the third stage of labour: prevention and treatment of postpartum hemorrhage.
J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Can. 31 , 980-993, (2009) To review the clinical aspects of postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) and provide guidelines to assist clinicians in the prevention and management of PPH. These guidelines are an update from the previous Soci... |
|
|
Management of NSAID-induced gastrointestinal toxicity: focus on proton pump inhibitors.
Drugs 69 , 51-69, (2009) The association between NSAIDs and the presence of upper gastrointestinal (GI) complications is well established. Evidence that acid aggravates NSAID-induced injury provides a rationale for minimizing... |
|
|
Prevention of NSAID-induced gastric ulcer with misoprostol: multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.
Lancet 2 , 1277, (1988) A double-blind, placebo-controlled study was carried out to see whether the synthetic E prostaglandin, misoprostol, would prevent gastric ulcer induced by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs... |
| Prost-13-en-1-oic acid, 11,16-dihydroxy-16-methyl-9-oxo-, (11α,13E)- |
| (11α,13E)-11,16-Dihydroxy-16-methyl-9-oxoprost-13-en-1-oic acid |
| Misoprostol Acid |
| MISOPROSTOL FREE ACID |