Chlorpheniramine
Modify Date: 2025-08-20 11:25:13
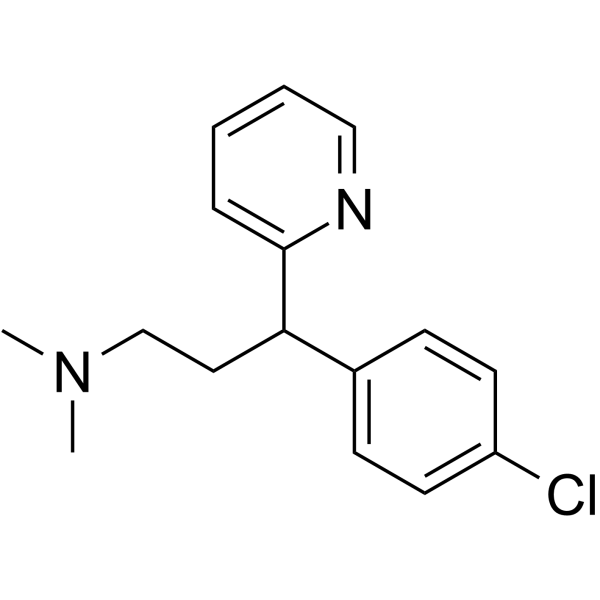
Chlorpheniramine structure
|
Common Name | Chlorpheniramine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 132-22-9 | Molecular Weight | 274.78800 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H19ClN2 | Melting Point | 25 °C (lit.) | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of ChlorpheniramineChlorpheniramine is a H1 antihistamines commonly used in allergic diseases[1]. [2]. . |
| Name | chlorphenamine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Chlorpheniramine is a H1 antihistamines commonly used in allergic diseases[1]. [2]. . |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 43μM in BV2 microglial cells |
| In Vitro | Chlorpheniramine has an inhibitory effects with an value of IC50 is 43μM on proton currents in BV2 microglial cells[1]. . Cell Viability Assay Cell Line: Murine microglial BV2 cells[1]. Concentration: 100 μM Incubation Time: 5 min Result: Inhibited proton currents with moderate potency. |
| In Vivo | Chloropheniramine (50, 100 and 200 μg/kg; IM; 3 times, at intervals of 1 week) enhances white blood cells in the peripheral blood[2]. . Animal Model: Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats[2]. Dosage: 50, 100 and 200 μg/kg Administration: Chlorpheniramine (50, 100 and 200 μg/kg; IM; 3 times, at intervals of 1 week) Result: Enhanced white blood cells in the peripheral blood, mostly due to the increases of B cells and monocytes, but not T cells and NK cells. |
| References |
| Melting Point | 25 °C (lit.) |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C16H19ClN2 |
| Molecular Weight | 274.78800 |
| Exact Mass | 274.12400 |
| PSA | 16.13000 |
| LogP | 3.81860 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 3 | |
| (S)-[3-(4-chloro-phenyl)-3-[2]pyridyl-propyl]-dimethyl-amine |
| D-Chlorpheniramine |
| Isomerine |
| Phendextro |
| Dexclorfeniramina |
| Polaramin |
| Chlor-Trimeton |
| Fortamine |
| (+)-Chlorpheniramine |
| DEXCHLORPHENIRAMINE |
| [3H]-Chlorpheniramine |
| chloropheniramine |
| 3-(4-chlorophenyl)-N,N-dimethyl-3-pyridin-2-ylpropan-1-amine |
| Destral |
| (S)-[3-(4-Chlor-phenyl)-3-[2]pyridyl-propyl]-dimethyl-amin |
| Trenelone |
 CAS#:124-40-3
CAS#:124-40-3 CAS#:73486-85-8
CAS#:73486-85-8 CAS#:73775-50-5
CAS#:73775-50-5 CAS#:74-86-2
CAS#:74-86-2 CAS#:65676-21-3
CAS#:65676-21-3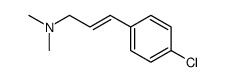 CAS#:42817-51-6
CAS#:42817-51-6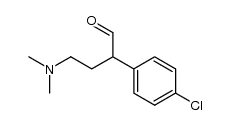 CAS#:158696-49-2
CAS#:158696-49-2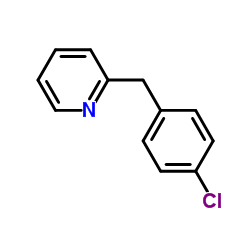 CAS#:4350-41-8
CAS#:4350-41-8 CAS#:25523-97-1
CAS#:25523-97-1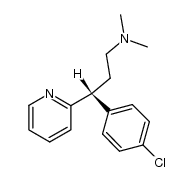 CAS#:32188-09-3
CAS#:32188-09-3 CAS#:6318-51-0
CAS#:6318-51-0