CNQX
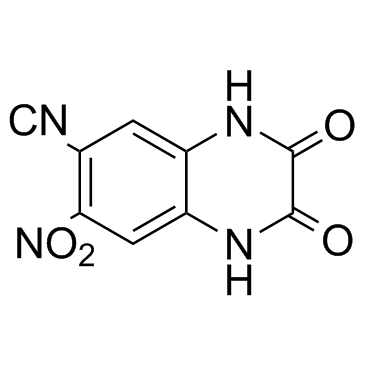
CNQX structure
|
Common Name | CNQX | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 115066-14-3 | Molecular Weight | 232.152 | |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 659.3ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H4N4O4 | Melting Point | 300 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 352.6ºC | |
Use of CNQXCNQX (FG9065) is a potent AMPA/kainate receptor antagonist. |
| Name | 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | CNQX (FG9065) is a potent AMPA/kainate receptor antagonist. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | In rat hippocampal slices bathed in Mg2+-free medium, 10 μM CNQX reversibly blocks responses to a-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionic acid (AMPA), quisqualate and kainate but not NMDA[1]. Superfusion of hippocampal slices with 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione (CNQX, 2-5 μM) reversibly blocks the Schaffer collateral and mossy fibre excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP), while sparing the fast and slow GABA-mediated inhibition[2]. CNQX (1-5 μM) produces a selective and dose-dependent reduction in the amplitude of the monosynaptic component of the DR-VRR recorded from lumbar spinal segments[3]. CNQX-mediated depolarizations are mediated by AMPAR but not kainate receptors in TRN neurons[4]. |
| In Vivo | The bilateral infusion of CNQX (0.5 or 1.25 μg) into the amygdala or dorsal hippocampus 10 min prior to a retention test partially blocks the expression of stepdown inhibitory avoidance in rats 24 h after training. CNQX causes a complete blockade at a dose of 0.5 μg[5]. |
| Cell Assay | CNQX is applied by injecting a bolus into the input line of the chamber over 60 s using a motorized syringe pump. In a subpopulation of neurons, CNQX is bath applied for 5 min. Control injections of physiological saline or vehicle (DMSO) does not alter membrane potential/input resistance during voltage recordings[4]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 659.3ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 300 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C9H4N4O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 232.152 |
| Flash Point | 352.6ºC |
| Exact Mass | 232.023254 |
| PSA | 135.33000 |
| LogP | 0.64 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.001mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.699 |
| InChIKey | RPXVIAFEQBNEAX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | N#Cc1cc2[nH]c(=O)c(=O)[nH]c2cc1[N+](=O)[O-] |
| Storage condition | Desiccate at RT |
| Stability | Store Tightly Sealed at RT |
| Water Solubility | H2O: 10 mg/mL |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
Glutamatergic receptor dysfunction in spinal cord contributes to the exaggerated exercise pressor reflex in heart failure.
Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 308(5) , H447-55, (2015) Excitatory amino acids (e.g., glutamate) released by contraction-activated skeletal muscle afferents into the dorsal horn of the spinal cord initiate the central component of the exercise pressor refl... |
|
|
Nitrous oxide directly inhibits action potential-dependent neurotransmission from single presynaptic boutons adhering to rat hippocampal CA3 neurons.
Brain Res. Bull. 118 , 34-45, (2015) We evaluated the effects of N2O on synaptic transmission using a preparation of mechanically dissociated rat hippocampal CA3 neurons that allowed assays of single bouton responses evoked from native f... |
|
|
HD iPSC-derived neural progenitors accumulate in culture and are susceptible to BDNF withdrawal due to glutamate toxicity.
Hum. Mol. Genet. 24 , 3257-71, (2015) Huntington's disease (HD) is a fatal neurodegenerative disease, caused by expansion of polyglutamine repeats in the Huntingtin gene, with longer expansions leading to earlier ages of onset. The HD iPS... |
| CNQX disodium salt hydrate |
| CNQX 2NA |
| 6-Nitro-7-cyanoquinoxaline-2,3-dione |
| MFCD00069232 |
| 6-Cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione FG-9065 |
| 7-Nitro-2,3-dioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoxaline-6-carbonitrile |
| 2,3-Dihydroxy-7-nitroquinoxaline-6-carbonitrile |
| 7-Nitro-2,3-dioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6-quinoxalinecarbonitrile |
| CNQX DISODIUM |
| CNOX |
| CNQX DISODIUM SALT |
| CNQX |
| 6-Quinoxalinecarbonitrile, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-7-nitro-2,3-dioxo- |
| 6-Cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione disodium salt hydrate |
| FG-9065 |
| CNQX DISODIUM KAINATE/AMPA RECEPTOR |