NHS-SS-(+)-Biotin
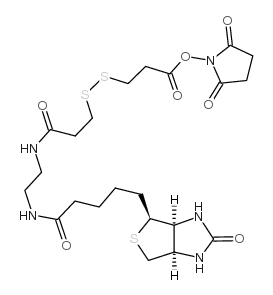
NHS-SS-(+)-Biotin structure
|
Common Name | NHS-SS-(+)-Biotin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 142439-92-7 | Molecular Weight | 575.72200 | |
| Density | 1.43 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C22H33N5O7S3 | Melting Point | 129-131ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of NHS-SS-(+)-BiotinBiotin-bis-amido-SS-NHS is an Alkyl/ether-based PROTAC linker can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs. |
| Name | (2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl) 3-[[3-[2-[5-[(3aS,4S,6aR)-2-oxo-1,3,3a,4,6,6a-hexahydrothieno[3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl]pentanoylamino]ethylamino]-3-oxopropyl]disulfanyl]propanoate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Biotin-bis-amido-SS-NHS is an Alkyl/ether-based PROTAC linker can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Alkyl/ether |
| In Vitro | Biotin-bis-amido-SS-NHS is a long arm biotin containing disulfide bond, and the compound can be applied to biochemistry detection field, reduce the influence of steric effect, improve the sensitivity of detection[1]. PROTACs contain two different ligands connected by a linker; one is a ligand for an E3 ubiquitin ligase and the other is for the target protein. PROTACs exploit the intracellular ubiquitin-proteasome system to selectively degrade target proteins. |
| References |
| Density | 1.43 |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 129-131ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C22H33N5O7S3 |
| Molecular Weight | 575.72200 |
| Exact Mass | 575.15400 |
| PSA | 238.91000 |
| LogP | 2.09070 |
| InChIKey | LWPHUVGDBNUVHA-GXZWQRSESA-N |
| SMILES | O=C(CCCCC1SCC2NC(=O)NC21)NCCNC(=O)CCSSCCC(=O)ON1C(=O)CCC1=O |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H360D |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P308 + P313 |
| Hazard Codes | T: Toxic; |
| Risk Phrases | 61 |
| Safety Phrases | 53-23-36/37/39-45 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
Chemical probes of extended biological structures: synthesis and properties of the cleavable protein cross-linking reagent [35S]dithiobis(succinimidyl propionate).
J. Mol. Biol. 104 , 243-261, (1976)
|
|
|
A mechanism-based affinity-labeling agent for possible use in isolating N-acetylglucosaminidase.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 11 , 1769-1773, (2001) We have prepared several mechanism-based affinity-labeling agents for possible use in isolating N-acetylglucosaminidase, in which an N-acetylglucosamine is linked to an o-monofluoro- or difluoro-methy... |
|
|
A dominant linear B-cell epitope of ricin A-chain is the target of a neutralizing antibody response in Hodgkin's lymphoma patients treated with an anti-CD25 immunotoxin.
Clin. Exp. Immunol. 136 , 365-372, (2004) Hodgkin's lymphoma patients treated with an anti-CD25 Ricin toxin A-chain (RTA)-based Immunotoxin (RFT5.dgA) develop an immune response against the toxic moiety of the immunoconjugate. The anti-RTA an... |
| Succinimidyl 3-[3-[2-(biotinamido)ethyl]amino-3-oxopropyl]dithio]propionate |
| NHS-SS-Biotin |
| Biotin disulfide N-hydroxysuccinimide ester |
| (2-[Biotinamido]ethylamido)-3,3 inverted exclamation marka-dithiodipropionic acid N-hydroxysuccinimide ester |