Hydroxyurea
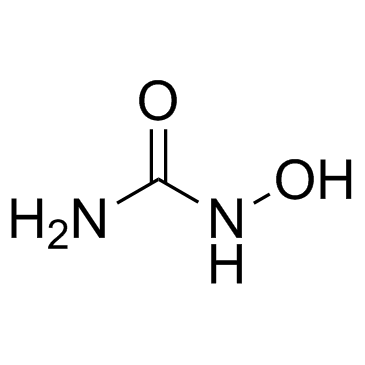
Hydroxyurea structure
|
Common Name | Hydroxyurea | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 127-07-1 | Molecular Weight | 76.055 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 222.1±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | CH4N2O2 | Melting Point | 135-140 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese | Flash Point | 88.1±22.6 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of HydroxyureaHydroxyurea is a cell apoptosis inducer that inhibitDNA synthesis through inhibition of ribonucleotide reductase. |
| Name | hydroxyurea |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Hydroxyurea is a cell apoptosis inducer that inhibitDNA synthesis through inhibition of ribonucleotide reductase. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Hydroxyurea is used in a number of myeloproliferative, neoplastic, HIV, and non-hematological diseases[1]. Treatment of cells in primary culture with 30 μM hydroxyurea for 96 hours significantly increases the fractional HbF content. The Gγ: Aγ-globin mRNA is induced 0.30- to 8-fold in vitro[2]. Hydroxyurea has been shown to block HIV-1 reverse transcription and/or replication in quiescent peripheral blood mononuclear cells and macrophages[3]. |
| In Vivo | Hydroxyurea therapy producs consistent reductions in WBC and ANC without improvement in anemia over 17 weeks. Hydroxyurea at 50mg/kg produces a reduced white blood cell count, absolute neutrophil count and no improvement in anemia compared to vehicle treated sickle cell mice[4]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice: To determine whether hydroxyurea would improve anemia and/or prevent or diminish the development of organ damage in the absence of HbF induction, hydroxyurea, at doses of 25 mg/kg, 50 mg/kg, and 100 mg/kg, or vehicle is administered five days per week to SCD mice[4]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 222.1±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 135-140 °C |
| Molecular Formula | CH4N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 76.055 |
| Flash Point | 88.1±22.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 76.027275 |
| PSA | 75.35000 |
| LogP | -1.80 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.501 |
| InChIKey | VSNHCAURESNICA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | NC(=O)NO |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H340-H361 |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P280-P308 + P313 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T:Toxic |
| Risk Phrases | R46;R61 |
| Safety Phrases | S53-S36/37-S45 |
| RIDADR | 2811 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | YT4900000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| HS Code | 2928000090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2924199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924199090. other acyclic amides (including acyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Rad23 interaction with the proteasome is regulated by phosphorylation of its ubiquitin-like (UbL) domain.
J. Mol. Biol. 426(24) , 4049-60, (2014) Rad23 was identified as a DNA repair protein, although a role in protein degradation has been described. The protein degradation function of Rad23 contributes to cell cycle progression, stress respons... |
|
|
A gemcitabine sensitivity screen identifies a role for NEK9 in the replication stress response.
Nucleic Acids Res. 42(18) , 11517-27, (2014) The Replication Stress Response (RSR) is a signaling network that recognizes challenges to DNA replication and coordinates diverse DNA repair and cell-cycle checkpoint pathways. Gemcitabine is a nucle... |
|
|
Celastrol induces proteasomal degradation of FANCD2 to sensitize lung cancer cells to DNA crosslinking agents.
Cancer Sci. 106 , 902-8, (2015) The Fanconi anemia (FA) pathway plays a key role in interstrand crosslink (ICL) repair and maintenance of the genomic stability, while inhibition of this pathway may sensitize cancer cells to DNA ICL ... |
| hydroxycarbamide |
| HYDROXYUREA (HYDROXYCARBAMIDE) |
| HYDROXYUREA 127-07-1 |
| Hydroxyurea |
| Droxia |
| HYDROXYCARBAMIDE, BP STANDARD |
| HYDROXYHARNSTOFF |
| amino-hydroxamic acid |
| Hydrea |
| HYDROXYHARNSTOFF(HYDROXYUREA) |
| 1-hydroxyure |
| hydroxyl urea |
| Hydroxy urea |
| HYDROXYCARBAMIDE (HYDROXYUREA) |
| MFCD00007943 |
| Urea, N-hydroxy- |
| Onco-carbide |
| Oxyurea |
| N-HYDROXYUREA |
| EINECS 204-821-7 |
| Litalir |
| 1-Hydroxyurea |
| Biosupressin |
| hydroxyure |
 CAS#:126669-78-1
CAS#:126669-78-1 CAS#:57-13-6
CAS#:57-13-6 CAS#:75-13-8
CAS#:75-13-8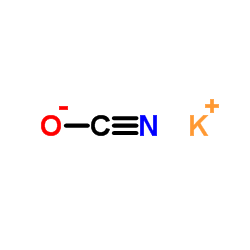 CAS#:590-28-3
CAS#:590-28-3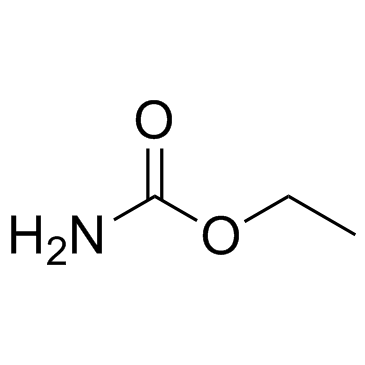 CAS#:51-79-6
CAS#:51-79-6 CAS#:22509-74-6
CAS#:22509-74-6 CAS#:2072-71-1
CAS#:2072-71-1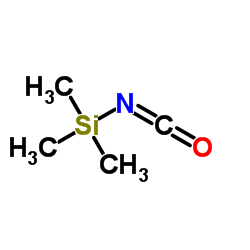 CAS#:1118-02-1
CAS#:1118-02-1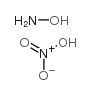 CAS#:13465-08-2
CAS#:13465-08-2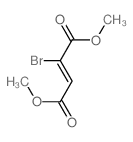 CAS#:2509-16-2
CAS#:2509-16-2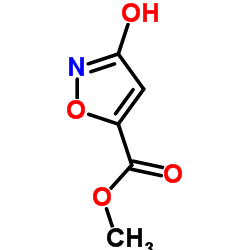 CAS#:10068-07-2
CAS#:10068-07-2![2-Oxa-3-azabicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-ene-3-carboxamide(9CI) structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/092/104308-36-3.png) CAS#:104308-36-3
CAS#:104308-36-3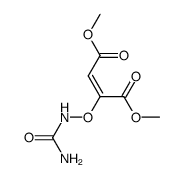 CAS#:77094-88-3
CAS#:77094-88-3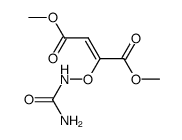 CAS#:77094-89-4
CAS#:77094-89-4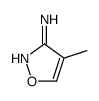 CAS#:1750-43-2
CAS#:1750-43-2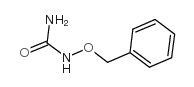 CAS#:2048-50-2
CAS#:2048-50-2 CAS#:124-38-9
CAS#:124-38-9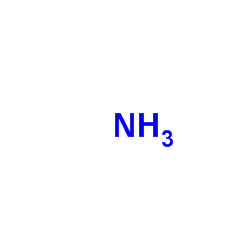 CAS#:7664-41-7
CAS#:7664-41-7
