4-Hydroperoxy Cyclophosphamide-d4
Modify Date: 2024-01-06 19:29:40
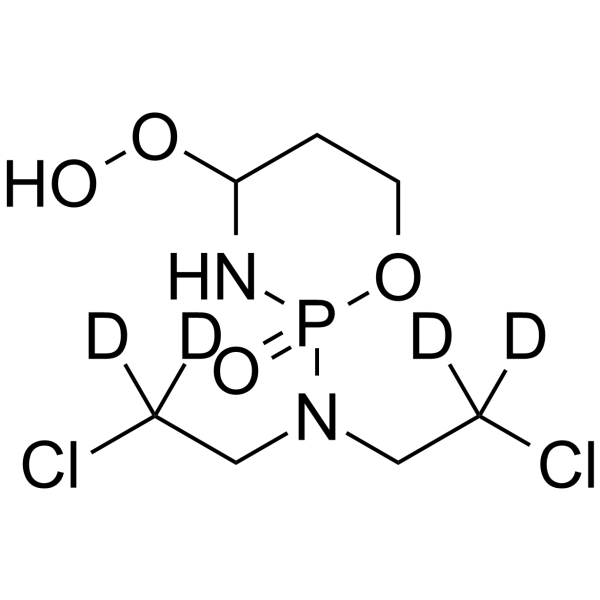
4-Hydroperoxy Cyclophosphamide-d4 structure
|
Common Name | 4-Hydroperoxy Cyclophosphamide-d4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1246816-71-6 | Molecular Weight | 297.11 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H11D4Cl2N2O4P | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of 4-Hydroperoxy Cyclophosphamide-d44-Hydroperoxy Cyclophosphamide-d4 is the deuterium labeled 4-Hydroperoxy cyclophosphamide. 4-Hydroperoxy cyclophosphamide is the active metabolite form of the prodrug Cyclophosphamide. 4-Hydroperoxy cyclophosphamide crosslinks DNA and induces T cell apoptosis independent of death receptor activation, but activates mitochondrial death pathways through production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). 4-Hydroperoxy cyclophosphamide has the potential for lymphomas and autoimmune disorders[1][2]. |
| Name | 4-Hydroperoxy Cyclophosphamide-d4 |
|---|
| Description | 4-Hydroperoxy Cyclophosphamide-d4 is the deuterium labeled 4-Hydroperoxy cyclophosphamide. 4-Hydroperoxy cyclophosphamide is the active metabolite form of the prodrug Cyclophosphamide. 4-Hydroperoxy cyclophosphamide crosslinks DNA and induces T cell apoptosis independent of death receptor activation, but activates mitochondrial death pathways through production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). 4-Hydroperoxy cyclophosphamide has the potential for lymphomas and autoimmune disorders[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C7H11D4Cl2N2O4P |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 297.11 |