Y-27632
Modify Date: 2024-01-02 10:14:00
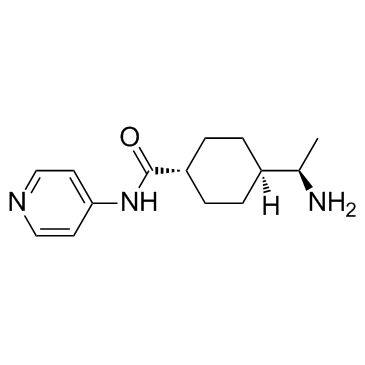
Y-27632 structure
|
Common Name | Y-27632 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 146986-50-7 | Molecular Weight | 247.34 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 462.6±15.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H21N3O | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 233.6±20.4 °C | |
Use of Y-27632Y-27632 is an ATP-competitive inhibitor of ROCK-I and ROCK-II, with Ki of 220 nM and 300 nM for ROCK-I and ROCK-II, respectively. |
| Name | y-27632 |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Y-27632 is an ATP-competitive inhibitor of ROCK-I and ROCK-II, with Ki of 220 nM and 300 nM for ROCK-I and ROCK-II, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
ROCK-I:220 nM (Ki) ROCK-II:300 nM (Ki) Citron kinase:5.3 μM (Ki) PKN:3.1 μM (Ki) PKCα:73 μM (Ki) PKA:25 μM (Ki) |
| In Vitro | Y-27632 inhibits the ROCK family of kinases 100 times more potently than other kinases including protein kinase C, cAMP-dependent kinase and myosin light chain kinase. Y-27632 prolongs the lag time and delays the appearance of BrdU-labeled cells in a concentration-dependent manner, delays of about 1 and 4 h are noticed in the Swiss 3T3 cells treated with 10 and 100 μM Y-27632, respectively[1]. Y-27632 promotes neuronal differentiation of adipose tissue-derived stem cells (ADSCs). Compared to 1.0 and 2.5 µM Y-27632 induced groups, percentages of neuroal-like cells achieved a peak in the 5.0 µM Y-27632 induced group[2]. |
| In Vivo | Y-27632 (5 and 10 mg/kg) significantly prolongs the onset time of myoclonic jerks when compare with saline group. Y-27632 (5 and 10 mg/kg) significantly prolongs the onset time of clonic convulsions when compare with saline group[3]. Treatment with Dimethylnitrosamine (DMN) causes a significant decrease in rat body and liver weight (DMN-S group) compared with control animals (S-S group). Oral Y27632 (30 mg/kg) essentially prevents this DMN-induced rat body and liver weight loss (DMN-Y group)[4]. |
| Kinase Assay | Recombinant ROCK-I, ROCK-II, PKN, or citron kinase is expressed in HeLa cells as Myc-tagged proteins by transfection using Lipofectamine, and is precipitated from the cell lysates by the use of 9E10 monoclonal anti-Myc antibody coupled to G protein-Sepharose. Recovered immunocomplexes are incubated with various concentrations of [32P]ATP and 10 mg of histone type 2 as substrates in the absence or presence of various concentrations of either Y-27632 or Y-30141 at 30°C for 30 min in a total volume of 30 μL of the kinase buffer containing 50 mM HEPES-NaOH, pH 7.4, 10 mM MgCl2, 5 mM MnCl2, 0.02% Briji 35, and 2 mM dithiothreitol. PKCa is incubated with 5 μM [32P]ATP and 200 μg/mL histone type 2 as substrates in the absence or presence of various concentrations of either Y-27632 or Y-30141 at 30°C for 10 min in a kinase buffer containing 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 0.5 mM CaCl2, 5 mM magnesium acetate, 25 μg/mL phosphatidyl serine, 50 ng/mL 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate and 0.001% leupeptin in a total volume of 30 μL. Incubation is terminated by the addition of 10 μL of 43 Laemmli sample buffer. After boiling for 5 min, the mixture is subjected to SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis on a 16% gel. The gel is stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue, and then dried. The bands corresponding to histone type 2 are excised, and the radioactivity is measured[1]. |
| Cell Assay | HeLa cells are plated at a density of 3×104 cells per 3.5-cm dish. The cells are cultured in DMEM containing 10% FBS in the presence of 10 mM Thymidine for 16 h. After the cells are washed with DMEM containing 10% FBS, they are cultured for an additional 8 h, and then 40 ng/mL of Nocodazole is added. After 11.5 h of the Nocodazole treatment, various concentrations of Y-27632 (0-300 μM), Y-30141, or vehicle is added and the cells are incubated for another 30 min[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[3] Male, inbred Swiss albino mice (2-3 months old) weighing 25-30 g are used. Mice are injected with a sub-convulsive dose of PTZ (35 mg/kg, i.p.) (on Mondays, Wednesdays and Fridays) of each week for a total of 11 injections. After each PTZ injection, mice are observed for 30 min and the occurrence of convulsive activity is recorded. After 30 min, the mice are then injected with either Fasudil (25 mg/kg, i.p.) or Y-27632 (5 mg/kg, i.p.) and returned to their home cages until the next injection. Control mice for Fasudil and Y-27632 receives saline. Rats[4] Male Wistar Kind A rats (200-250 g) are used. DMN (1 g/mL) is diluted ten times with saline (final concentration 1%) and 10 mg/kg per day of DMN is injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) on the first 3 days of each week for 4 weeks. Y27632 is given orally once per day at a dose of 30 mg/kg for 4 weeks starting on the day of the first injection of DMN. The dose of 30 mg/kg corrects hypertension in several rat models without toxicity. Twenty rats are randomized into four experimental groups (n=5 in each group) as follows: (1) S-S (injection of saline i.p. and oral administration of saline); (2) S-Y (injection of saline i.p. and oral administration of Y27632); (3) DMN-S (DMN i.p. and oral administration of saline); (4) DMN-Y (DMN i.p. and oral administration of Y27632). The rats are weighed every week. They are sacrificed at the end of the fourth week and the liver is excised. In addition, a blood sample is taken immediately before the rats are sacrificed. |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 462.6±15.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C14H21N3O |
| Molecular Weight | 247.34 |
| Flash Point | 233.6±20.4 °C |
| PSA | 68.01000 |
| LogP | 1.54 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.579 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful; |
|---|
| 4-[(1R)-1-aminoethyl]-N-pyridin-4-ylcyclohexane-1-carboxamide |
| trans-4-[(1R)-1-Aminoethyl]-N-(pyridin-4-yl)cyclohexanecarboxamide dihydrochloride |
| Y-27632 |
| trans-4-[(1R)-1-Aminoethyl]-N-(4-pyridinyl)cyclohexanecarboxamide |
| (R)-(+)-trans-4-(1-Aminoethyl)-N-(4-Pyridyl)cyclohexanecarboxamide dihydrochloride |
| Y-27632 (hydrochloride) |
| Y-27632 dihydrochloride |
| Cyclohexanecarboxamide, 4-[(1R)-1-aminoethyl]-N-4-pyridinyl-, trans-, hydrochloride (1:2) |
| trans-4-[(1R)-1-Aminoethyl]-N-(4-pyridinyl)cyclohexanecarboxamide dihydrochloride |
| Cyclohexanecarboxamide, 4-[(1R)-1-aminoethyl]-N-4-pyridinyl-, trans- |